Javascript Form Validation Tutorial with Examples
1. Form Validation
No ADS
Quite regularly, you meet a website where users enter information into a form before sending it to the server, for example, the account registration form. The information that the user enters into the form needs to be validated to ensure data rationality.
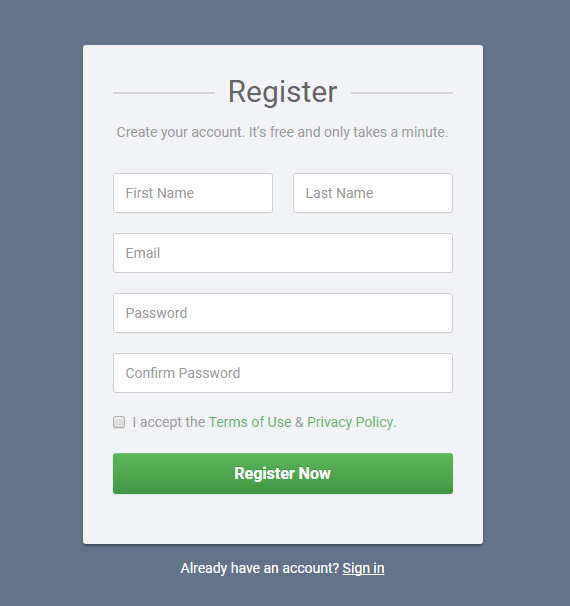
Some examples of authentication:
- Check to ensure that the data is not empty.
- Check email format
- Check telephone number format
- ..
There are basically 3 ways for data validation:
- form data will be sent to the server, and validation will be done on the server side.
- form data will be validated on the client side by using Javascript, which helps server not have to work too much and increase performance for the application.
- Use both above methods to validate form.
In this lesson, I will discuss using Javascript to validate form. Below is the illustration of the program's behavior when the user clicks the Submit button.
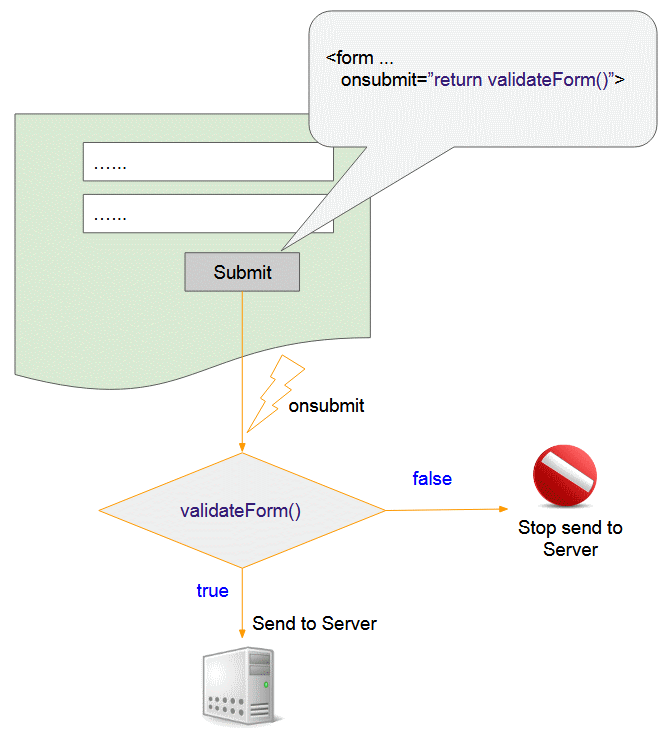
- You have to register a function in combination with the onsubmit event of form. The duty of this function is to check the data which an user has entered in form, and return true if all the information entered by the user is valid and vice versa return false.
- When the user clicks Submit, the function in combination with the onsubmit event will be called.
- Ifthe function in combination with the onsubmit event returns true, the data of form will be sent to the server and vice versa the Submit action will be cancelled.
2. Simple example
No ADS
OK, this is a simple example helping you understand the operating rules of Form before practising more complex examples.
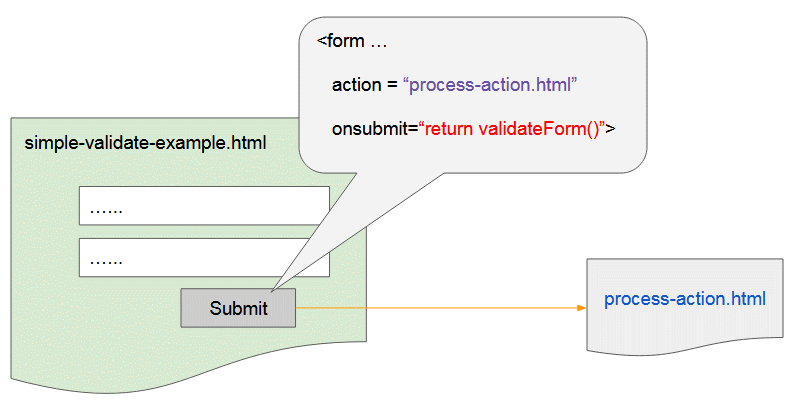
The action attribute of <form> is used to specify the page to which data will be given or in other words, this is the page that will process the data sent from the <form> of the current page.
The pages processing the data sent from form are usually written by Servlet/JSP, PHP technology or a technology on the Server side instead of an HTML page. However, I do not mention data processing in this lesson.
simple-validation-example.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Hello Javascript</title>
<script type = "text/javascript">
function validateForm() {
var u = document.getElementById("username").value;
var p = document.getElementById("password").value;
if(u== "") {
alert("Please enter your Username");
return false;
}
if(p == "") {
alert("Please enter you Password");
return false;
}
alert("All datas are valid!, send it to the server!")
return true;
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<h2>Enter your Username and Password</h2>
<div style="border:1px solid #ddd; padding: 5px;">
<form method="GET" action="process-action.html" onsubmit = "return validateForm()">
Username: <input type="text" name="username" id="username"/>
<br><br>
Password: <input type="password" name = "password" id="password"/>
<br><br>
<button type="submit">Submit</button>
</form>
</div>
</body>
</html>process-action.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Process Action</title>
</head>
<body>
<h3>Process Action Page</h3>
OK, I got data!
<br/><br/>
<a href="javascript:history.back();">[Go Back]</a>
</body>
</html>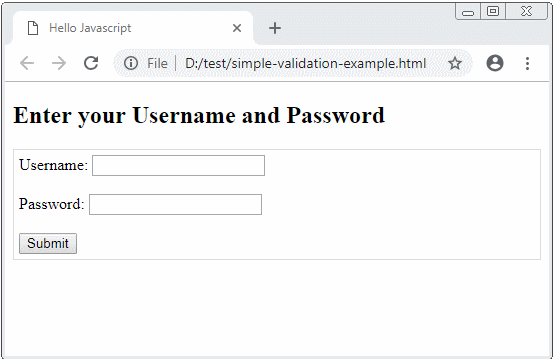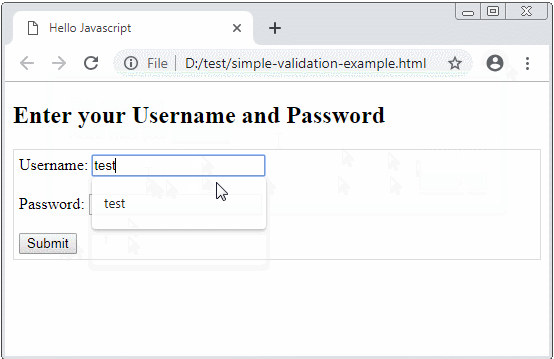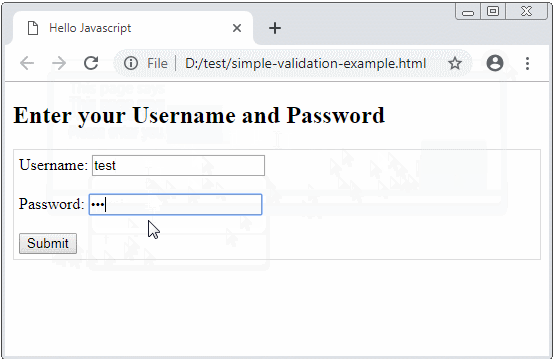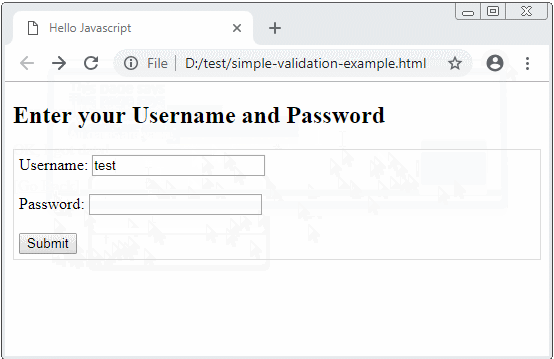
3. Access the form data
No ADS
Access a field data through the field ID.
<input type="text" id="username"/>
<input type="password" id="password"/>// Access field via ID:
var field = document.getElementById("fieldId");
var value = field.value;Access Form fields through the name attribute:
<form name="myForm" ...>
<input type="text" name="username"/>
<input type="password" name = "password"/>
<button type="submit">Submit</button>
</form>// Get form via form name:
var myForm = document.forms["myForm"];
var u = myForm["username"].value;
var p = myForm["password"].value;When a user enters inaccurate data on a form field, you should notify the user and focus on that field.
validation-example1.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Validation</title>
<script type = "text/javascript">
function validateForm() {
// Get form via form name:
var myForm = document.forms["myForm"];
var u = myForm["username"].value;
var p = myForm["password"].value;
if(u== "") {
alert("Please enter your Username");
myForm["username"].focus(); // Focus
return false;
}
if(p == "") {
alert("Please enter you Password");
myForm["password"].focus(); // Focus
return false;
}
alert("All datas are valid!, send it to the server!")
return true;
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<h2>Enter your Username and Password</h2>
<div style="border:1px solid #ddd; padding: 5px;">
<form name="myForm" method="GET" action="process-action.html" onsubmit = "return validateForm()">
Username: <input type="text" name="username"/>
<br><br>
Password: <input type="password" name = "password"/>
<br><br>
<button type="submit">Submit</button>
</form>
</div>
</body>
</html>Example: Ask an user to enter a number between 0 and 10.
validation-number-example.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Validation</title>
<script type = "text/javascript">
function validateForm() {
var myField = document.getElementById("myNumber");
var value = myField.value;
if( value == "" || isNaN(value) || value < 0 || value > 10) {
alert("Invalid input!");
myField.focus();
return false;
}
return true;
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<h2>Enter a Number between 0 and 10</h2>
<div style="border:1px solid #ddd; padding: 5px;">
<form name="myForm" action="process-action.html" onsubmit = "return validateForm()">
Number: <input type="text" id= "myNumber"/>
<br/><br/>
<button type="submit">Submit</button>
</form>
</div>
</body>
</html>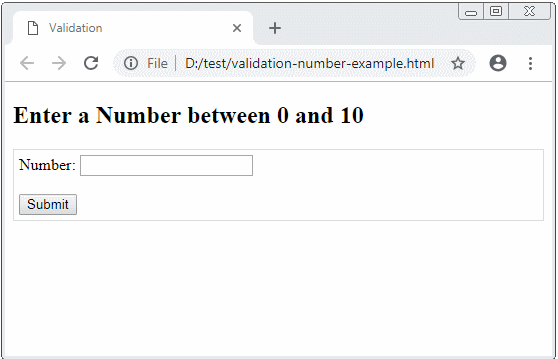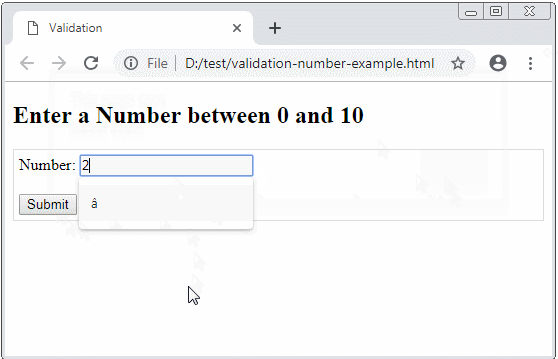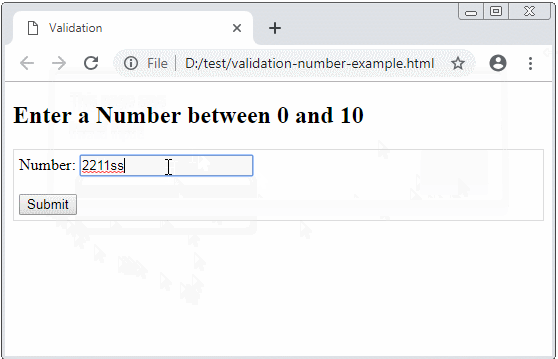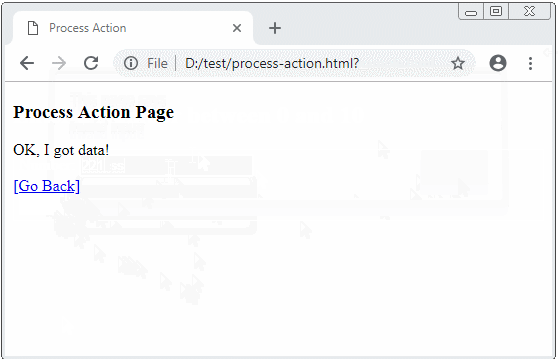
4. Submit through Javascript
Clicking <button type="submit"> or <input type="submit"> inside form helps you to send the data of this form to the server, however, you can also do it through Javascript.
javascript-submit-example.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Javascript Submit</title>
<script type = "text/javascript">
function validateForm() {
var name = document.forms["myForm"]["fullName"].value;
if(name == "") {
alert("Please enter your name");
return false;
}
return true;
}
function submitByJavascript() {
var valid = validateForm();
if(!valid) {
return;
}
var myForm = document.forms["myForm"];
myForm.submit();
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<h2>Submit a from with Javascript</h2>
<div style="border:1px solid #ddd; padding: 5px;">
<form name="myForm" action="process-action.html" onsubmit = "return validateForm()">
Your Name: <input type="text" name = "fullName" value =""/>
<br/><br/>
<button type="submit">Submit</button>
</form>
</div>
<br/>
<!-- A Button outside the form -->
Button outside the form:
<button onclick="submitByJavascript()">Click Me to submit form</button>
</body>
</html>5. Validate automatically
No ADS
The browser can automatically validate several types of data on the form, such as adding a required attribute to a form field to tell the browser that this field is mandatory. The browser will automatically check and notify an user if an user does not enter that field.
Note: Too old browsers such as IE version 9 or older do not support automatic validate.
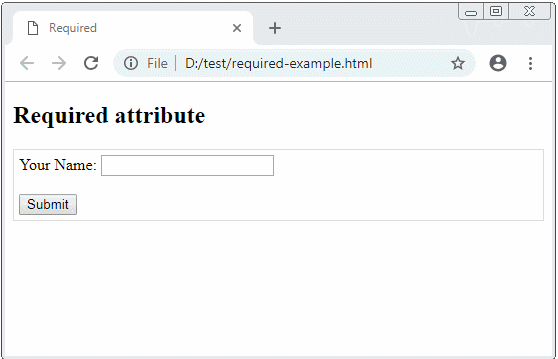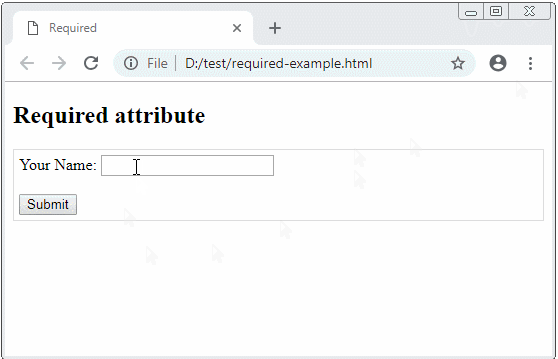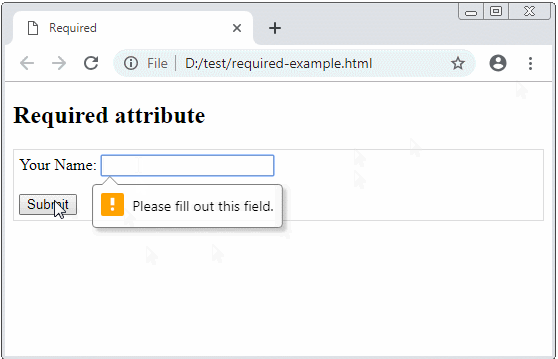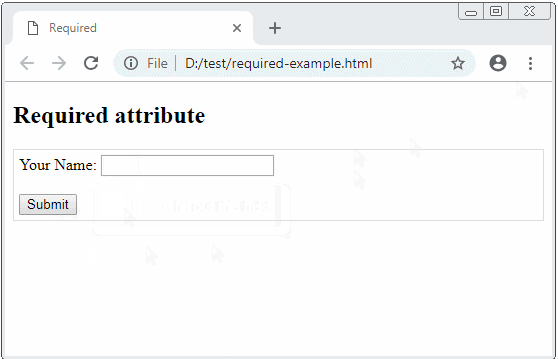
required-example.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Required</title>
</head>
<body>
<h2>Required attribute</h2>
<div style="border:1px solid #ddd; padding: 5px;">
<form name="myForm" action="process-action.html" onsubmit = "return validateForm()">
Your Name: <input type="text" name = "fullName" value ="" required/>
<br/><br/>
<button type="submit">Submit</button>
</form>
</div>
</body>
</html>Some <input> elements newly introduced in HTML 5, for example color, date, datetime-local, email, month, number, range, search, tel, time, url, week,. These elements have special attributes to help the browser to know how to validate its data automatically. Below is list of some such attributes:
Attribute | Description |
disabled | Specifies that the Input element should be disabled |
max | Specifies the maximum value of an Input element |
min | Specifies the minimum value of an Input element |
pattern | Specifies the value pattern of an Input element |
required | Specifies that the Input field requires an element |
type | Specifies the type of an Input element |
See the details of the list of <input> elements and attributes corresponding to each of these elements:
- HTML Input types
Example: A <input type="number"> with min, max attributes, the browser will notify an user if he/she enters a number beyond the allowed range.
attr-min-max-example.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Min Max Attributes</title>
</head>
<body>
<h2>Attribute min, max</h2>
<div style="border:1px solid #ddd; padding: 5px;">
<form name="myForm" action="process-action.html">
Enter your score (0-100):
<input type="number" name = "score" min= "0" max = "100"/>
<br/><br/>
<button type="submit">Submit</button>
</form>
</div>
</body>
</html>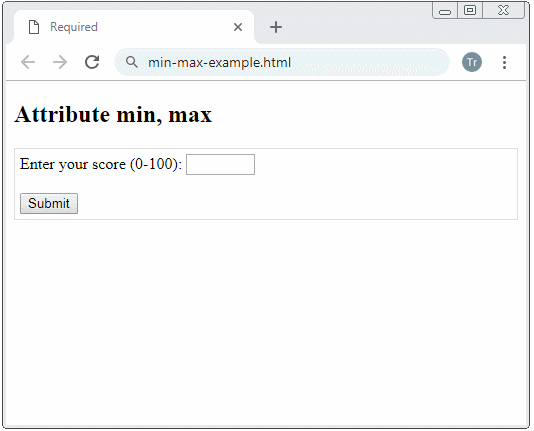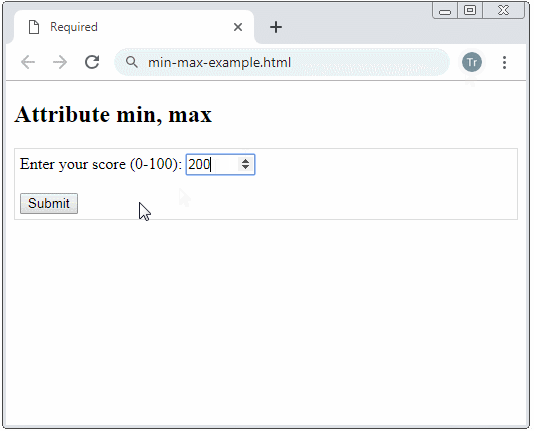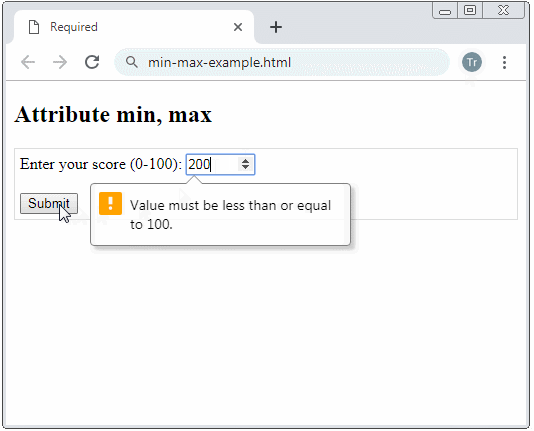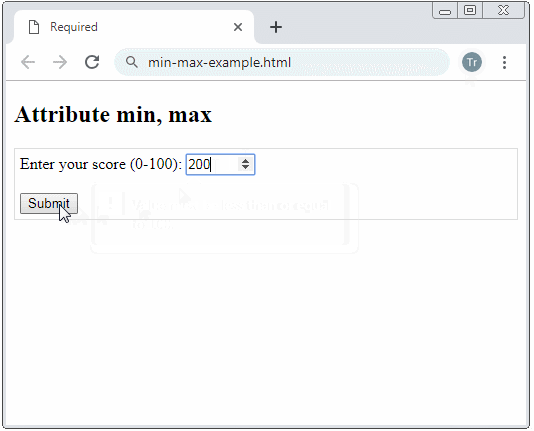
Example: Require an user to enter a country code with 2 characters.
attr-pattern-example.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>pattern attribute</title>
</head>
<body>
<h2>Attribute: pattern</h2>
<div style="border:1px solid #ddd; padding: 5px;">
<form name="myForm" action="process-action.html">
Country code:
<input type="text" name = "countryCode" pattern="[A-Za-z]{2}"
title="Two letter country code"/>
<br/><br/>
<button type="submit">Submit</button>
</form>
</div>
</body>
</html>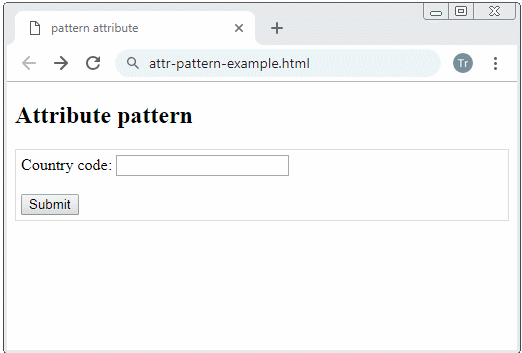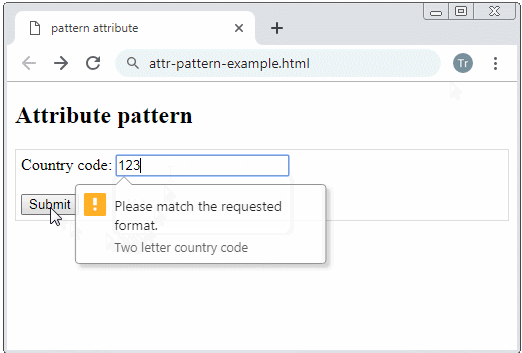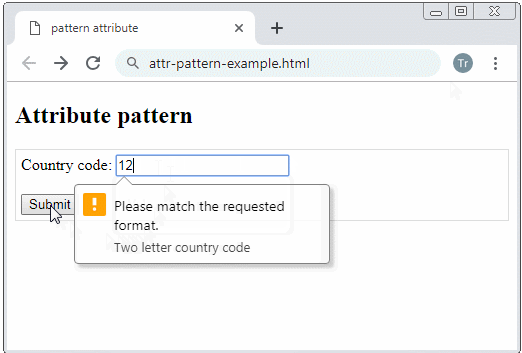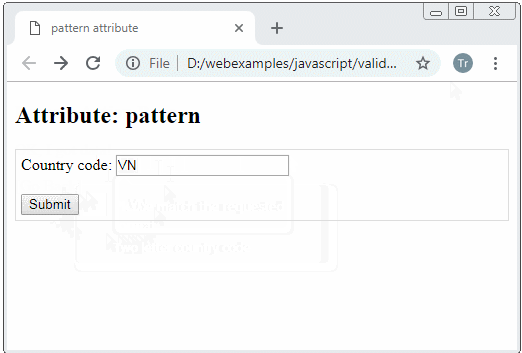
Example: Ask an user to enter a password having at least 8 characters.
attr-pattern-example2.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>pattern attribute</title>
</head>
<body>
<h2>Attribute: pattern</h2>
<div style="border:1px solid #ddd; padding: 5px;">
<form name="myForm" action="process-action.html">
Password:
<input type="password" name = "password" pattern=".{8,}"
title="8 or more characters"/>
<br/><br/>
<button type="submit">Submit</button>
</form>
</div>
</body>
</html>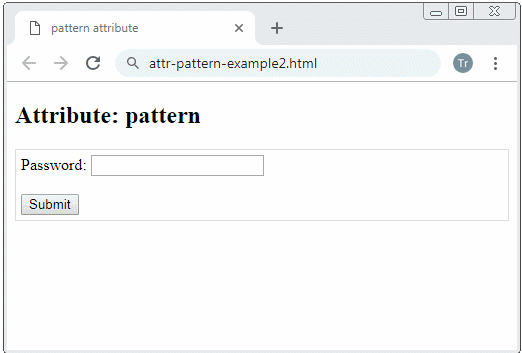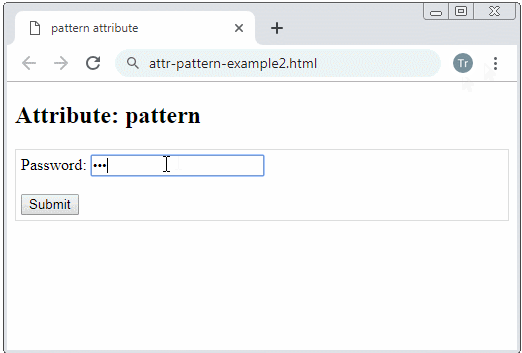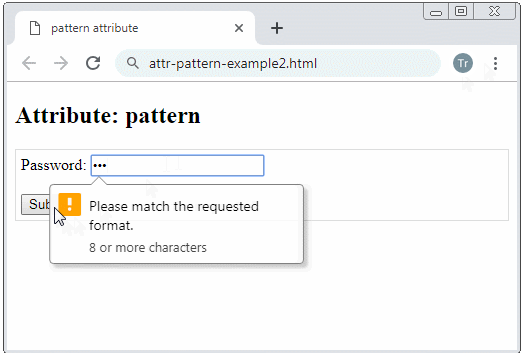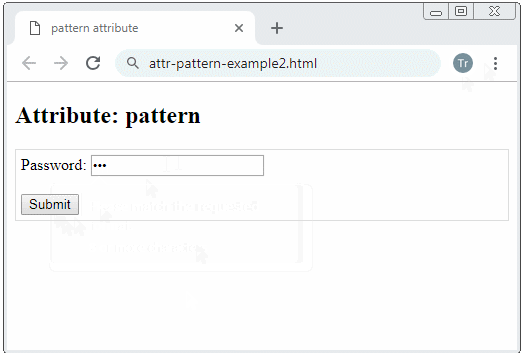
Example: Ask an user to enter a strong password, having at least 8 characters, at least one uppercase, and at least one lowercase.
attr-pattern-password-example.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>pattern attribute</title>
</head>
<body>
<h2>Attribute: pattern</h2>
Password must contain 8 or more characters that are of at least one number,
and one uppercase and lowercase letter:
<br/><br/>
<div style="border:1px solid #ddd; padding: 5px;">
<form name="myForm" action="process-action.html">
Password:
<input type="password" name = "password"
pattern="(?=.*\d)(?=.*[a-z])(?=.*[A-Z]).{8,}"
title="Invalid password!"/>
<br/><br/>
<button type="submit">Submit</button>
</form>
</div>
</body>
</html>Example: Ask an user to enter an email address, use the pattern attribute to ensure that the user enters an email in the correct format.
attr-pattern-email-example.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>pattern attribute</title>
</head>
<body>
<h2>Attribute: pattern</h2>
<div style="border:1px solid #ddd; padding: 5px;">
<form name="myForm" action="process-action.html">
Email:
<input type="password" name = "password"
pattern="[a-z0-9._%+-]+@[a-z0-9.-]+\.[a-z]{2,}$"
title="Invalid password!"/>
<br/><br/>
<button type="submit">Submit</button>
</form>
</div>
</body>
</html>No ADS
ECMAScript, Javascript Tutorials
- Javascript Screen Tutorial with Examples
- Javascript MouseEvent Tutorial with Examples
- Javascript XMLHttpRequest Tutorial with Examples
- JavaScript if else Statement Tutorial with Examples
- JavaScript Promise, Async/Await Tutorial with Examples
- Javascript History API Tutorial with Examples
- Javascript Menubar Tutorial with Examples
- Javascript Location Tutorial with Examples
- JavaScript Boolean Tutorial with Examples
- JavaScript setTimeout and setInterval Function
- Javascript FocusEvent Tutorial with Examples
- JavaScript Functions Tutorial with Examples
- Introduction to Javascript HTML5 Canvas API
- Javascript Navigator Tutorial with Examples
- Javascript URL Encoding Tutorial with Examples
- JavaScript Variables Tutorial with Examples
- Javascript InputEvent Tutorial with Examples
- Javascript HashChangeEvent Tutorial with Examples
- Introduction to Javascript and ECMAScript
- Javascript Window Tutorial with Examples
- Alert, Confirm, Prompt Dialog Box in Javascript
- Javascript WheelEvent Tutorial with Examples
- JavaScript Switch Statement
- Javascript Locationbar Tutorial with Examples
- Highlighting code with SyntaxHighlighter Javascript library
- What are polyfills in programming science?
- Class and inheritance simulation techniques in JavaScript
- Bitwise Operations
- Javascript Geolocation API Tutorial with Examples
- JavaScript Symbols Tutorial with Examples
- Javascript FileReader Tutorial with Examples
- JavaScript JSON Tutorial with Examples
- JavaScript Date Tutorial with Examples
- JavaScript Map Collection Tutorial with Examples
- Javascript Console Tutorial with Examples
- JavaScript Strings Tutorial with Examples
- JavaScript Modules Tutorial with Examples
- Javascript Form Validation Tutorial with Examples
- Javascript ChangeEvent Tutorial with Examples
- JavaScript Number Tutorial with Examples
- The History of Modules in JavaScript
- Javascript Statusbar Tutorial with Examples
- Undertanding JavaScript Iterables and Iterators
- Quickstart with Javascript
- JavaScript Event Handling Tutorial with Examples
- JavaScript void Keyword Tutorial with Examples
- Classes and Objects in JavaScript
- JavaScript Set Collection Tutorial with Examples
- Javascript DragEvent Tutorial with Examples
- JavaScript Loops Tutorial with Examples
- Inheritance and polymorphism in JavaScript
- Javascript Scrollbars Tutorial with Examples
- Parsing XML in Javascript with DOMParser
- Quickstart with JavaScript
- JavaScript Web Cookies Tutorial with Examples
- Javascript KeyboardEvent Tutorial with Examples
- Javascript Fetch API Tutorial with Examples
- JavaScript Error Handling Tutorial with Examples
- Undertanding Duck Typing in JavaScript
- JavaScript Arrays Tutorial with Examples
- JavaScript Regular Expressions Tutorial with Examples
Show More