Java XStream Tutorial with Examples
1. What is XStream?
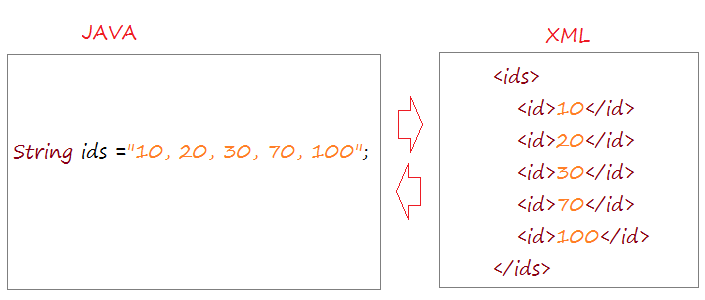
XStream is an open source Java library, which is used to convert a Java object to an XML document and vice versa.
2. XStream Library
You can download the XStream library at:
Or declare XStream library with Maven
<!-- http://mvnrepository.com/artifact/com.thoughtworks.xstream/xstream -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.thoughtworks.xstream</groupId>
<artifactId>xstream</artifactId>
<version>1.4.8</version>
</dependency>3. Some classes participated in the examples
Address.java
package org.o7planning.xstreamtutorial.beans;
public class Address {
private String street;
private String city;
public Address() {
}
public Address(String street, String city) {
this.street = street;
this.city = city;
}
public String getStreet() {
return street;
}
public void setStreet(String street) {
this.street = street;
}
public String getCity() {
return city;
}
public void setCity(String city) {
this.city = city;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return street + ", " + city;
}
}Company.java
package org.o7planning.xstreamtutorial.beans;
public class Company {
private int id;
private String name;
private String[] websites;
private Address address;
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String[] getWebsites() {
return websites;
}
public void setWebsites(String[] websites) {
this.websites = websites;
}
public Address getAddress() {
return address;
}
public void setAddress(Address address) {
this.address = address;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
sb.append("\n id:" + this.id);
sb.append("\n name:" + this.name);
if (this.websites != null) {
sb.append("\n website: ");
for (String website : this.websites) {
sb.append(website + ", ");
}
}
if (this.address != null) {
sb.append("\n address:" + this.address.toString());
}
return sb.toString();
}
}DataDAO.java
package org.o7planning.xstreamtutorial;
import org.o7planning.xstreamtutorial.beans.Address;
import org.o7planning.xstreamtutorial.beans.Company;
public class DataDAO {
public static Company createCompany() {
Company company = new Company();
company.setId(111);
company.setName("Microsoft");
String[] websites = { "http://microsoft.com",
"http://msn.com", "http://hotmail.com" };
company.setWebsites(websites);
Address address = new Address();
address.setCity("Redmond");
address.setStreet("1 Microsoft Way");
company.setAddress(address);
return company;
}
}4. Converting Java object to XML
No ADS
Unlike JAXB, XStream can convert a Java object to XML without a mapping, it uses a default mapping. Consider the following example:
JavaObject2Xml.java
package org.o7planning.xstreamtutorial;
import org.o7planning.xstreamtutorial.beans.Company;
import com.thoughtworks.xstream.XStream;
public class JavaObject2Xml {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Company company = DataDAO.createCompany();
XStream xs = new XStream();
// JAVA OBJECT --> XML
String xml = xs.toXML(company);
System.out.println(xml);
}
}Running the example:
<org.o7planning.xstreamtutorial.beans.Company>
<id>111</id>
<name>Microsoft</name>
<websites>
<string>http://microsoft.com</string>
<string>http://msn.com</string>
<string>http://hotmail.com</string>
</websites>
<address>
<street>1 Microsoft Way</street>
<city>Redmond</city>
</address>
</org.o7planning.xstreamtutorial.beans.Company>5. Using Alias
No ADS
When converting Java object into XML, By default XStream convert class name to XML tag name. Aliasing is technique to customize XML created. There are 5 types of alias:
- Class Aliasing
- Field Aliasing
- Implicit Collections Aliasing
- Attribute Aliasing
- Package Aliasing
Class Aliasing
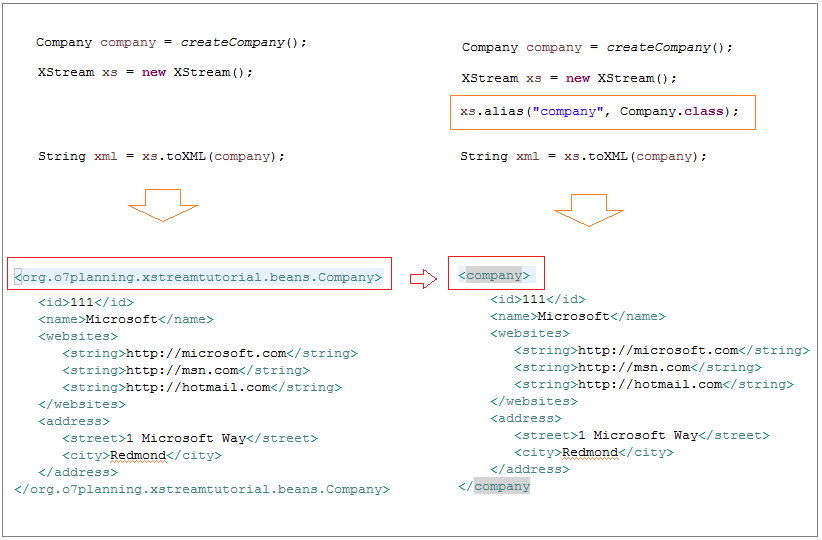
ClassAliasingExample.java
package org.o7planning.xstreamtutorial;
import org.o7planning.xstreamtutorial.beans.Company;
import com.thoughtworks.xstream.XStream;
public class ClassAliasingExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Company company = DataDAO.createCompany();
XStream xs = new XStream();
xs.alias("company", Company.class);
// JAVA OBJECT --> XML
String xml = xs.toXML(company);
System.out.println(xml);
}
}Running the example:
<company>
<id>111</id>
<name>Microsoft</name>
<websites>
<string>http://microsoft.com</string>
<string>http://msn.com</string>
<string>http://hotmail.com</string>
</websites>
<address>
<street>1 Microsoft Way</street>
<city>Redmond</city>
</address>
</companyField Aliasing

FieldAliasingExample.java
package org.o7planning.xstreamtutorial;
import org.o7planning.xstreamtutorial.beans.Company;
import com.thoughtworks.xstream.XStream;
public class FieldAliasingExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Company company = DataDAO.createCompany();
XStream xstream = new XStream();
// Class aliasing.
xstream.alias("company", Company.class);
// Field aliasing.
// aliasField(String alias, Class definedIn, String fieldName).
xstream.aliasField("companyName", Company.class, "name");
xstream.aliasField("companyId", Company.class, "id");
// JAVA OBJECT --> XML
String xml = xstream.toXML(company);
System.out.println(xml);
}
}Running the example:
<company>
<companyId>111</companyId>
<companyName>Microsoft</companyName>
<websites>
<string>http://microsoft.com</string>
<string>http://msn.com</string>
<string>http://hotmail.com</string>
</websites>
<address>
<street>1 Microsoft Way</street>
<city>Redmond</city>
</address>
</company>Implicit Collection Aliasing
Usually a collection (Array/Collection) in Java when it is converted to XML it is enclosed in a tag. You can use the implicit alias for the collection to remove this tag.
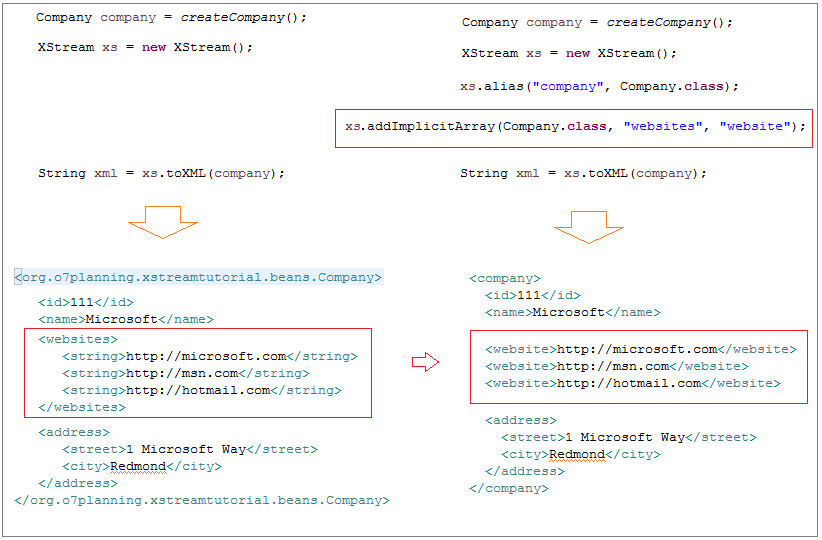
ImplicitCollectionsAliasingExample.java
package org.o7planning.xstreamtutorial;
import org.o7planning.xstreamtutorial.beans.Company;
import com.thoughtworks.xstream.XStream;
public class ImplicitCollectionsAliasingExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Company company = DataDAO.createCompany();
XStream xstream = new XStream();
// Class aliasing.
xstream.alias("company", Company.class);
// addImplicitArray(Class ownerType, String fieldName).
xstream.addImplicitArray(Company.class, "websites", "website");
// JAVA OBJECT --> XML
String xml = xstream.toXML(company);
System.out.println(xml);
}
}Running the example:
<company>
<id>111</id>
<name>Microsoft</name>
<website>http://microsoft.com</website>
<website>http://msn.com</website>
<website>http://hotmail.com</website>
<address>
<street>1 Microsoft Way</street>
<city>Redmond</city>
</address>
</company>Attribute Aliasing

AttributeAliasingExample.java
package org.o7planning.xstreamtutorial;
import org.o7planning.xstreamtutorial.beans.Company;
import com.thoughtworks.xstream.XStream;
public class AttributeAliasingExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Company company = DataDAO.createCompany();
XStream xstream = new XStream();
// Class aliasing.
xstream.alias("company", Company.class);
// useAttributeFor(Class definedIn, String fieldName).
xstream.useAttributeFor(Company.class, "id");
xstream.useAttributeFor(Company.class, "name");
xstream.aliasAttribute("companyName", "name");
// JAVA OBJECT --> XML
String xml = xstream.toXML(company);
System.out.println(xml);
}
}Running the example:
<company id="111" companyName="Microsoft">
<websites>
<string>http://microsoft.com</string>
<string>http://msn.com</string>
<string>http://hotmail.com</string>
</websites>
<address>
<street>1 Microsoft Way</street>
<city>Redmond</city>
</address>
</company>Package Aliasing
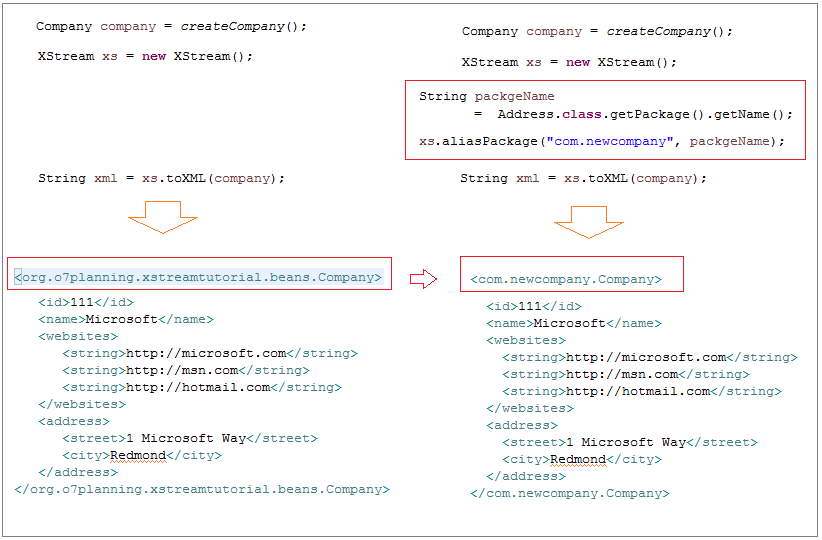
PackageAliasingExample.java
package org.o7planning.xstreamtutorial;
import org.o7planning.xstreamtutorial.beans.Address;
import org.o7planning.xstreamtutorial.beans.Company;
import com.thoughtworks.xstream.XStream;
public class PackageAliasingExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Company company = DataDAO.createCompany();
XStream xstream = new XStream();
String packgeName= Address.class.getPackage().getName();
// aliasPackage(String name, String pkgName).
xstream.aliasPackage("com.newcompany", packgeName);
// JAVA OBJECT --> XML
String xml = xstream.toXML(company);
System.out.println(xml);
}
}Running the example:
<com.newcompany.Company>
<id>111</id>
<name>Microsoft</name>
<websites>
<string>http://microsoft.com</string>
<string>http://msn.com</string>
<string>http://hotmail.com</string>
</websites>
<address>
<street>1 Microsoft Way</street>
<city>Redmond</city>
</address>
</com.newcompany.Company>6. XStream Annotation
No ADS

With XStream you can use the code to customize the XML generated from Java objects, in using the Alias has been mentioned above. However you can also use Annotation to tell XStream how to generate XML from Java objects.
Below is a list of Annotation:
Below is a list of Annotation:
- @XStreamAlias
- @XStreamAsAttribute
- @XStreamImplicit
- @XStreamOmitField
Using Code | Using Annotation |
xs.alias("dept", Department.class); | @XStreamAlias("dept")
public class Department { } |
xs.aliasField("no", Department.class, "deptNo"); | @XStreamAlias("no")
private int deptNo; |
xs.useAttributeFor(Department.class, "deptNo") | @XStreamAsAttribute
private int deptNo; |
xs.omitField(Employee.class, "bonus"); | @XStreamOmitField
private float bonus; |
xs.addImplicitCollection(Department.class, "employees"); | @XStreamImplicit
private List<Employee> employees; |
Department.java
package org.o7planning.xstreamtutorial.beans;
import java.util.List;
import com.thoughtworks.xstream.annotations.XStreamAlias;
import com.thoughtworks.xstream.annotations.XStreamAsAttribute;
import com.thoughtworks.xstream.annotations.XStreamImplicit;
@XStreamAlias("dept")
public class Department {
@XStreamAlias("no")
@XStreamAsAttribute
private int deptNo;
@XStreamAlias("name")
private String deptName;
@XStreamImplicit
private List<Employee> employees;
public int getDeptNo() {
return deptNo;
}
public void setDeptNo(int deptNo) {
this.deptNo = deptNo;
}
public String getDeptName() {
return deptName;
}
public void setDeptName(String deptName) {
this.deptName = deptName;
}
public List<Employee> getEmployees() {
return employees;
}
public void setEmployees(List<Employee> employees) {
this.employees = employees;
}
}Employee.java
package org.o7planning.xstreamtutorial.beans;
import com.thoughtworks.xstream.annotations.XStreamAlias;
import com.thoughtworks.xstream.annotations.XStreamAsAttribute;
import com.thoughtworks.xstream.annotations.XStreamOmitField;
@XStreamAlias("emp")
public class Employee {
@XStreamAlias("no")
@XStreamAsAttribute
private int empNo;
private String empName;
private float salary;
// Ignore this field.
@XStreamOmitField
private float bonus;
public Employee(int empNo, String empName, float salary) {
this.empNo = empNo;
this.empName = empName;
this.salary = salary;
}
public int getEmpNo() {
return empNo;
}
public void setEmpNo(int empNo) {
this.empNo = empNo;
}
public String getEmpName() {
return empName;
}
public void setEmpName(String empName) {
this.empName = empName;
}
public float getSalary() {
return salary;
}
public void setSalary(float salary) {
this.salary = salary;
}
public float getBonus() {
return bonus;
}
public void setBonus(float bonus) {
this.bonus = bonus;
}
}XStreamAnnotationExample.java
package org.o7planning.xstreamtutorial;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import org.o7planning.xstreamtutorial.beans.Department;
import org.o7planning.xstreamtutorial.beans.Employee;
import com.thoughtworks.xstream.XStream;
public class XStreamAnnotationExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Department dept = createDepartment();
XStream xstream = new XStream();
// Using annotations in class Department
xstream.processAnnotations(Department.class);
// Using annotations in class Employee
xstream.processAnnotations(Employee.class);
String xml = xstream.toXML(dept);
System.out.println(xml);
}
public static Department createDepartment() {
Department dept = new Department();
dept.setDeptNo(10);
dept.setDeptName("ACCOUNTING");
Employee king = new Employee(7839, "KING", 5000f);
Employee clark = new Employee(7839, "CLARK", 2450f);
Employee miller = new Employee(7839, "MILLER", 1300f);
List<Employee> list = new ArrayList<Employee>();
list.add(king);
list.add(clark);
list.add(miller);
dept.setEmployees(list);
return dept;
}
}Running the example:
<dept no="10">
<name>ACCOUNTING</name>
<emp no="7839">
<empName>KING</empName>
<salary>5000.0</salary>
</emp>
<emp no="7839">
<empName>CLARK</empName>
<salary>2450.0</salary>
</emp>
<emp no="7839">
<empName>MILLER</empName>
<salary>1300.0</salary>
</emp>
</dept>No ADS
Java Open Source Libraries
- Java JSON Processing API Tutorial (JSONP)
- Using Scribe OAuth Java API with Google OAuth2
- Get Hardware information in Java application
- Restfb Java API for Facebook
- Create Credentials for Google Drive API
- Manipulating files and folders on Google Drive using Java
- Java JDOM2 Tutorial with Examples
- Java XStream Tutorial with Examples
- Jsoup Java Html Parser Tutorial with Examples
- Retrieve Geographic information based on IP Address using GeoIP2 Java API
- Read and Write Excel file in Java using Apache POI
- Explore the Facebook Graph API
- Java Sejda WebP ImageIO convert Images to WEBP
- Java JAVE Convert audio and video to mp3
Show More