Java JDOM2 Tutorial with Examples
1. Introduction
JDOM is an in-memory XML model that can be used to read, write, create and modify XML Documents. JDOM is similar to DOM in that they both provide an in-memory XML document model.
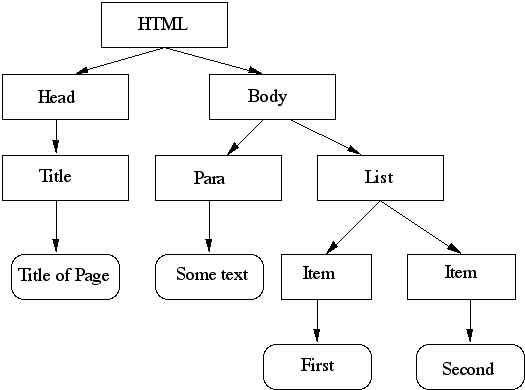
- DOM is designed to work the same in multiple languages (C, C++, ECMAScript, Java, JScript, Lingo, PHP, PLSQL, and Python),
- JDOM is designed only for Java and uses the natural Java-specific features that the DOM model avoids. For this reason JDOM intentionally does not follow the w3c DOM standard. JDOM is not an XML parser but it can use a SAX, StAX or DOM parser to build the JDOM document. JDOM versions since JDOM 2.0.0 (JDOM2) all use the native language features of Java6 and later like Generics, Enums, var-args, co-variant return types, etc.
See more:
2. Library
No ADS
Unlike DOM available in JDK , JDOM you have to download the library to use:
You can download the JDOM2 library at homepage:
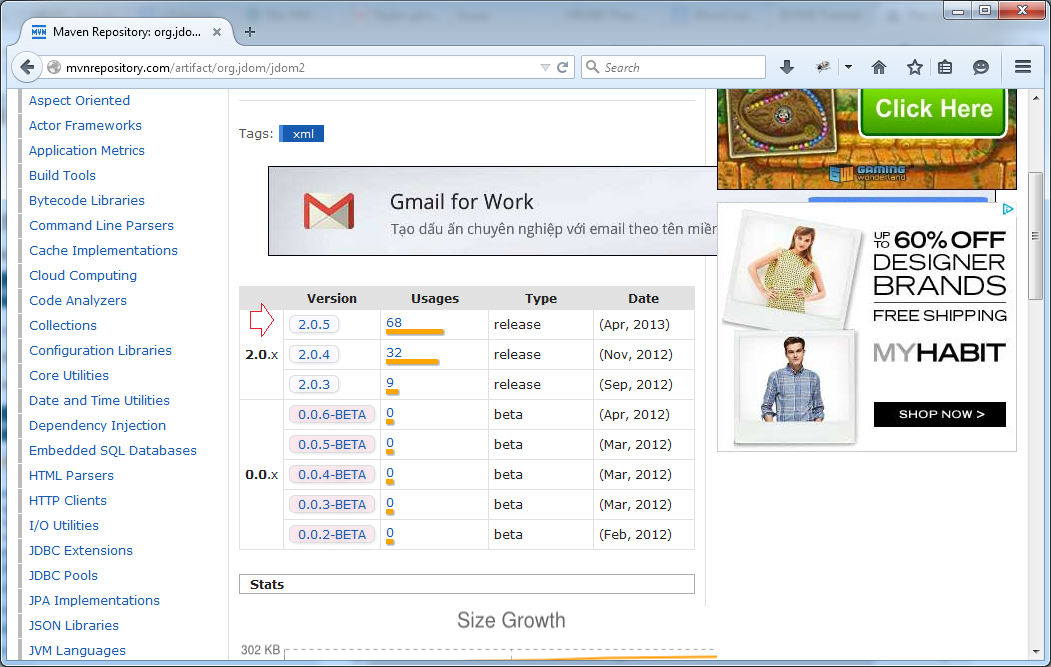
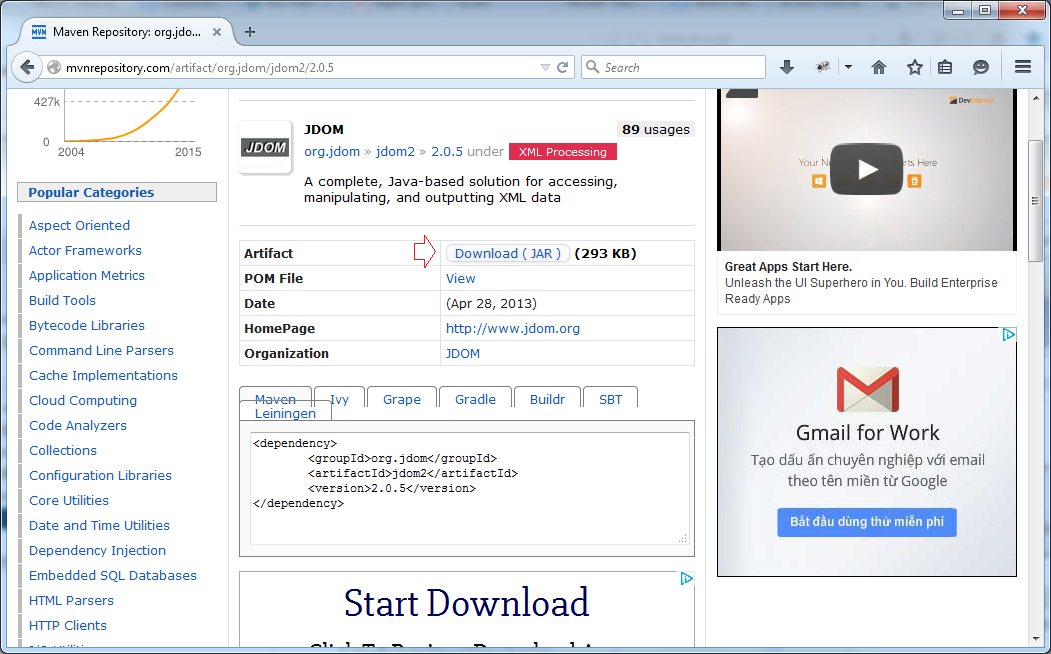
Or simply download from Maven Repository:
3. Begin Example
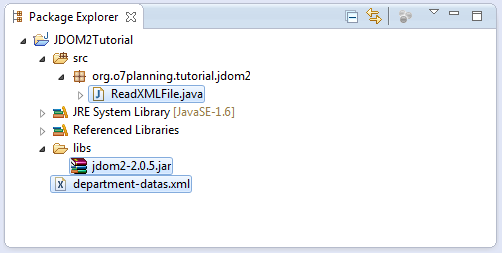
This is the image after completion of the Project:
department-datas.xml
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<department>
<employee>
<empNo>E01</empNo>
<empName>KING</empName>
<hireDate>17-11-1981</hireDate>
<salary>100000</salary>
</employee>
<employee>
<empNo>E02</empNo>
<empName>JONES</empName>
<hireDate>02-04-1981</hireDate>
<salary>200000</salary>
</employee>
</department>ReadXMLFile.java
package org.o7planning.tutorial.jdom2;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.List;
import org.jdom2.Document;
import org.jdom2.Element;
import org.jdom2.JDOMException;
import org.jdom2.input.SAXBuilder;
public class ReadXMLFile {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SAXBuilder builder = new SAXBuilder();
File xmlFile = new File("department-datas.xml");
System.out.println("Parsing FILE: "+ xmlFile.getAbsolutePath());
try {
Document document = (Document) builder.build(xmlFile);
Element rootNode = document.getRootElement();
List<Element> list = rootNode.getChildren("employee");
for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) {
Element node = (Element) list.get(i);
System.out.println(" ------ ");
System.out.println("Emp No : " + node.getChildText("empNo"));
System.out.println("Emp Name : " + node.getChildText("empName"));
System.out.println("Hire Date : " + node.getChildText("hireDate"));
System.out.println("Salary : " + node.getChildText("salary"));
}
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
} catch (JDOMException e) {
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
}
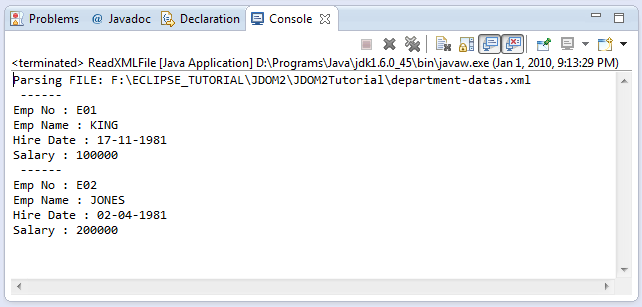
}Results after running ReadXMLFile class:
No ADS
Java Open Source Libraries
- Java JSON Processing API Tutorial (JSONP)
- Using Scribe OAuth Java API with Google OAuth2
- Get Hardware information in Java application
- Restfb Java API for Facebook
- Create Credentials for Google Drive API
- Manipulating files and folders on Google Drive using Java
- Java JDOM2 Tutorial with Examples
- Java XStream Tutorial with Examples
- Jsoup Java Html Parser Tutorial with Examples
- Retrieve Geographic information based on IP Address using GeoIP2 Java API
- Read and Write Excel file in Java using Apache POI
- Explore the Facebook Graph API
- Java Sejda WebP ImageIO convert Images to WEBP
- Java JAVE Convert audio and video to mp3
Show More