NodeJS EventEmitter Tutorial with Examples
1. NodeJS EventEmitter
var fs = require('fs');
// Create a stream to read file
var rs = fs.createReadStream('C:/test/demo.txt');
// The event 'open':
rs.on('open', function() {
console.log('File opened!');
});
2. Example of EventEmitter
// Import events module
var events = require('events');
// Create an EventEmitter object
var eventEmitter = new events.EventEmitter();// Add Event Listener
eventEmitter.addListener('bellRing', bellRingHandler1);
// Add Event Listener
eventEmitter.addListener('bellRing', bellRingHandler2);// Fire bellRing event!!
eventEmitter.emit('bellRing', 'Jerry');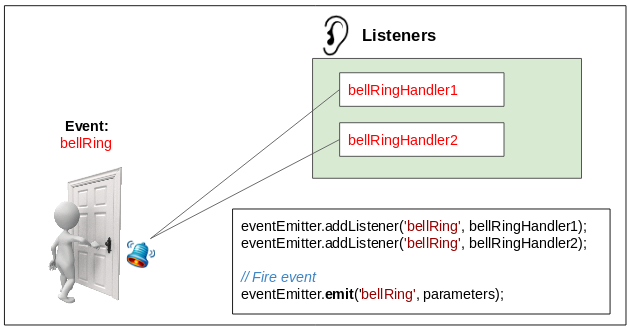
// Import events module
var events = require('events');
// Create an eventEmitter object
var eventEmitter = new events.EventEmitter();
// A Listener
var bellRingHandler1 = function bellRingHandler1(who) {
console.log("\n");
console.log('The Bell Ringing..... (Handler 1)');
console.log(" " + who + " was standing behind the door!");
if(who == 'Jerry') {
console.log(' Tom, help me!!');
return;
}
console.log(" Welcome " + who);
}
// A Listener
var bellRingHandler2 = function bellRingHandler2(who) {
console.log("\n");
console.log('The Bell Ringing..... (Handler 2)');
eventEmitter.emit("nobodyIsAtHome");
}
// A Listener
var nobodyIsAtHomeHandler = function nobodyIsAtHomeHandler() {
console.log("\n");
console.log(" Sorry, Nobody is at home now, Please leave your message!")
}
// Add Event Listeners
eventEmitter.addListener('bellRing', bellRingHandler1);
eventEmitter.addListener('bellRing', bellRingHandler2);
eventEmitter.addListener('nobodyIsAtHome', nobodyIsAtHomeHandler);
// ----- Testing ------
// Fire bellRing event!!
eventEmitter.emit('bellRing', 'Jerry');node eventemitter-examples/first-example.js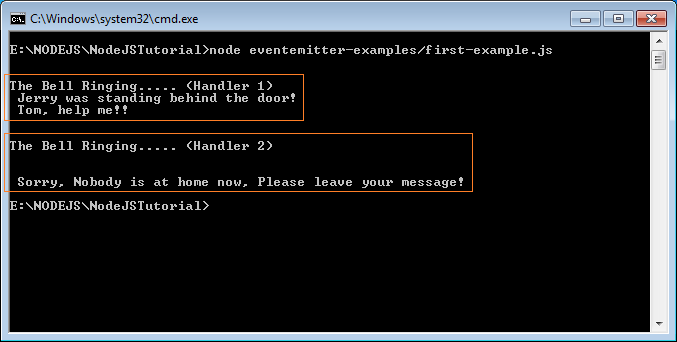
3. EventEmitter Class
No | Method | Description |
1 | addListener(event, listener) | Add a listener the end of the listeners array forthe specified event. This method doesn't check whether this listener has ever been added or not. |
2 | on(event, listener) | Exactly, this method is 100% identical to the addListener method. |
3 | once(event, listener) | Add a listener to the listeners array of the specified event. But this listener is only called one time when an event happens. After that it is removed from the array. |
4 | removeListener(event, listener) | Remove a listener from the listeners array of the specified event. If a listener has been added to this array many times. To remove this listener fully, you need to call this method many times. |
5 | removeAllListeners([event]) | Remove all listeners, or remove all listeners of an event designated. |
6 | setMaxListeners(n) | By default, EventEmitters will print a warning if more than 10 listeners are added for a particular event. This is a useful default which helps finding memory leaks. Obviously not all Emitters should be limited to 10. You can set a different number, or set to zero for unlimited. |
7 | listeners(event) | Return a listeners array to the specified event. |
8 | emit(event, [arg1], [arg2], [...]) | Executes each listener in the array in turn, with parameters. Return true if the array has at least one listener. On the contrary, return false. |
NodeJS Tutorials
- Introduction to NodeJs
- What is NPM?
- NodeJS Tutorial for Beginners
- Install Atom Editor
- Install NodeJS on Windows
- NodeJS Modules Tutorial with Examples
- The concept of Callback in NodeJS
- Create a Simple HTTP Server with NodeJS
- Understanding Event Loop in NodeJS
- NodeJS EventEmitter Tutorial with Examples
- Connect to MySQL database in NodeJS