Bootstrap Scrollspy Tutorial with Examples
1. Bootstrap Scrollspy
No ADS
Before giving a definition of Scrollspy, please observe a following Scrollspy:
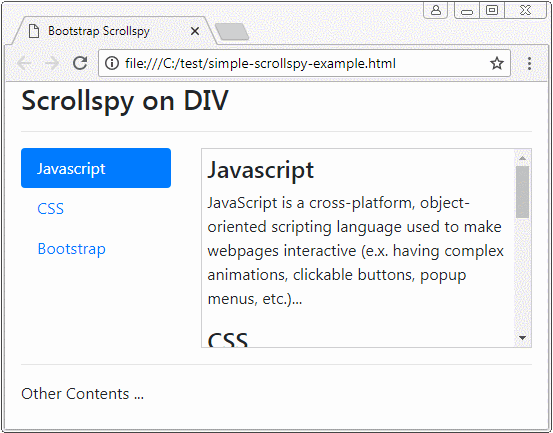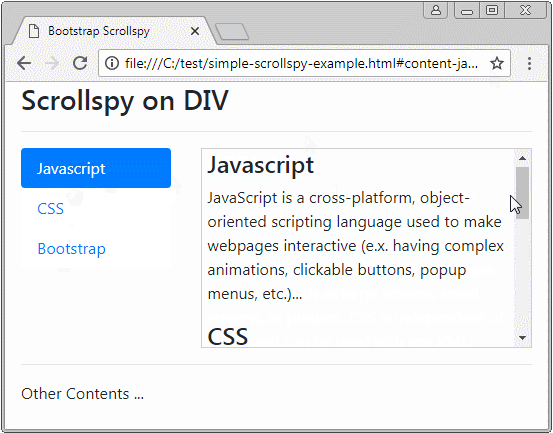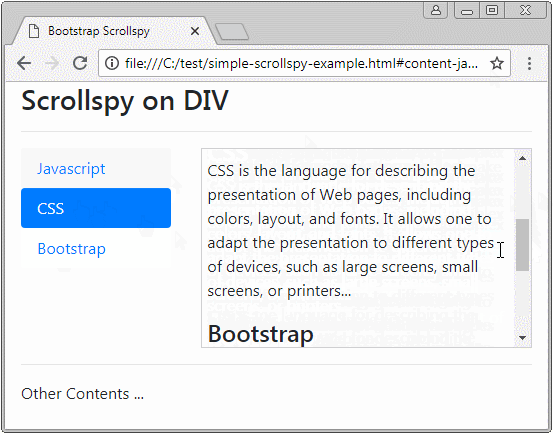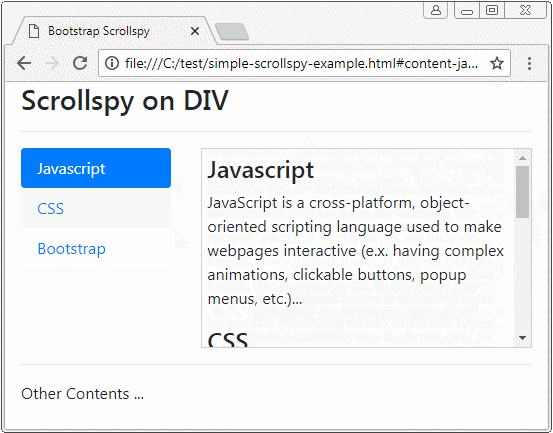
Scrollspy, in accordance wth its name, means Scroll + Spy. Scrollspy operates based on 2 components:
- The first component is a Nav (or List-Group).
- The second component is a scrollable content area, which may be <body> or <div>,<span>,.... If the content area is not a <body>, it needs establishing height and overflow-y: scroll.
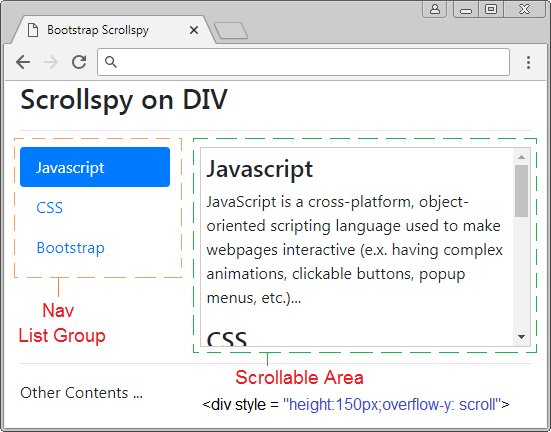
Principles of operation:
- In component 1, users clicks on an Item of Nav (or List-Group),the scroll bar on the component 2 will work to display the right content corresponding to the Item clicked by users.
- In component 2, when users drag the scroll bar, the item of component 1, corresponding to the displayed content shall be activated.
simple-scrollspy-example.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>Bootstrap Scrollspy</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="https://stackpath.bootstrapcdn.com/bootstrap/4.1.1/css/bootstrap.min.css">
</head>
<body>
<div class="container-fluid">
<h3>Scrollspy on DIV</h3>
<hr>
<div class="row">
<div class="col-4">
<nav id="myScrollspy">
<ul class="nav nav-pills flex-column">
<li class="nav-item"><a class="nav-link" href="#content-javascript">Javascript</a></li>
<li class="nav-item"><a class="nav-link" href="#content-css">CSS</a></li>
<li class="nav-item"><a class="nav-link" href="#content-bootstrap">Bootstrap</a></li>
</ul>
</nav>
</div>
<div class="col-8">
<div data-spy="scroll" data-target="#myScrollspy" data-offset="10"
style="height:200px;overflow-y: scroll;padding:5px; border: 1px solid #ccc;">
<h4 id="content-javascript">Javascript</h4>
<p>
JavaScript is a cross-platform, object-oriented scripting language used to make webpages interactive
(e.x. having complex animations, clickable buttons, popup menus, etc.)...
</p>
<h4 id="content-css">CSS</h4>
<p>
CSS is the language for describing the presentation of Web pages, including colors,
layout, and fonts. It allows one to adapt the presentation to different types of devices,
such as large screens, small screens, or printers...
</p>
<h4 id="content-bootstrap">Bootstrap</h4>
<p>
CSS is the language for describing the presentation of Web pages, including colors,
layout, and fonts. It allows one to adapt the presentation to different types of devices,
such as large screens, small screens, or printers. CSS is independent of HTML
and can be used with any XML-based markup language...
</p>
</div>
</div>
</div>
<hr>
Other Contents ...
</div>
<script src="https://code.jquery.com/jquery-3.3.1.slim.min.js"></script>
<script src="https://cdnjs.cloudflare.com/ajax/libs/popper.js/1.14.3/umd/popper.min.js"></script>
<script src="https://stackpath.bootstrapcdn.com/bootstrap/4.1.1/js/bootstrap.min.js"></script>
</body>
</html>See Also:
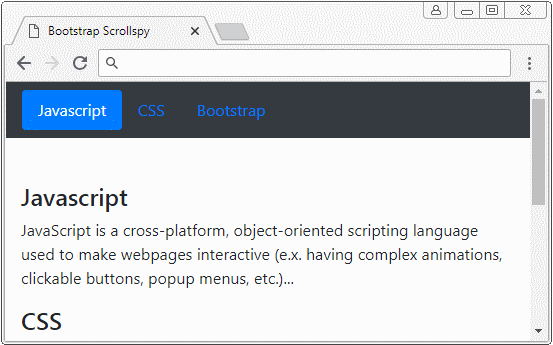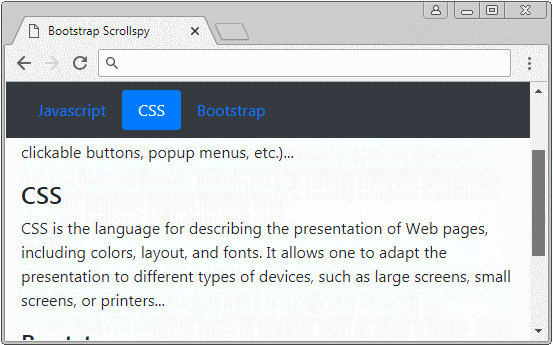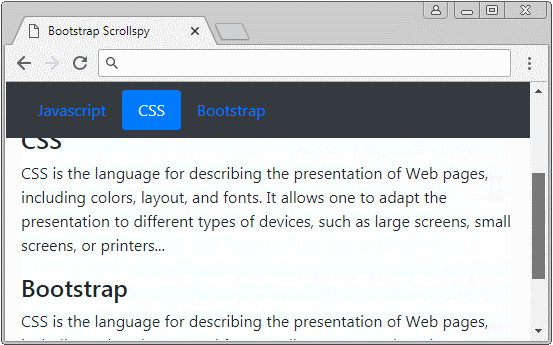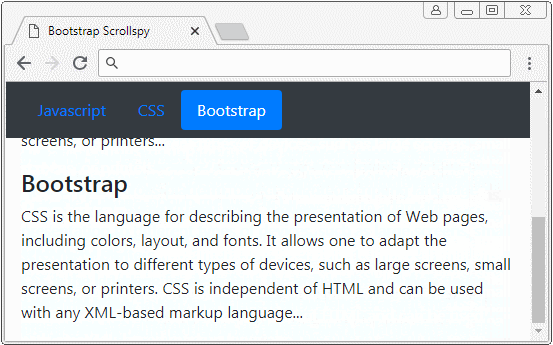
2. Scrollspy + BODY
In this example, I will create a Scrollspy to "spy" the content on <body>. It is noted that the default <body> has vertical scrollbar, which is the scrollbar of the browser. Below is the illustration of structure of this example:
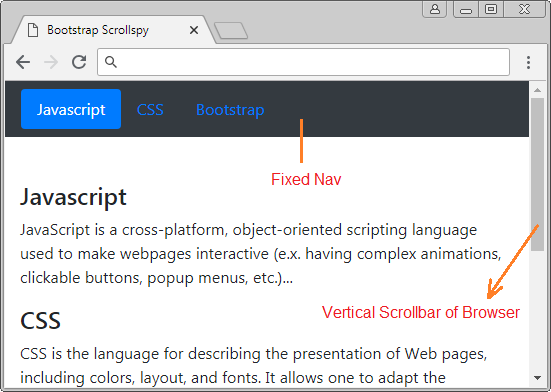
body-scrollspy-example.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>Bootstrap Scrollspy</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="https://stackpath.bootstrapcdn.com/bootstrap/4.1.1/css/bootstrap.min.css">
</head>
<body data-spy="scroll" data-target="#scrollspy-nav" data-offset="110">
<div class="container-fluid">
<nav id="scrollspy-nav" class="navbar bg-dark fixed-top">
<ul class="nav nav-pills">
<li class="nav-item"><a class="nav-link" href="#content-javascript">Javascript</a></li>
<li class="nav-item"><a class="nav-link" href="#content-css">CSS</a></li>
<li class="nav-item"><a class="nav-link" href="#content-bootstrap">Bootstrap</a></li>
</ul>
</nav>
<div style="margin-top:100px;">
<h4 id="content-javascript">Javascript</h4>
<p>
JavaScript is a cross-platform, object-oriented scripting language used to make webpages interactive
(e.x. having complex animations, clickable buttons, popup menus, etc.)...
</p>
<h4 id="content-css">CSS</h4>
<p>
CSS is the language for describing the presentation of Web pages, including colors,
layout, and fonts. It allows one to adapt the presentation to different types of devices,
such as large screens, small screens, or printers...
</p>
<h4 id="content-bootstrap">Bootstrap</h4>
<p>
CSS is the language for describing the presentation of Web pages, including colors,
layout, and fonts. It allows one to adapt the presentation to different types of devices,
such as large screens, small screens, or printers. CSS is independent of HTML
and can be used with any XML-based markup language...
</p>
</div>
</div>
<script src="https://code.jquery.com/jquery-3.3.1.slim.min.js"></script>
<script src="https://cdnjs.cloudflare.com/ajax/libs/popper.js/1.14.3/umd/popper.min.js"></script>
<script src="https://stackpath.bootstrapcdn.com/bootstrap/4.1.1/js/bootstrap.min.js"></script>
</body>
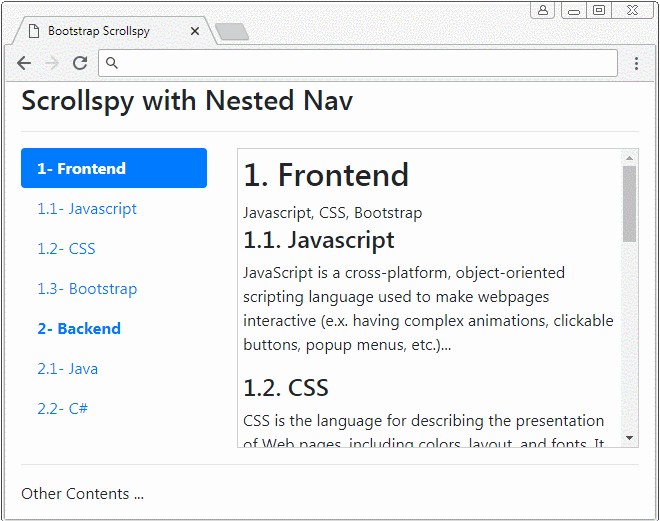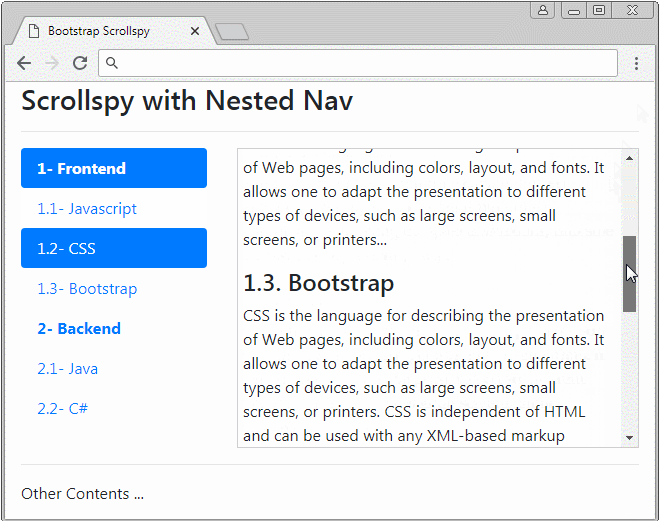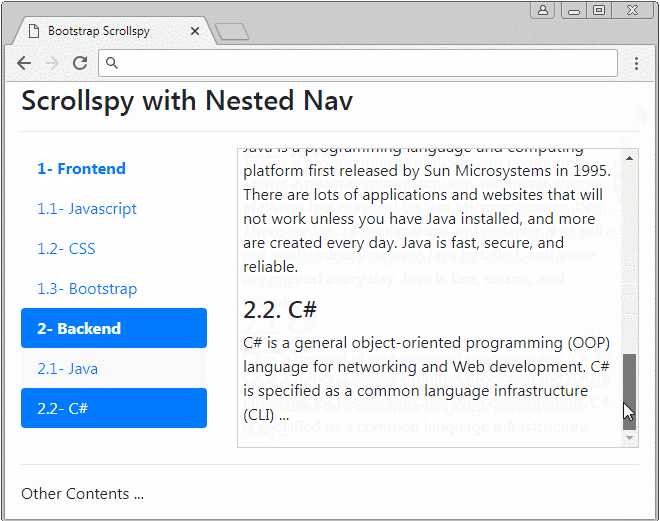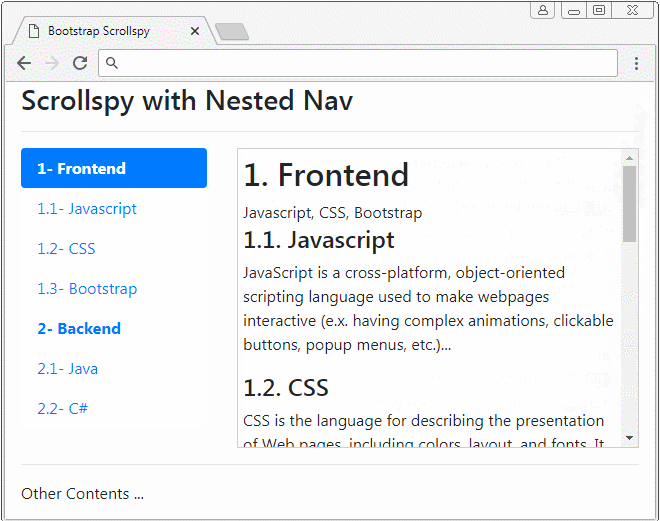
</html>3. Example of Nested Nav
No ADS
Scrollspy also works with Nested Navs. If a Nav is activated the father Nav is also activated.
nested-nav-scrollspy-example.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>Bootstrap Scrollspy</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="https://stackpath.bootstrapcdn.com/bootstrap/4.1.1/css/bootstrap.min.css">
</head>
<body>
<div class="container-fluid">
<h3>Scrollspy with Nested Navs</h3>
<hr>
<div class="row">
<div class="col-4">
<nav id="myScrollspy">
<ul class="nav nav-pills flex-column">
<li class="nav-item">
<a class="nav-link" href="#content-frontend">
<strong>1- Frontend</strong>
</a>
<ul class="nav nav-pills flex-column">
<li class="nav-item">
<a class="nav-link" href="#content-javascript"> 1.1- Javascript</a>
</li>
<li class="nav-item">
<a class="nav-link" href="#content-css"> 1.2- CSS</a>
</li>
<li class="nav-item">
<a class="nav-link" href="#content-bootstrap"> 1.3- Bootstrap</a>
</li>
</ul>
</li>
<li class="nav-item">
<a class="nav-link" href="#content-backend">
<strong>2- Backend</strong>
</a>
<ul class="nav nav-pills flex-column">
<li class="nav-item">
<a class="nav-link" href="#content-java"> 2.1- Java</a>
</li>
<li class="nav-item">
<a class="nav-link" href="#content-csharp"> 2.2- C#</a>
</li>
</ul>
</li>
</ul>
</nav>
</div>
<div class="col-8">
<div data-spy="scroll" data-target="#myScrollspy" data-offset="10"
style="height:300px;overflow-y: scroll;padding:5px; border: 1px solid #ccc;">
<h2 id="content-frontend">1. Frontend</h2>
Javascript, CSS, Bootstrap
<h4 id="content-javascript">1.1. Javascript</h4>
<p>
JavaScript is a cross-platform, object-oriented scripting language
used to make webpages interactive
(e.x. having complex animations, clickable buttons, popup menus, etc.)...
</p>
<h4 id="content-css">1.2. CSS</h4>
<p>
CSS is the language for describing the presentation of Web pages,
including colors, layout, and fonts.
It allows one to adapt the presentation to different types of devices,
such as large screens, small screens, or printers...
</p>
<h4 id="content-bootstrap">1.3. Bootstrap</h4>
<p>
CSS is the language for describing the presentation of Web pages,
including colors, layout, and fonts.
It allows one to adapt the presentation to different types of devices,
such as large screens, small screens, or printers. CSS is independent of HTML
and can be used with any XML-based markup language...
</p>
<h2 id="content-backend">2. Backend</h2>
Java, C#
<h4 id="content-java">2.1. Java</h4>
<p>
Java is a programming language and computing platform first released by Sun Microsystems in 1995.
There are lots of applications and websites that will not work unless you have Java installed,
and more are created every day. Java is fast, secure, and reliable.
</p>
<h4 id="content-csharp">2.2. C#</h4>
<p>
C# is a general object-oriented programming (OOP) language for networking and Web development.
C# is specified as a common language infrastructure (CLI) ...
</p>
</div>
</div>
</div>
<hr>
Other Contents ...
</div>
<script src="https://code.jquery.com/jquery-3.3.1.slim.min.js"></script>
<script src="https://cdnjs.cloudflare.com/ajax/libs/popper.js/1.14.3/umd/popper.min.js"></script>
<script src="https://stackpath.bootstrapcdn.com/bootstrap/4.1.1/js/bootstrap.min.js"></script>
</body>
</html>4. Example of List Group
Scrollspy also works with List Groups. Below is an example:
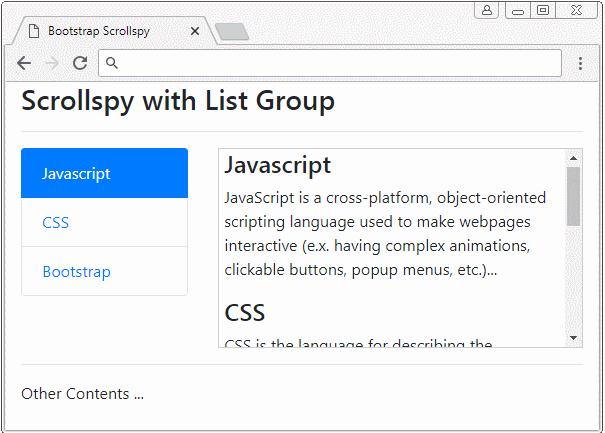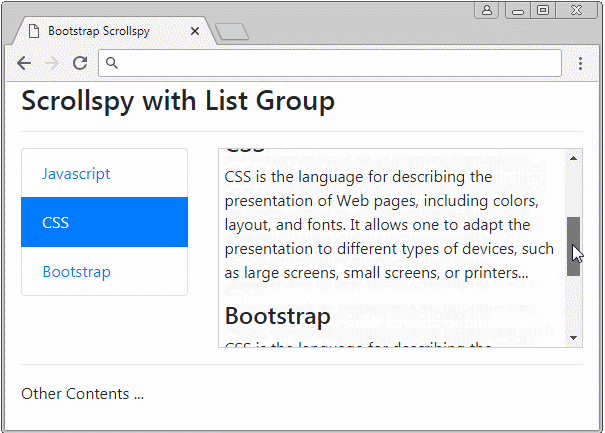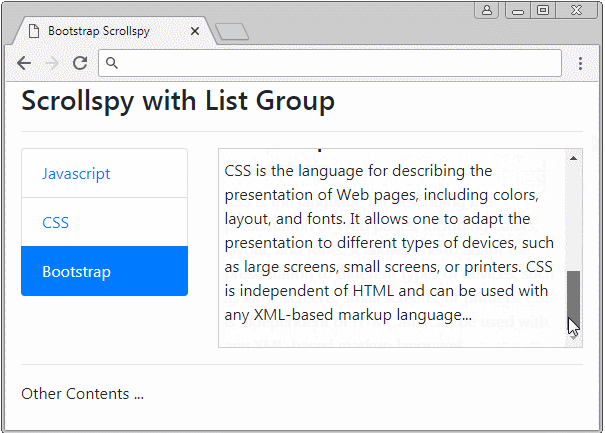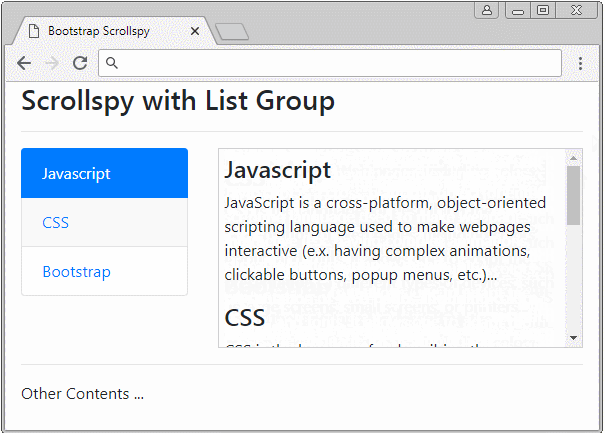
list-group-scrollspy-example.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>Bootstrap Scrollspy</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="https://stackpath.bootstrapcdn.com/bootstrap/4.1.1/css/bootstrap.min.css">
</head>
<body>
<div class="container-fluid">
<h3>Scrollspy with List Group</h3>
<hr>
<div class="row">
<div class="col-4">
<div class="list-group" id="myScrollspy">
<a class="list-group-item" href="#content-javascript">Javascript</a>
<a class="list-group-item" href="#content-css">CSS</a>
<a class="list-group-item" href="#content-bootstrap">Bootstrap</a>
</div>
</div>
<div class="col-8">
<div data-spy="scroll" data-target="#myScrollspy" data-offset="10"
style="height:200px;overflow-y: scroll;padding:5px; border: 1px solid #ccc;">
<h4 id="content-javascript">Javascript</h4>
<p>
JavaScript is a cross-platform, object-oriented scripting language used to make webpages interactive
(e.x. having complex animations, clickable buttons, popup menus, etc.)...
</p>
<h4 id="content-css">CSS</h4>
<p>
CSS is the language for describing the presentation of Web pages, including colors,
layout, and fonts. It allows one to adapt the presentation to different types of devices,
such as large screens, small screens, or printers...
</p>
<h4 id="content-bootstrap">Bootstrap</h4>
<p>
CSS is the language for describing the presentation of Web pages, including colors,
layout, and fonts. It allows one to adapt the presentation to different types of devices,
such as large screens, small screens, or printers. CSS is independent of HTML
and can be used with any XML-based markup language...
</p>
</div>
</div>
</div>
<hr>
Other Contents ...
</div>
<script src="https://code.jquery.com/jquery-3.3.1.slim.min.js"></script>
<script src="https://cdnjs.cloudflare.com/ajax/libs/popper.js/1.14.3/umd/popper.min.js"></script>
<script src="https://stackpath.bootstrapcdn.com/bootstrap/4.1.1/js/bootstrap.min.js"></script>
</body>
</html>No ADS
Bootstrap Tutorials
- Bootstrap Jumbotron Tutorial with Examples
- Bootstrap Dropdowns Tutorial with Examples
- Bootstrap Alerts Tutorial with Examples
- Bootstrap Buttons Tutorial with Examples
- Bootstrap Button Group Tutorial with Examples
- Bootstrap Popovers (Tooltips) Tutorial with Examples
- Bootstrap Spinners Tutorial with Examples
- Introduction to Bootstrap
- Bootstrap Grid System Tutorial with Examples
- Bootstrap Cards Tutorial with Examples
- Bootstrap Containers Tutorial with Examples
- Bootstrap Nav Tab/Pill Tutorial with Examples
- Bootstrap NavBars Tutorial with Examples
- Bootstrap Tables Tutorial with Examples
- Bootstrap Modal Tutorial with Examples
- Bootstrap Forms Tutorial with Examples
- Bootstrap Pagination Tutorial with Examples
- Bootstrap Badges Tutorial with Examples
- Bootstrap Input Group Tutorial with Examples
- Bootstrap List Groups Tutorial with Examples
- Bootstrap ProgressBars Tutorial with Examples
- Bootstrap Collapse and Accordion Tutorial with Examples
- Bootstrap Scrollspy Tutorial with Examples
- Bootstrap Breadcrumb Tutorial with Examples
- Bootstrap Carousel Tutorial with Examples
- Bootstrap Spacing Utilities Tutorial with Examples
- Bootstrap Border Utilities Tutorial with Examples
- Bootstrap Color Utilities Tutorial with Examples
- Bootstrap Text Utilities Tutorial with Examples
- Bootstrap Sizing Utilities Tutorial with Examples
- Bootstrap Position Utilities Tutorial with Examples
- Bootstrap Flex Utilities Tutorial with Examples
- Bootstrap Display Utilities Tutorial with Examples
- Bootstrap Visibility Utilities Tutorial with Examples
- Bootstrap Embed Utilities Tutorial with Examples
Show More