Java Reflection Tutorial with Examples
1. What is Java Reflection?
No ADS
Java uses the words "Java Reflection" to namean important API in its standard library. Why is this API named so? Let's analyze its meaning.
Reflection is animage reflection of an object. For example, your image in a mirror, or a reflected image of a tree on a lake. The "Java Reflection" term simply insinuates another image, another approach of the Java.

Java is anObject-oriented language. Normally, you need to create an object and you can access fields, or call the method of this object through the dot operator ( . ).
The Java Reflection introduces another approach. You can access a field of an object if you know the name of such field or you can call a method of the object if you know the method name, the types of its parameters, and parameter values to pass to ...
The Java Reflecion allows you to evaluate, modify the structure and behavior of an object at the runtime of the program. And it gives you access to private members anywhere in the application, which is not allowed for a traditional approach.
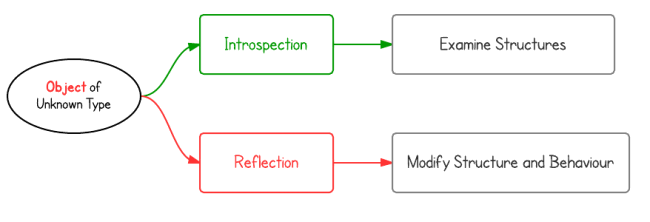
- Java can generally be called Java Introspection, which can evaluate the structure of an object at runtime.
- With Java Reflection, the program can evaluate the structure of an object at runtime, and modify the structure and behavior of the object.
2. Some classes participated in the examples
No ADS
Here are some of the class participated in the examples in this document.
Animal.java
package org.o7planning.tutorial.beans;
public abstract class Animal {
public String getLocation() {
return "Earth";
}
public abstract int getNumberOfLegs() ;
}Say.java
package org.o7planning.tutorial.beans;
public interface Say {
public String say();
}Cat.java
package org.o7planning.tutorial.beans;
public class Cat extends Animal implements Say {
public static final String SAY = "Meo meo";
public static final int NUMBER_OF_LEGS = 4;
// Private field.
private String name;
// Private field
public int age;
public Cat() {
}
public Cat(String name) {
this.name = name;
this.age = 1;
}
public Cat(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return this.name;
}
// Private Method.
private void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return this.age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
/**
* Implements from interface Say.
*/
@Override
public String say() {
return SAY;
}
/**
* Implements from Animal.
*/
@Override
public int getNumberOfLegs() {
return NUMBER_OF_LEGS;
}
}3. Getting Started With a Simple Example
No ADS
Here is a simple example retrieves a list of public methods of a class, including methods inherited from the parent class, and interfaces.
ListMethod.java
package org.o7planning.tutorial.reflect.helloreflect;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
public class ListMethod {
// Protected method
protected void info() {
}
public static void testMethod1() {
}
public void testMethod2() {
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Get a list of public methods of this class
// Include methods inherited from the parent class, or interface.
// Lấy ra danh sách các method public của class này
// Bao gồm các các method thừa kế từ class cha, hoặc các interface.
Method[] methods = ListMethod.class.getMethods();
for (Method method : methods) {
System.out.println("Method " + method.getName());
}
}
}Running example:
Method testMethod1
Method testMethod2
Method main
Method wait
Method wait
Method wait
Method equals
Method toString
Method hashCode
Method getClass
Method notify
Method notifyAll4. Class
No ADS
Some important method of Reflection relating to Class.
Example for print out basic informations of class such as class name, package, modifier, ..
ShowClassInfo.java
package org.o7planning.tutorial.reflect.clazz;
import java.lang.reflect.Modifier;
public final class ShowClassInfo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Get Class object represent ShowClassInfo class.
Class<ShowClassInfo> aClass = ShowClassInfo.class;
// Print out class name, including the package name.
System.out.println("Class Name= " + aClass.getName());
// Print out simple class name (without package name).
System.out.println("Simple Class Name= " + aClass.getSimpleName());
// Package info
Package pkg = aClass.getPackage();
System.out.println("Package Name = " + pkg.getName());
// Modifier
int modifiers = aClass.getModifiers();
boolean isPublic = Modifier.isPublic(modifiers);
boolean isInterface = Modifier.isInterface(modifiers);
boolean isAbstract = Modifier.isAbstract(modifiers);
boolean isFinal = Modifier.isFinal(modifiers);
// true
System.out.println("Is Public? " + isPublic);
// true
System.out.println("Is Final? " + isFinal);
// false
System.out.println("Is Interface? " + isInterface);
// false
System.out.println("Is Abstract? " + isAbstract);
}
}Running the example:
Class Name= org.o7planning.tutorial.reflect.clazz.ShowClassInfo
Simple Class Name= ShowClassInfo
Package Name = org.o7planning.tutorial.reflect.clazz
Is Public? true
Is Final? true
Is Interface? false
Is Abstract? falseExample for writing out information of Cat class,such as class name, and interfaces that this class implements.
ShowClassCatInfo.java
package org.o7planning.tutorial.reflect.clazz;
import org.o7planning.tutorial.beans.Cat;
public class ShowClassCatInfo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// The Class object represent Cat class
Class<Cat> aClass = Cat.class;
// Class name
System.out.println("Simple Class Name = " + aClass.getSimpleName());
// Get the Class object represent parent of Cat class
Class<?> aSuperClass = aClass.getSuperclass();
System.out.println("Simple Class Name of Super class = "
+ aSuperClass.getSimpleName());
// Determines the interfaces implemented by the class
// or interface represented by this object.
Class<?>[] itfClasses = aClass.getInterfaces();
for (Class<?> itfClass : itfClasses) {
System.out.println("Interface: " + itfClass.getSimpleName());
}
}
}Running the example:
Simple Class Name = Cat
Simple Class Name of Super class = Animal
Interface: SayExample for retrieving information of the constructor, method, field of class (public only), including the public methods, public field, inherited from the parent class, interfaces.
ShowMemberInfo.java
package org.o7planning.tutorial.reflect.clazz;
import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import org.o7planning.tutorial.beans.Cat;
public class ShowMemberInfo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Get object represent Cat class.
Class<Cat> aClass = Cat.class;
// Get Constructor array of Cat.
Constructor<?>[] constructors = aClass.getConstructors();
System.out.println(" ==== CONSTRUCTORs: ===== ");
for (Constructor<?> constructor : constructors) {
System.out.println("Constructor: " + constructor.getName());
}
// Get a list of public method of Cat
// Include the methods inherited from the parent class and the interfaces
Method[] methods = aClass.getMethods();
System.out.println(" ==== METHODs: ====== ");
for (Method method : methods) {
System.out.println("Method: " + method.getName());
}
// Get the list of the public fields
// Include the fields inherited from the parent class, and the interfaces
Field[] fields = aClass.getFields();
System.out.println(" ==== FIELDs: ====== ");
for (Field field : fields) {
System.out.println("Field: " + field.getName());
}
}
}Running the example:
==== CONSTRUCTORs: =====
Constructor: org.o7planning.tutorial.beans.Cat
Constructor: org.o7planning.tutorial.beans.Cat
Constructor: org.o7planning.tutorial.beans.Cat
==== METHODs: ======
Method: getAge
Method: setAge
Method: say
Method: getNumberOfLegs
Method: getName
Method: getLocation
Method: wait
Method: wait
Method: wait
Method: equals
Method: toString
Method: hashCode
Method: getClass
Method: notify
Method: notifyAll
==== FIELDs: ======
Field: SAY
Field: NUMBER_OF_LEGS
Field: age5. Constructor
No ADS
For example, taking out a constructor with the parameters specified. And print out information about this constructor.
ConstructorExample.java
package org.o7planning.tutorial.reflect.constructor;
import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
import org.o7planning.tutorial.beans.Cat;
public class ConstructorExample {
public static void main(String[] args) throws NoSuchMethodException,
SecurityException, InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException,
IllegalArgumentException, InvocationTargetException {
// Get Class object represent Cat class.
Class<Cat> aClass = Cat.class;
// Get the Constructor object of the public constructor
// that matches the specified parameterTypes
Constructor<?> constructor = aClass.getConstructor(String.class,
int.class);
// Get parameter array of this constructor.
Class<?>[] paramClasses = constructor.getParameterTypes();
for (Class<?> paramClass : paramClasses) {
System.out.println("Param: " + paramClass.getSimpleName());
}
// Initialize the object in the usual way
Cat tom = new Cat("Tom", 3);
System.out
.println("Cat 1: " + tom.getName() + ", age =" + tom.getAge());
// Using Java reflection to create object
Cat tom2 = (Cat) constructor.newInstance("Tom", 2);
System.out.println("Cat 2: " + tom.getName() + ", age ="
+ tom2.getAge());
}
}Running the example:
Param: String
Param: int
Cat 1: Tom, age =3
Cat 2: Tom, age =26. Field
No ADS
The example below retrieves Field with the specified name.
FieldExample.java
package org.o7planning.tutorial.reflect.field;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import org.o7planning.tutorial.beans.Cat;
public class FieldExample {
public static void main(String[] args) throws NoSuchFieldException,
SecurityException, IllegalArgumentException, IllegalAccessException {
// Get Class object represent Cat class
Class<Cat> aClass = Cat.class;
// Get Field object represent field 'NUMBER_OF_LEGS'.
Field field = aClass.getField("NUMBER_OF_LEGS");
Class<?> fieldType = field.getType();
System.out.println("Field type: " + fieldType.getSimpleName());
Field ageField = aClass.getField("age");
Cat tom = new Cat("Tom", 5);
// Returns the value of the field represented by this Field,
// on the specified object.
Integer age = (Integer) ageField.get(tom);
System.out.println("Age = " + age);
// Sets the field represented by this Field object on
// the specified object argument to the specified new value.
ageField.set(tom, 7);
System.out.println("New Age = "+ tom.getAge());
}
}Running the example:
Field type: int
Age = 5
New Age = 77. Method
No ADS
For example, taking out a method with the name and the parameters specified. Print out the information about this method, such as the return type, a list of parameters, ...
MethodExample.java
package org.o7planning.tutorial.reflect.method;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import org.o7planning.tutorial.beans.Cat;
public class MethodExample {
public static void main(String[] args) throws NoSuchMethodException,
SecurityException, IllegalAccessException,
IllegalArgumentException, InvocationTargetException {
// Class object represent Cat class
Class<Cat> aClass = Cat.class;
// Method object represent getAge() method.
Method getAgeMethod = aClass.getMethod("getAge");
// return type of method.
Class<?> returnType= getAgeMethod.getReturnType();
System.out.println("Return type of getAge: "+ returnType.getSimpleName());
Cat tom = new Cat("Tom", 7);
// Call method 'getAge' way Reflect
// This is equivalent to calling: tom.getAge()
int age = (int) getAgeMethod.invoke(tom);
System.out.println("Age = " + age);
// Method object represent setAge(int) method of Cat class.
Method setAgeMethod = aClass.getMethod("setAge", int.class);
// Call method setAge(int) way Reflect
// This is equivalent to calling: tom.setAge(5)
setAgeMethod.invoke(tom, 5);
System.out.println("New Age = " + tom.getAge());
}
}Running the example
Return type of getAge: int
Age = 7
New Age = 58. Getter and setter methods
No ADS
The example below, list the public setter methods,and the public getter methods of the class.
GetSetExample.java
package org.o7planning.tutorial.reflect.getset;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import org.o7planning.tutorial.beans.Cat;
public class GetSetExample {
// Method is getter if names start with get, and no parameters.
public static boolean isGetter(Method method) {
if (!method.getName().startsWith("get")) {
return false;
}
if (method.getParameterTypes().length != 0) {
return false;
}
if (void.class.equals(method.getReturnType())) {
return false;
}
return true;
}
// Method is setter if names start with set, and only one parameter.
public static boolean isSetter(Method method) {
if (!method.getName().startsWith("set")) {
return false;
}
if (method.getParameterTypes().length != 1) {
return false;
}
return true;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Class object represet Cat class
Class<Cat> aClass = Cat.class;
// public methods
Method[] methods = aClass.getMethods();
for (Method method : methods) {
boolean isSetter = isSetter(method);
boolean isGetter = isGetter(method);
System.out.println("Method: " + method.getName());
System.out.println(" - Is Setter? " + isSetter);
System.out.println(" - Is Getter? " + isGetter);
}
}
}Running the example:
Method: getName
- Is Setter? false
- Is Getter? true
Method: getNumberOfLegs
- Is Setter? false
- Is Getter? true
Method: getAge
- Is Setter? false
- Is Getter? true
Method: setAge
- Is Setter? true
- Is Getter? false
Method: say
- Is Setter? false
- Is Getter? false
Method: getLocation
- Is Setter? false
- Is Getter? true
Method: wait
- Is Setter? false
- Is Getter? false
Method: wait
- Is Setter? false
- Is Getter? false
Method: wait
- Is Setter? false
- Is Getter? false
Method: equals
- Is Setter? false
- Is Getter? false
Method: toString
- Is Setter? false
- Is Getter? false
Method: hashCode
- Is Setter? false
- Is Getter? false
Method: getClass
- Is Setter? false
- Is Getter? true
Method: notify
- Is Setter? false
- Is Getter? false
Method: notifyAll
- Is Setter? false
- Is Getter? false9. Access to the private methods, fields
No ADS
You can not access the method or field when it is private in the usual way, java compiler does not allow that. But with the reflect, it is absolutely possible.
AccessPrivateFieldExample.java
package org.o7planning.tutorial.reflect.privateaccess;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import org.o7planning.tutorial.beans.Cat;
public class AccessPrivateFieldExample {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IllegalArgumentException,
IllegalAccessException, NoSuchFieldException, SecurityException {
// Class object represent Cat class
Class<Cat> aClass = Cat.class;
// Class.getField(String) get public field only.
// Use Class.getDeclaredField(String):
// Get the Field object of field declared in class.
Field private_nameField = aClass.getDeclaredField("name");
// Allows for access to private field.
// Avoid IllegalAccessException
private_nameField.setAccessible(true);
Cat tom = new Cat("Tom");
String fieldValue = (String) private_nameField.get(tom);
System.out.println("Value field name = " + fieldValue);
// Set new valud for 'name' field.
private_nameField.set(tom, "Tom Cat");
System.out.println("New name = " + tom.getName());
}
}Running the example:
Value field name = Tom
New name = Tom Cat
The next example, access to the private method.
AccessPrivateMethodExample.java
package org.o7planning.tutorial.reflect.privateaccess;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import org.o7planning.tutorial.beans.Cat;
public class AccessPrivateMethodExample {
public static void main(String[] args) throws NoSuchMethodException,
SecurityException, IllegalAccessException,
IllegalArgumentException, InvocationTargetException {
// Class object represent Cat class.
Class<Cat> aClass = Cat.class;
// Class.getMethod(String) get public method only.
// Use Class.getDeclaredMethod(String):
// Get the Method object of method declared in class.
Method private_setNameMethod = aClass.getDeclaredMethod("setName",
String.class);
// Allows for access to private method.
// Avoid IllegalAccessException
private_setNameMethod.setAccessible(true);
Cat tom = new Cat("Tom");
// Call private method
private_setNameMethod.invoke(tom, "Tom Cat");
System.out.println("New name = " + tom.getName());
}
}Running the example:
New name = Tom Cat10. Annotation
No ADS
MyAnnotation.java
package org.o7planning.tutorial.reflect.annotation;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
// Annotation can be used at runtime.
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
// Use for class, interface, method, field, parameter.
@Target({ ElementType.TYPE, ElementType.METHOD, ElementType.FIELD,
ElementType.PARAMETER })
public @interface MyAnnotation {
String name();
String value() default "";
}Annotation with class example:
ClassAnnotationExample.java
package org.o7planning.tutorial.reflect.annotation;
import java.lang.annotation.Annotation;
@MyAnnotation(name = "Table", value = "Employee")
public class ClassAnnotationExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Class<?> aClass = ClassAnnotationExample.class;
// Get array of the Annotation of class
Annotation[] annotations = aClass.getAnnotations();
for (Annotation ann : annotations) {
System.out.println("Annotation: " + ann.annotationType().getSimpleName());
}
// Or More specific
Annotation ann = aClass.getAnnotation(MyAnnotation.class);
MyAnnotation myAnn = (MyAnnotation) ann;
System.out.println("Name = " + myAnn.name());
System.out.println("Value = " + myAnn.value());
}
}Running the example:
Annotation: MyAnnotation
Name = Table
Value = EmployeeAnnotation with field & method example:
FieldMethodAnnotationExample.java
package org.o7planning.tutorial.reflect.annotation;
import java.lang.annotation.Annotation;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
public class FieldMethodAnnotationExample {
@MyAnnotation(name = "My Field")
private int myField;
@MyAnnotation(name = "My Method", value = "My Method Value")
protected void myMethod(String str) {
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws NoSuchFieldException,
SecurityException, NoSuchMethodException {
Class<?> aClass = FieldMethodAnnotationExample.class;
//
System.out.println(" == FIELD == ");
Field field = aClass.getDeclaredField("myField");
// Get array of Annotation of field
Annotation[] fieldAnns = field.getAnnotations();
for (Annotation methodAnn : fieldAnns) {
System.out.println("Annotation: "
+ methodAnn.annotationType().getSimpleName());
}
// Or more specific
Annotation fieldAnn = field.getAnnotation(MyAnnotation.class);
MyAnnotation myAnn1 = (MyAnnotation) fieldAnn;
System.out.println("Name = " + myAnn1.name());
System.out.println("Value = " + myAnn1.value());
// Similar for method ...
System.out.println(" == METHOD == ");
Method method = aClass.getDeclaredMethod("myMethod", String.class);
// Get array of Annotation of method
Annotation[] methodAnns = method.getAnnotations();
for (Annotation methodAnn : methodAnns) {
System.out.println("Annotation: "
+ methodAnn.annotationType().getSimpleName());
}
// For more specific
Annotation methodAnn = method.getAnnotation(MyAnnotation.class);
MyAnnotation myAnn2 = (MyAnnotation) methodAnn;
System.out.println("Name = " + myAnn2.name());
System.out.println("Value = " + myAnn2.value());
}
}Running the example:
== FIELD ==
Annotation: MyAnnotation
Name = My Field
Value =
== METHOD ==
Annotation: MyAnnotation
Name = My Method
Value = My Method ValueAnnotation with method parameters example:
ParameterAnnotationExample.java
package org.o7planning.tutorial.reflect.annotation;
import java.lang.annotation.Annotation;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
public class ParameterAnnotationExample {
// For example, a method with annotations in parameters.
protected void doSomething(int jobType,
@MyAnnotation(name = "Table", value = "Employee") String info) {
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws NoSuchMethodException,
SecurityException {
Class<?> aClass = ParameterAnnotationExample.class;
// Get Method object of doSomething(int,String) method.
Method method = aClass.getDeclaredMethod("doSomething", int.class,
String.class);
// Get parameters list of method
Class<?>[] parameterTypes = method.getParameterTypes();
for (Class<?> parameterType : parameterTypes) {
System.out.println("Parametete Type: "
+ parameterType.getSimpleName());
}
System.out.println(" ---- ");
// Returns an array of arrays of Annotations that
// represent the annotations on the formal parameters
Annotation[][] annotationss = method.getParameterAnnotations();
// Get Annotation list of parameter index 1.
Annotation[] annotations = annotationss[1];
for (Annotation ann : annotations) {
System.out.println("Annotation: "
+ ann.annotationType().getSimpleName());
}
}
}Parametete Type: int
Parametete Type: String
----
Annotation: MyAnnotationNo ADS
Java Basic
- Data Types in java
- Java PhantomReference Tutorial with Examples
- JDK Javadoc in CHM format
- Java Stream Tutorial with Examples
- Java Predicate Tutorial with Examples
- Java BiConsumer Tutorial with Examples
- Arrays in Java
- JDBC Driver Libraries for different types of database in Java
- Abstract class and Interface in Java
- Java Commons Email Tutorial with Examples
- Install Eclipse
- Bitwise Operations
- Install Eclipse on Ubuntu
- Configuring Eclipse to use the JDK instead of JRE
- Java Commons Logging Tutorial with Examples
- Java Enums Tutorial with Examples
- Loops in Java
- Java Regular Expressions Tutorial with Examples
- Install Java on Ubuntu
- Quick Learning Java for beginners
- Install Java on Windows
- Comparing and Sorting in Java
- Inheritance and polymorphism in Java
- Java Consumer Tutorial with Examples
- Java String, StringBuffer and StringBuilder Tutorial with Examples
- Java Exception Handling Tutorial with Examples
- Example of Java encoding and decoding using Apache Base64
- if else statement in java
- Switch Statement in Java
- Java Supplier Tutorial with Examples
- Java Programming for team using Eclipse and SVN
- Java JDBC Tutorial with Examples
- Java remote method invocation - Java RMI Tutorial with Examples
- Java Multithreading Programming Tutorial with Examples
- Customize java compiler processing your Annotation (Annotation Processing Tool)
- What is needed to get started with Java?
- Java Aspect Oriented Programming with AspectJ (AOP)
- Understanding Java System.identityHashCode, Object.hashCode and Object.equals
- Java Compression and Decompression Tutorial with Examples
- Java Reflection Tutorial with Examples
- Install OpenJDK on Ubuntu
- Java String.format() and printf() methods
- History of Java and the difference between Oracle JDK and OpenJDK
- Introduction to the Raspberry Pi
- Java Socket Programming Tutorial with Examples
- Java Generics Tutorial with Examples
- Manipulating files and directories in Java
- Java WeakReference Tutorial with Examples
- Java Commons IO Tutorial with Examples
- History of bits and bytes in computer science
- Which Platform Should You Choose for Developing Java Desktop Applications?
- Java SoftReference Tutorial with Examples
- Syntax and new features in Java 8
- Java Annotations Tutorial with Examples
- Java Function Tutorial with Examples
- Access modifiers in Java
- Java BiFunction Tutorial with Examples
- Get the values of the columns automatically increment when Insert a record using JDBC
- Java Functional Interface Tutorial with Examples
- Java BiPredicate Tutorial with Examples
Show More
- Java Servlet/Jsp Tutorials
- Java Collections Framework Tutorials
- Java API for HTML & XML
- Java IO Tutorials
- Java Date Time Tutorials
- Spring Boot Tutorials
- Maven Tutorials
- Gradle Tutorials
- Java Web Services Tutorials
- Java SWT Tutorials
- JavaFX Tutorials
- Java Oracle ADF Tutorials
- Struts2 Framework Tutorials
- Spring Cloud Tutorials