Oracle String functions
1. ASCII
No ADS
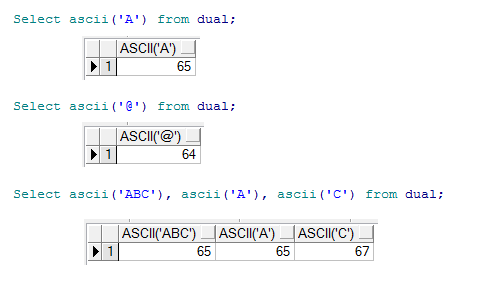
The Oracle/PLSQL ASCII function returns the NUMBER code that represents the specified character.
Syntax:
ASCII( p_character )Arguments:
p_character
- The specified character to retrieve the NUMBER code for. If more than one character is entered, the ASCII function will return the value for the first character and ignore all of the characters after the first.
See also ASCII table:
Dec | Hex | Oct | Char | Description | Dec | Hex | Oct | Char | Description | |
0 | 0 | 0 | null | 64 | 40 | 100 | @ | |||
1 | 1 | 1 | start of heading | 65 | 41 | 101 | A | |||
2 | 2 | 2 | start of text | 66 | 42 | 102 | B | |||
3 | 3 | 3 | end of text | 67 | 43 | 103 | C | |||
4 | 4 | 4 | end of transmission | 68 | 44 | 104 | D | |||
5 | 5 | 5 | enquiry | 69 | 45 | 105 | E | |||
6 | 6 | 6 | acknowledge | 70 | 46 | 106 | F | |||
7 | 7 | 7 | bell | 71 | 47 | 107 | G | |||
8 | 8 | 10 | backspace | 72 | 48 | 110 | H | |||
9 | 9 | 11 | horizontal tab | 73 | 49 | 111 | I | |||
10 | A | 12 | new line | 74 | 4A | 112 | J | |||
11 | B | 13 | vertical tab | 75 | 4B | 113 | K | |||
12 | C | 14 | new page | 76 | 4C | 114 | L | |||
13 | D | 15 | carriage return | 77 | 4D | 115 | M | |||
14 | E | 16 | shift out | 78 | 4E | 116 | N | |||
15 | F | 17 | shift in | 79 | 4F | 117 | O | |||
16 | 10 | 20 | data link escape | 80 | 50 | 120 | P | |||
17 | 11 | 21 | device control 1 | 81 | 51 | 121 | Q | |||
18 | 12 | 22 | device control 2 | 82 | 52 | 122 | R | |||
19 | 13 | 23 | device control 3 | 83 | 53 | 123 | S | |||
20 | 14 | 24 | device control 4 | 84 | 54 | 124 | T | |||
21 | 15 | 25 | negative acknowledge | 85 | 55 | 125 | U | |||
22 | 16 | 26 | synchronous idle | 86 | 56 | 126 | V | |||
23 | 17 | 27 | end of trans. block | 87 | 57 | 127 | W | |||
24 | 18 | 30 | cancel | 88 | 58 | 130 | X | |||
25 | 19 | 31 | end of medium | 89 | 59 | 131 | Y | |||
26 | 1A | 32 | substitute | 90 | 5A | 132 | Z | |||
27 | 1B | 33 | escape | 91 | 5B | 133 | [ | |||
28 | 1C | 34 | file separator | 92 | 5C | 134 | \ | |||
29 | 1D | 35 | group separator | 93 | 5D | 135 | ] | |||
30 | 1E | 36 | record separator | 94 | 5E | 136 | ^ | |||
31 | 1F | 37 | unit separator | 95 | 5F | 137 | _ | |||
32 | 20 | 40 | space | 96 | 60 | 140 | ` | |||
33 | 21 | 41 | ! | 97 | 61 | 141 | a | |||
34 | 22 | 42 | " | 98 | 62 | 142 | b | |||
35 | 23 | 43 | # | 99 | 63 | 143 | c | |||
36 | 24 | 44 | $ | 100 | 64 | 144 | d | |||
37 | 25 | 45 | % | 101 | 65 | 145 | e | |||
38 | 26 | 46 | & | 102 | 66 | 146 | f | |||
39 | 27 | 47 | ' | 103 | 67 | 147 | g | |||
40 | 28 | 50 | ( | 104 | 68 | 150 | h | |||
41 | 29 | 51 | ) | 105 | 69 | 151 | i | |||
42 | 2A | 52 | * | 106 | 6A | 152 | j | |||
43 | 2B | 53 | + | 107 | 6B | 153 | k | |||
44 | 2C | 54 | , | 108 | 6C | 154 | l | |||
45 | 2D | 55 | - | 109 | 6D | 155 | m | |||
46 | 2E | 56 | . | 110 | 6E | 156 | n | |||
47 | 2F | 57 | / | 111 | 6F | 157 | o | |||
48 | 30 | 60 | 0 | 112 | 70 | 160 | p | |||
49 | 31 | 61 | 1 | 113 | 71 | 161 | q | |||
50 | 32 | 62 | 2 | 114 | 72 | 162 | r | |||
51 | 33 | 63 | 3 | 115 | 73 | 163 | s | |||
52 | 34 | 64 | 4 | 116 | 74 | 164 | t | |||
53 | 35 | 65 | 5 | 117 | 75 | 165 | u | |||
54 | 36 | 66 | 6 | 118 | 76 | 166 | v | |||
55 | 37 | 67 | 7 | 119 | 77 | 167 | w | |||
56 | 38 | 70 | 8 | 120 | 78 | 170 | x | |||
57 | 39 | 71 | 9 | 121 | 79 | 171 | y | |||
58 | 3A | 72 | : | 122 | 7A | 172 | z | |||
59 | 3B | 73 | ; | 123 | 7B | 173 | { | |||
60 | 3C | 74 | < | 124 | 7C | 174 | | | |||
61 | 3D | 75 | = | 125 | 7D | 175 | } | |||
62 | 3E | 76 | > | 126 | 7E | 176 | ~ | |||
63 | 3F | 77 | ? | 127 | 7F | 177 | DEL |
2. COALESCE
The Oracle COALESCE function returns the first non-NULL expression in the list. If all expressions in the list evaluate to NULL, then the COALESCE function will return NULL. The Oracle COALESCE function makes use of "short-circuit evaluation". The database evaluates each expression's value and determines whether it is NULL, rather than evaluating all of the expressions before determining if any of them are NULL.
Syntax:
COALESCE( p_expression1, p_expression2, ... p_expressionN )Arguments:
- p_expression1, p_expression2, .. p_expressionN
- The expressions to test for non-null values.
Example:
-- --> 'Abc'
Select COALESCE(null, 'Abc', '123') as Column1 from dual;
-- --> 'Aaa'
Select COALESCE('Aaa', null, '345') as Column1 from dual;
-- --> 'Sss'
Select COALESCE(null, null, null, 'Sss') as Column1 from dual;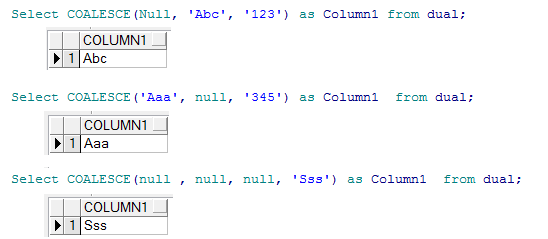
5. INITCAP
No ADS
The Oracle INITCAP function returns a character string with the first letter of each word converted to uppercase (also called "title case"). All other letters in the string will be converted to lowercase. Words are delimited by white space (spaces, tabs, carriage returns, formfeeds, vertical-tabs, newlines) or characters that are not alphanumeric.
Syntax:
INITCAP( p_string )Argument:
p_string
- The string argument whose first character in each word will be converted to uppercase and all remaining characters converted to lowercase.
Example:
-- --> Tom Cat
Select Initcap('TOM CAT') From Dual;
-- --> Tom Cat
Select Initcap('tom cat') From Dual;6. CHR
The Oracle CHR() function returns the ASCII character that corresponds to the value passed to it. If using NCHAR_CS is specified, it returns the character that corresponds to the national character set.
Syntax:
CHR( p_number )
CHR( p_number using nchar_cs)Arguments:
p_number
- The NUMBER code used to retrieve the character.
Example:
-- --> @
Select chr(64) From dual;
-- --> A
Select chr(65) From dual;
-- --> â
Select chr(50082) From dual;
-- --> 쎢
Select chr(50082 using nchar_cs) From dual;8. CONCAT(Clob, Clob)
The CONCAT function allows you to concatenate two strings together.
Syntax:
CONCAT( p_string1, p_string2 )- CONCAT(CLOB, NCLOB) returns NCLOB
- CONCAT(NCLOB, NCHAR) returns NCLOB
- CONCAT(NCLOB, CHAR) returns NCLOB
- CONCAT(NCHAR, CLOB) returns NCLOB
Arguments:
p_string1
- The first string to concatenate.
- The second string to concatenate.
Example:
Declare
C1 Clob := To_Clob('Tom ');
C2 Clob := To_Clob('Cat');
C3 Clob;
C4 Clob;
Begin
Select Concat(C1
,C2)
Into C3
From Dual;
----
-- --> Tom Cat
Dbms_Output.Put_Line(C3);
----
C4 := Concat(C1
,C2);
-- --> Tom Cat
Dbms_Output.Put_Line(C4);
End;9. INSTR
No ADS
The INSTR function returns the location of a substring in a string.
Syntax:
INSTR( p_string, p_substring [, p_start_position [, p_occurrence ] ] )p_string
- The string to search. p_string can be CHAR, VARCHAR2, NCHAR, NVARCHAR2, CLOB, or NCLOB.
- The substring to search for in p_string. p_substring can be CHAR, VARCHAR2, NCHAR, NVARCHAR2, CLOB, or NCLOB.
- Optional. The position in p_string where the search will start. If omitted, it defaults to 1. The first position in the string is 1. If the p_start_position is negative, the INSTR function counts back p_start_position number of characters from the end of string and then searches towards the beginning of string.
- Optional. The nth appearance of p_substring. If omitted, it defaults to 1.
If p_substring is not found in p_string, then the INSTR function will return 0.
Example:
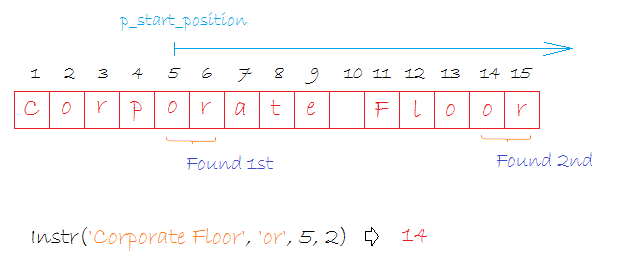
-- --> 14
Select Instr('Corporate Floor', 'or', 5, 2) as Column1 from dual;
-- --> 5
Select Instr('Corporate Floor', 'or', -10) as Column1 from dual;See also:
10. INSTRB
The INSTRB function returns the location of a substring in a string, using bytes instead of characters.
Syntax:
INSTRB (p_string , p_substring [, p_start_position [, p_occurrence]])The INSTRB function returns the location of a p_substring in a p_string, using bytes instead of characters.
Arguments:
p_string
- The text expression to search.
- The string to search for.
- A nonzero INTEGER indicating the byte of string where the function begins the search. When p_start_position is negative, then INSTRB counts and searches backward from the end of string. The default value of p_start_position is 1, which means that the function begins searching at the first byte of string.
- An INTEGER indicating which occurrence of string the function should search for. The value of occurrence must be positive. The default values of p_occurrence is 1, meaning the function searches for the first occurrence of substring.
If p_substring is not found in p_string, then the INSTRB function will return 0.
12. LENGTHB
No ADS
The LENGTHB function returns the length of the specified string, using bytes instead of characters.
Syntax:
LENGTHB( p_string )Arguments:
p_string (CHAR, VARCHAR2, NCHAR, NVARCHAR2)
- The string to return the length (in bytes).
Example:
-- Null - Null
Select Lengthb(Null) Column1
,Lengthb('') Column2
From Dual;
-- 7
Select Lengthb('Tom Cat') Column1 From dual;
-- 2
Select Lengthb('Â') As Column1 From Dual;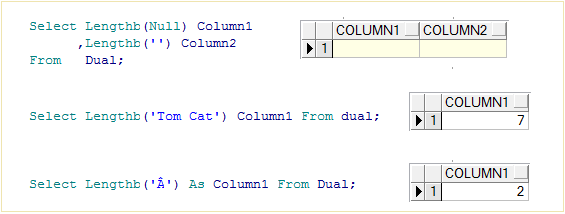
-- length of characters
-- --> 10
Select Length('Tiếng Việt') from dual;
-- length of bytes
-- --> 14
Select Lengthb('Tiếng Việt') from dual;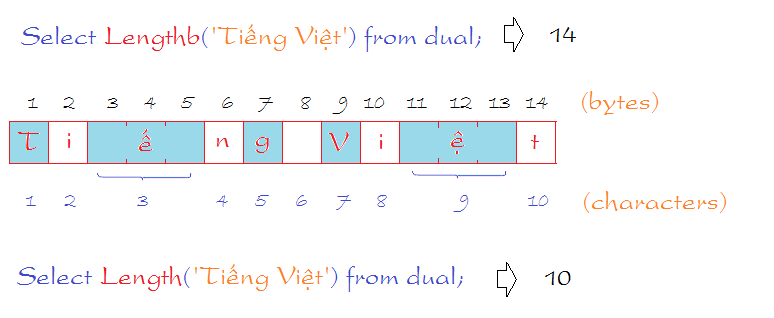
13. LPAD
The LPAD function pads (adds characters to) the left-side of a string with a given set of characters.
Syntax:
LPAD( p_string, p_padded_length [, p_pad_string] )Arguments:
p_string
- The string to pad characters to (the left-hand side).
- The number of characters to return. If the padded_length is smaller than the original string, the LPAD function will truncate the string to the size of p_padded_length.
- Optional. This is the string that will be padded to the left-hand side of p_string. If this parameter is omitted, the LPAD function will pad spaces to the left-side of p_string.
Example:
-- 00123
Select Lpad('123', 5, '0') From Dual;
-- 12345
Select Lpad('1234567', 5, '0') From Dual;
-- ' Tom'
Select Lpad('Tom', 10) From Dual;
-- 'To'
Select Lpad('Tom', 2) From Dual;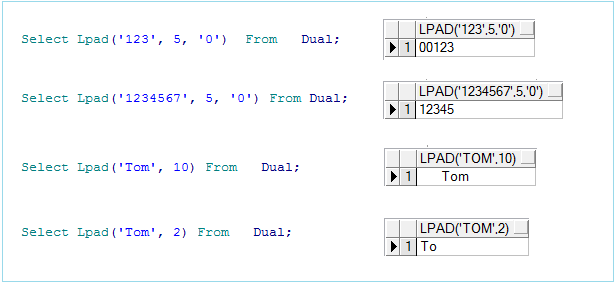
14. LTRIM
No ADS
The Oracle LTRIM function removes leading spaces from a string or column. Space characters are the default, but you can also specify the character(s) to be removed. Characters can be specified as literals ('A', 'm', etc) or by their CHR equivalents. For example 'CHR(112)', 'CHR(68)'.
The LTRIM function returns a value with datatype VARCHAR2.
The LTRIM function returns a value with datatype VARCHAR2.
Syntax:
LTRIM( p_string [, p_trim_string] )Arguments:
p_string
- The string to trim the characters from the left-hand side.
- Optional. The string that will be removed from the left-hand side of p_string. If this parameter is omitted, the LTRIM function will remove all leading spaces from p_string.
Example:
-- --> TOM
Select LTRIM(' TOM') From dual;
-- --> 789
Select LTRIM('000789', '0') From Dual;
-- --> ABC01
Select LTRIM('0101ABC01', '01') From dual;
-- --> 4210ABC
Select LTRIM('34210ABC', '0123') From dual;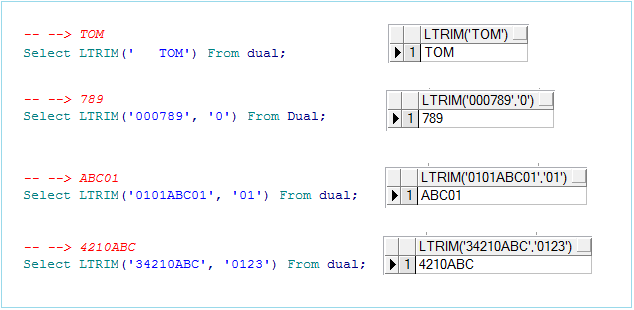
15. RTRIM
The Oracle RTRIM function removes trailing spaces from a string or column. Space characters are the default, but you can also specify the character(s) to be removed. Characters can be specified as literals ('A', 'm', etc) or by their CHR equivalents: 'CHR(112)', 'CHR(68)'.
The RTRIM function returns a value with datatype VARCHAR2.
The RTRIM function returns a value with datatype VARCHAR2.
Syntax:
RTRIM( p_string [, trim_string ] )Arguments:
p_string
- The string to trim the characters from the right-hand side.
- Optional. The string that will be removed from the right-hand side of p_string. If this parameter is omitted, the RTRIM function will remove all trailing spaces from p_string.
Example:
-- --> TOM
Select RTRIM('TOM ') From dual;
-- --> 000789
Select RTRIM('00078900', '0') From Dual;
-- --> 0101ABC
Select RTRIM('0101ABC0101', '01') From dual;
-- --> ABC34
Select RTRIM('ABC34210', '0123') From dual;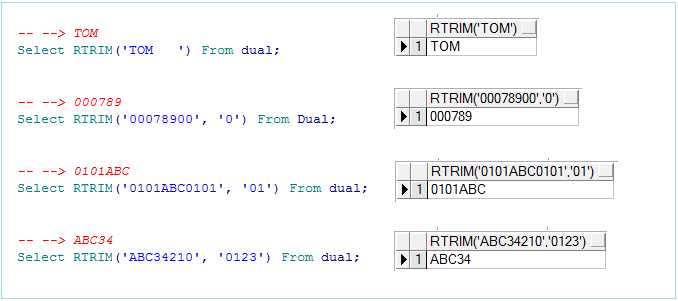
16. TRIM
The Oracle TRIM function removes leading and trailing spaces from a string or column. Space characters are the default, but you can also specify the character(s) to be removed. Characters can be specified as literals ('A', 'm', etc) or by their CHR equivalents: 'CHR(112)', 'CHR(68)'.
The TRIM function returns a value with datatype VARCHAR2.
The TRIM function returns a value with datatype VARCHAR2.
Syntax:
TRIM( [ [ LEADING | TRAILING | BOTH ] p_trim_character FROM ] p_string )Arguments:
LEADING
- The function will remove p_trim_character from the front of p_string.
- The function will remove p_trim_character from the end of p_string.
- The function will remove p_trim_character from the front and end of p_string.
- The character that will be removed from p_string. If this parameter is omitted, the TRIM function will remove space characters from p_string.
- The string to trim.
Example:
-- --> TOM
Select TRIM(' TOM ') From dual;
-- --> 78900
Select TRIM(Leading '0' from '00078900') From Dual;
-- --> 001ABC
Select TRIM(Trailing '0' from '001ABC00') From dual;
-- --> ABC21
Select TRIM(Both '0' from '00ABC21000' ) From dual;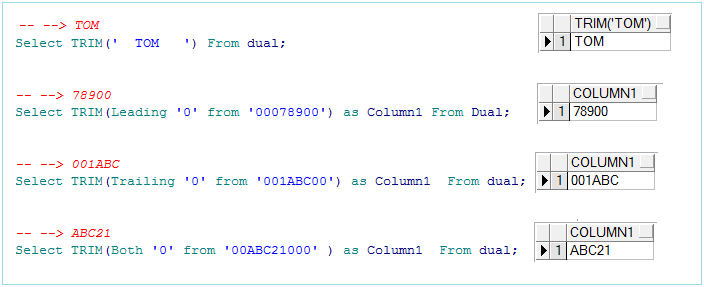
17. SUBSTR
No ADS
The Oracle SUBSTR (Or SUBSTRING) function lets you extract a portion of a string (a 'substring') from a string.
Syntax:
SUBSTR( p_string, p_start_position [, p_length ] )Arguments:
p_string
- The source string.
- The starting position for extraction. The first position in the string is always 1.
- Optional. It is the number of characters to extract. If this parameter is omitted, the SUBSTR function will return the substring from p_start_position to end of p_string.
If p_start_position is 0, then the SUBSTR function treats p_start_position as 1 (ie: the first position in the string).If p_start_position is a negative number, then the SUBSTR function starts from the end of the string and counts backwards.If p_length is a negative number, then the SUBSTR function will return a NULL value.
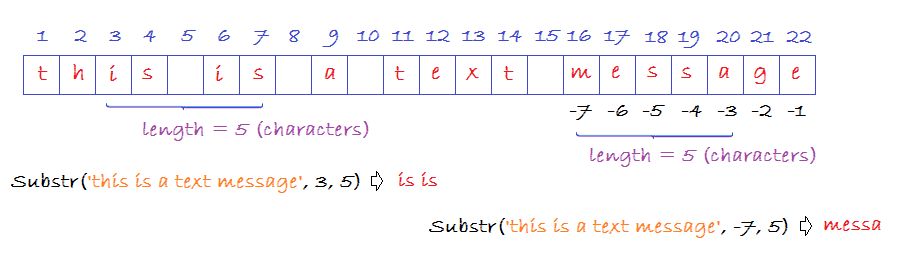
-- 'is is'
Select substr('this is a text message',3,5) Column1 from dual;
-- 'is is a text message'
Select substr('this is a text message',3) Column1 from dual;
-- 'messa'
Select substr('this is a text message',-7,5) Column1 from dual;
-- 'message'
Select substr('this is a text message',-7) Column1 from dual;
-- 'age'
Select substr('this is a text message',-3, 5) Column1 from dual;
-- null
Select substr('this is a text message',-3, -5) Column1 from dual;18. SUBSTRB
Returns a substring counting bytes rather than characters
Syntax:
SUBSTRB( p_string, p_start_position [, p_length ] )Arguments:
p_string
- The source string.
- The starting position for extraction. The first position in the string is always 1.
- Optional. It is the number of characters to extract. If this parameter is omitted, the SUBSTRB function will return the substring from p_start_position to end of p_string.
Example:
-- ây là
Select Substrb('Đây là Tiếng Việt', 3, 7) from dual;
-- y là Ti
Select Substr('Đây là Tiếng Việt', 3, 7) from dual;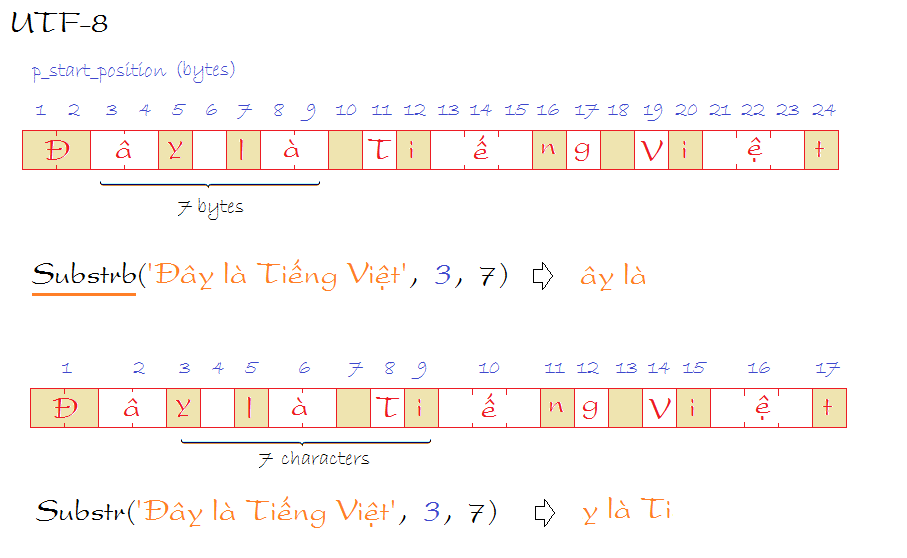
No ADS
Oracle Database Tutorials
- Install PL/SQL Developer on Windows
- Sample Oracle Database for Learning SQL
- SQL Tutorial for Beginners with Oracle
- Install Oracle Database 11g on Windows
- Install Oracle Database 12c on Windows
- Install Oracle Client on Windows
- Create Oracle SCOTT Schema
- Sample Database
- Database structure and Cloud features in Oracle 12c
- Importing and Exporting Oracle Database
- Oracle String functions
- Split comma separated string and pass to IN clause of select statement in Oracle
- Hierarchical Queries in Oracle
- Oracle Database Link and Synonym Tutorial with Examples
- Oracle PL/SQL Programming Tutorial with Examples
- XML Parser for Oracle PL/SQL
- Standard Database Auditing in Oracle
- Creating and Managing Oracle Wallet
Show More
