Python Loops Tutorial with Examples
1. Overview of the loops in Python
In Python, statements are executed sequentially from top to bottom. However, when you want to execute a sequence of statements multiple times, you can use loop.
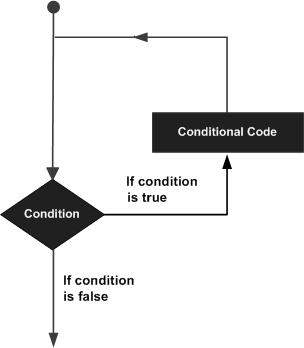
Python provides you with 2 types of loops:
- while loop
- for loop
Statements are associated with the loop
- else
Statements can be used within a loop:
- continue
- break
- pass
Control Statement | Description |
break | Terminates the loop statement. |
continue | Causes the loop to skip the remainder of its body and immediately retest its condition prior to reiterating. |
pass | The pass statement in the loop is simply a mark, prompting you to add some code in the future. It is a null statement (Do nothing). |
2. while loop
No ADS
The syntax of a while loop:
while (condition) :
# Do something here
# ....Example:
whileLoopExample.py
print("While loop example");
# Declare a variable, and assign value of 2.
x = 2;
# Condition is x < 10
# If x < 10 is true then run block
while (x < 10) :
print("Value of x = ", x);
x = x + 3;
# This statment is outside of while block.
print("Finish");Running the example:
While loop example
Value of x = 2
Value of x = 5
Value of x = 8
Finish3. for loop with range
The simplest example of a for loop in Python is to use 'for' with 'range'. For example, the variable 'x' has a value that runs within the scope (3, 7) (x = 3, 4, 5, 6).
forLoopExample.py
print("For loop example");
# for x = 3, 4, 5, 6
for x in range (3, 7) :
print("Value of x = ", x);
print(" x^2 = ", x * x);
# This statment is outside of for block.
print("End of example");Running the example:
For loop example
Value of x = 3
x^2 = 9
Value of x = 4
x^2 = 16
Value of x = 5
x^2 = 25
Value of x = 6
x^2 = 36
End of example4. Use for loop and array
No ADS
Using the for loop can help you traverse on the elements of the array.
forLoopExample3.py
print("For loop example");
# Declare an array.
names =["Tom","Jerry", "Donald"];
for name in names:
print("Name = ", name);
print("End of example");Output:
For loop example
Name = Tom
Name = Jerry
Name = Donald
End of exampleTraverse elements of the array through index:
forLoopExample3b.py
print("For loop example");
# Declare an array.
names =["Tom","Jerry", "Donald"];
# len() function return length of array.
# index = 0,1,.. len-1
for index in range(len(names)):
print("Name = ", names[index] );
print("End of example");5. Use the break statement in the loop
break is a statement that may be located in a loop. This statement ends the loop unconditionally.
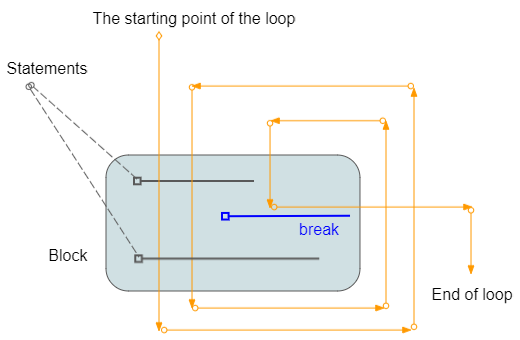
loopBreakExample.py
print("Break example");
# Declare a variable and assign value of 2.
x = 2;
while (x < 15) :
print("----------------------\n");
print("x = ", x);
# If x = 5 then exit the loop.
if (x == 5) :
break;
# Increase value of x by 1
x = x + 1;
print("x after + 1 = ", x);
print("End of example");Output:
Beak example
----------------------
x = 2
x after + 1 = 3
----------------------
x = 3
x after + 1 = 4
----------------------
x = 4
x after + 1 = 5
----------------------
x = 5
End of example6. Use the continue statement in the loop
No ADS
continue is a statement which may be located in a loop. When caught the continue statement, the program will ignore the command lines in block, below of continue and start of a new loop.
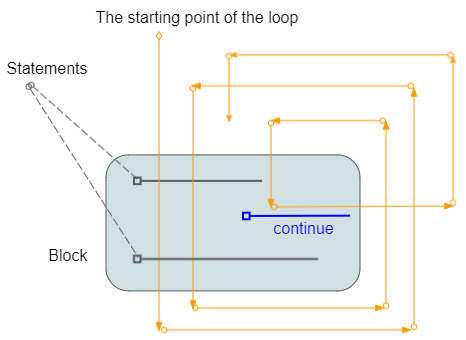
loopContinueExample.py
print("Continue example");
# Declare a variable and assign value of 2
x = 2
while (x < 7) :
print("----------------------\n")
print("x = ", x)
# % is used for calculating remainder
# If x is even, then ignore the command line below of continue
# and start new iteration.
if (x % 2 == 0) :
# Increase x by 1.
x = x + 1
continue
else :
# Increase x by 1.
x = x + 1
print("x after + 1 =", x)
print("End of example");Output:
Continue example
----------------------
x = 2
----------------------
x = 3
x after + 1 = 4
----------------------
x = 4
----------------------
x = 5
x after + 1 = 6
----------------------
x = 6
End of example7. Use the pass statement in the loop
In Python programming, pass is a null statement. The difference between a comment and pass statement in Python is that, while the interpreter ignores a comment entirely, pass is not ignored.
However, nothing happens when pass is executed
However, nothing happens when pass is executed
The pass statement in the loop is simply a mark, prompting you to add some code in the future. It is a null command (Nothing).
loopPassExample.py
number = 0
for number in range(5):
number = number + 1
if number == 3:
print(" do something here " , number)
pass
print(" >> " ,number )
print('Out of loop')Running the example:
>> 1
>> 2
do somthing here 3
>> 3
>> 4
>> 5
Out of loopYou can remove the pass statement in the example without changing anything.
loopPassExample.py (Remove pass statement)
number = 0
for number in range(5):
number = number + 1
if number == 3:
print(" do something here " , number)
# pass (Remove pass)
print(" >> " ,number )
print('Out of loop')8. Use the 'else' statement with a loop
No ADS
The else statement can be associated with a loop. The else statement is executed if the loop runs and ends in normal way, not broken by the break statement.
forLoopElseExample.py
print("For loop example");
# for x = 3, 4, 5, 6
for x in range (3, 7) :
print("Value of x = ", x);
print(" x^2 = ", x * x);
else :
print("finish for loop")
# This statment is outside of for block.
print("End of example");Output:
For loop example
Value of x = 3
x^2 = 9
Value of x = 4
x^2 = 16
Value of x = 5
x^2 = 25
Value of x = 6
x^2 = 36
finish for loop
End of exampleIf the loop is stopped by the break statement, the else statement is associated with the loop will not be executed.
forLoopElseExample2.py
print("For loop example");
# for x = 3, 4, 5, 6
for x in range (3, 7) :
print("Value of x = ", x);
if x == 5:
print("Break!")
break;
else :
# If the break statement has been called in the loop,
# this statement will not be executed.
print("This command will not be executed!")
# This statment is outside of for block.
print("End of example");Output:
For loop example
Value of x = 3
Value of x = 4
Value of x = 5
Break!
End of exampleNo ADS
Python Programming Tutorials
- Lookup Python documentation
- Branching statements in Python
- Python Function Tutorial with Examples
- Class and Object in Python
- Inheritance and polymorphism in Python
- Python Dictionary Tutorial with Examples
- Python Lists Tutorial with Examples
- Python Tuples Tutorial with Examples
- Python Date Time Tutorial with Examples
- Connect to MySQL Database in Python using PyMySQL
- Python exception handling Tutorial with Examples
- Python String Tutorial with Examples
- Introduction to Python
- Install Python on Windows
- Install Python on Ubuntu
- Install PyDev for Eclipse
- Conventions and Grammar versions in Python
- Python Tutorial for Beginners
- Python Loops Tutorial with Examples
Show More