Get the values of the columns automatically increment when Insert a record using JDBC
1. Problem
No ADS
In some databases, the ID column of a table can be of type of which values automatically increase. Whenever you insert a record into a table, the value of this column is assigned by the database. You can not proactively assign a value to it. Your question in this case is how to obtain the ID of the inserted record.
In addition, some columns may not be invoilved in your Insert statement, in which case their values are assigned by default by a database. You want to get these values without creating a more query statement.
PostGres
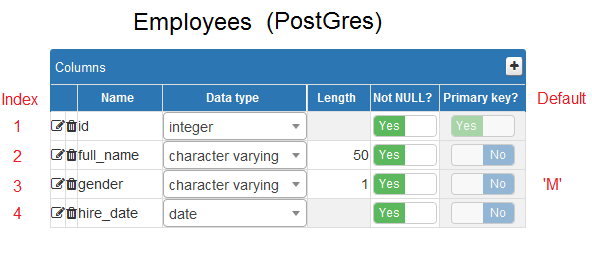
In PostGres, the column with Serial type will have values automatically increasing by database.
** Employees (PostGres) **
CREATE TABLE Employees
(
ID serial NOT NULL,
Full_Name character varying(50) NOT NULL,
Gender character varying(1) default 'M' NOT NULL,
Hire_Date date NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (ID)
);
MySQL
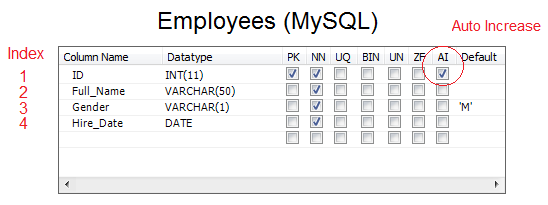
In MySQL, for a column to have automatically increasing value, it must be assigned the "Auto_Increase" attribute.
** Employees (MySQL) **
CREATE TABLE Employees
(
ID Int Auto_Increase NOT NULL,
Full_Name Varchar(50) NOT NULL,
Gender Varchar(1) default 'M' NOT NULL,
Hire_Date date NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (ID)
);
2. Get the value of ID column inserted
No ADS
When you use JDBC toInsert a recordto thedatabase. The ID column can not be involved in the Insert statement. The position of ID column is defined by the design of such table. The first column has index 1 and the second column has index 2,...
GeneratedIDValueExample.java
package org.o7planning.tutorial.jdbc.others;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.Statement;
import org.o7planning.tutorial.jdbc.ConnectionUtils;
public class GeneratedIDValueExample {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, SQLException {
// Get a connection
Connection conn = ConnectionUtils.getMyConnection();
// Employees (id, full_name, gender, hire_date)
// ID: Auto Increase
String sql = "Insert into Employees " //
+ " (full_name, gender, hire_date) " //
+ " values " //
+ " (?, ?, ?)";
// Create a PreparedStatement object.
PreparedStatement pstm = conn.prepareStatement(sql, Statement.RETURN_GENERATED_KEYS);
pstm.setString(1, "Tran");
pstm.setString(2, "M");
pstm.setDate(3, new java.sql.Date(System.currentTimeMillis()));
// Execute!
pstm.execute();
ResultSet rs = pstm.getGeneratedKeys();
int idValue = 0;
if (rs.next()) {
// Value of ID (Index 1 by table design).
idValue = rs.getInt(1);
}
System.out.println("ID value: " + idValue);
}
}The index of the ID column of the table isn't probably 1 (depending on the design of the table). In this case, you best access its value by name.
GeneratedIDValueExample2.java
package org.o7planning.tutorial.jdbc.others;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.Statement;
import org.o7planning.tutorial.jdbc.ConnectionUtils;
public class GeneratedIDValueExample2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, SQLException {
Connection conn = ConnectionUtils.getMyConnection();
// Employees (id, full_name, gender, hire_date)
// ID: Auto Increase
String sql = "Insert into Employees " //
+ " (full_name, gender, hire_date) " //
+ " values " //
+ " (?, ?, ?)";
// Create a PreparedStatement object.
PreparedStatement pstm = conn.prepareStatement(sql, Statement.RETURN_GENERATED_KEYS);
pstm.setString(1, "Tran");
pstm.setString(2, "M");
pstm.setDate(3, new java.sql.Date(System.currentTimeMillis()));
// Execute!
pstm.execute();
ResultSet rs = pstm.getGeneratedKeys();
int idValue = 0;
if (rs.next()) {
// Value of ID.
// Note, for some DB, column names are case sensitive.
// (eg Postgres, column names are always lowercase).
idValue = rs.getInt("id");
}
System.out.println("ID value: " + idValue);
}
}3. Get the values of many columns inserted
Some columns may not participate in your Insert statement . Their values are assigned by the database. You can get their values without creating a query statement.
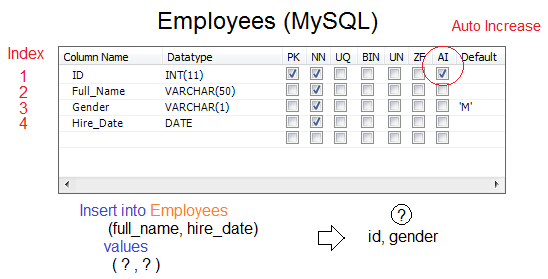
GetGeneratedValueExample2.java
package org.o7planning.tutorial.jdbc.others;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import org.o7planning.tutorial.jdbc.ConnectionUtils;
public class GetGeneratedValueExample2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, SQLException {
Connection conn = ConnectionUtils.getMyConnection();
// Employees (id, full_name, gender, hire_date)
// ID: Auto Increase
// gender: Default
String sql = "Insert into Employees " //
+ " (Full_Name, Hire_Date) " //
+ " values " //
+ " (?, ?)";
// Create a PreparedStatement object.
// And register the output parameters by name ("id", "gender", "hire_date")
PreparedStatement pstm = conn.prepareStatement(sql, new String[] { "id", "gender", "hire_date" });
pstm.setString(1, "Tran");
pstm.setDate(2, new java.sql.Date(System.currentTimeMillis()));
// Execute!
pstm.execute();
ResultSet rs = pstm.getGeneratedKeys();
int idValue = 0;
String gender = null;
java.sql.Date hireDate = null;
if (rs.next()) {
idValue = rs.getInt("ID");
gender = rs.getString("Gender");
hireDate = rs.getDate("Hire_Date");
}
System.out.println("ID value: " + idValue + " Gender: " + gender + ", Hidedate: " + hireDate);
}
}No ADS
Java Basic
- Data Types in java
- Java PhantomReference Tutorial with Examples
- JDK Javadoc in CHM format
- Java Stream Tutorial with Examples
- Java Predicate Tutorial with Examples
- Java BiConsumer Tutorial with Examples
- Arrays in Java
- JDBC Driver Libraries for different types of database in Java
- Abstract class and Interface in Java
- Java Commons Email Tutorial with Examples
- Install Eclipse
- Bitwise Operations
- Install Eclipse on Ubuntu
- Configuring Eclipse to use the JDK instead of JRE
- Java Commons Logging Tutorial with Examples
- Java Enums Tutorial with Examples
- Loops in Java
- Java Regular Expressions Tutorial with Examples
- Install Java on Ubuntu
- Quick Learning Java for beginners
- Install Java on Windows
- Comparing and Sorting in Java
- Inheritance and polymorphism in Java
- Java Consumer Tutorial with Examples
- Java String, StringBuffer and StringBuilder Tutorial with Examples
- Java Exception Handling Tutorial with Examples
- Example of Java encoding and decoding using Apache Base64
- if else statement in java
- Switch Statement in Java
- Java Supplier Tutorial with Examples
- Java Programming for team using Eclipse and SVN
- Java JDBC Tutorial with Examples
- Java remote method invocation - Java RMI Tutorial with Examples
- Java Multithreading Programming Tutorial with Examples
- Customize java compiler processing your Annotation (Annotation Processing Tool)
- What is needed to get started with Java?
- Java Aspect Oriented Programming with AspectJ (AOP)
- Understanding Java System.identityHashCode, Object.hashCode and Object.equals
- Java Compression and Decompression Tutorial with Examples
- Java Reflection Tutorial with Examples
- Install OpenJDK on Ubuntu
- Java String.format() and printf() methods
- History of Java and the difference between Oracle JDK and OpenJDK
- Introduction to the Raspberry Pi
- Java Socket Programming Tutorial with Examples
- Java Generics Tutorial with Examples
- Manipulating files and directories in Java
- Java WeakReference Tutorial with Examples
- Java Commons IO Tutorial with Examples
- History of bits and bytes in computer science
- Which Platform Should You Choose for Developing Java Desktop Applications?
- Java SoftReference Tutorial with Examples
- Syntax and new features in Java 8
- Java Annotations Tutorial with Examples
- Java Function Tutorial with Examples
- Access modifiers in Java
- Java BiFunction Tutorial with Examples
- Get the values of the columns automatically increment when Insert a record using JDBC
- Java Functional Interface Tutorial with Examples
- Java BiPredicate Tutorial with Examples
Show More
- Java Servlet/Jsp Tutorials
- Java Collections Framework Tutorials
- Java API for HTML & XML
- Java IO Tutorials
- Java Date Time Tutorials
- Spring Boot Tutorials
- Maven Tutorials
- Gradle Tutorials
- Java Web Services Tutorials
- Java SWT Tutorials
- JavaFX Tutorials
- Java Oracle ADF Tutorials
- Struts2 Framework Tutorials
- Spring Cloud Tutorials