Bitwise Operations
1. Bitwise
No ADS
In digital computer programming. The bitwise operation works on one or more binary numerals, or binary numerals-like strings. This is a simple and fast operation, directly supported by processor. Normally, bitwise operations are much faster than multiplication, division, sometimes significantly faster than addition. bitwise calculations use less energy because it rarely uses resources.
There are 7 bitwise operations :
Operator | Name | Description |
& | AND | If both bits are 1, the return value is 1, otherwise it returns 0. |
| | OR | If one of two bits is 1, the return value is 1, otherwise it returns 0. |
^ | XOR | If 2 bits are different, the return value is 1, otherwise it returns 0. |
~ | NOT | Inverts all the bits, 0 to 1 and 1 to 0. |
<< | Zero fill left shift | Shifts all bits to the left. |
>> | Signed right shift | Shifts all bits to the right except the first bit. |
>>> | Zero fill right shift | Shifts all bits to the right. |
Bitwise AND
When a bitwise AND is performed on a pair of bits, it returns 1 if both bits are 1, otherwise returns 0.
Example with 1 bit:
Operation | Result |
0 & 0 | 0 |
0 & 1 | 0 |
1 & 0 | 0 |
1 & 1 | 1 |
Example with 4 bit:
Operation | Result |
1111 & 0000 | 0000 |
1111 & 0001 | 0001 |
1111 & 0010 | 0010 |
1111 & 0100 | 0100 |
Bitwise OR:
When a bitwise OR is performed on a pair of bits, it returns 1 if one of the bits are 1, otherwise returns 0.
Example with 1 bit:
Operation | Result |
0 | 0 | 0 |
0 | 1 | 1 |
1 | 0 | 1 |
1 | 1 | 1 |
Example with 4 bits:
Operation | Result |
1111 | 0000 | 1111 |
1111 | 0001 | 1111 |
1111 | 0010 | 1111 |
1111 | 0100 | 1111 |
Bitwise XOR
When a bitwise XOR is performed on a pair of bits, it returns 1 if the bits are different, otherwise returns 0.
Example with 1 bit:
Operation | Result |
0 ^ 0 | 0 |
0 ^ 1 | 1 |
1 ^ 0 | 1 |
1 ^ 1 | 0 |
Example with 4 bits:
Operation | Result |
1111 ^ 0000 | 1111 |
1111 ^ 0001 | 1110 |
1111 ^ 0010 | 1101 |
1111 ^ 0100 | 1011 |
Bitwise NOT
When a Bitwise NOT is used, it will reverse all bits, 1 to 0, and 0 to 1.
Example with 1 bit:
Operation | Result |
~ 0 | 1 |
~ 1 | 0 |
Example with 4 bits:
Operation | Result |
~ 0000 | 1111 |
~ 0001 | 0001 |
~ 0010 | 1101 |
~ 1100 | 0011 |
2. Bitwise operation on numbers
No ADS
Different languages can have multiple data types to represent numbers.
- Java: byte, short, int, long, double.
- C#:byte, sbyte, short, ushort, int, uint, long, ulong, float, double
- Javascript: double
- .....
Javascript stores numbers as 64 bits floating point numbers. But bitwise operations are performed on 32-bit integers. Other languages such as Java, C#,.. bitwise operations are also performed on 32-bit integers.
Therefore, before carrying out the bitwise operations with numbers, you have to convert each number into a sequence of 32 binary numbers.
Base 10 | Base 2 | 32 bits |
5 | 101 | 00000000000000000000000000000101 |
218 | 11011010 | 00000000000000000000000011011010 |
In Javascript, the toString(base) method helps you change any number from base 10 to other base.
toString-base-example.js (Javascript)
let a = 8;
// Base 2 string.
console.log( a.toString(2) );// 1000
// Base 8 string
console.log( a.toString(8) ); // 10
// Base 16 string
console.log( a.toString(16) ); // 8
let b = 218;
// Base 2 string.
console.log( b.toString(2) );// 11011010
// Base 8 string
console.log( b.toString(8) ); // 332
// Base 16 string
console.log( b.toString(16) ); // daExample:
Decimal | Binary |
5 | 00000000000000000000000000000101 |
1 | 00000000000000000000000000000001 |
5 & 1 = 1 | 00000000000000000000000000000001 |
5 | 1 = 5 | 00000000000000000000000000000101 |
5 ^ 1 = 4 | 00000000000000000000000000000100 |
~ 5 = -6 | 11111111111111111111111111111010 |
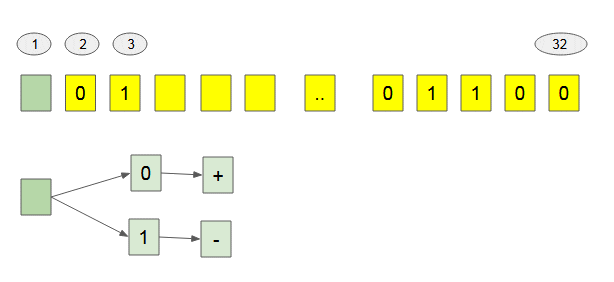
Note: Of 32 bits, the first bit is used to determine the sign of number. If this bit is 1, it corresponds to the ( - ) sign. If this bit is 0 , it corresponds to the ( + ) sign
Bitwise Left Shift (<<)
Decimal | Binary |
5 | 00000000000000000000000000000101 |
5 << 1 = 10 | 00000000000000000000000000001010 |
5 << 2 = 20 | 00000000000000000000000000010100 |
The Bitwise Left Shift ( << ) Operator can change the sign of number.
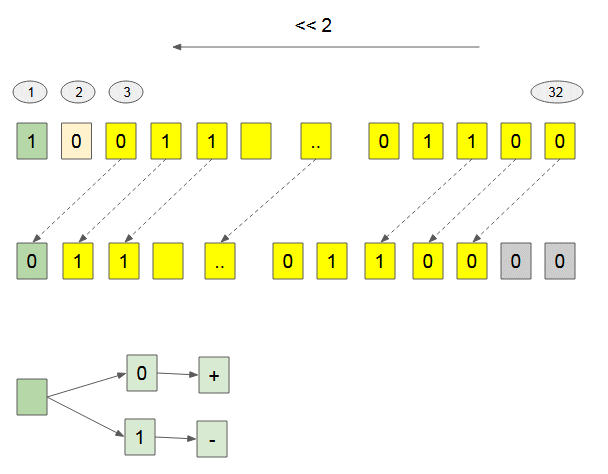
(Javascript code)
console.log( 1073741824 << 1); // -2147483648
console.log( 2684354560 << 1); // 1073741824Bitwise Right Shift (>>) [Unsigned Right Shift]
Decimal | Binary |
29 | 00000000000000000000000000011101 |
29 >> 1 = 14 | 00000000000000000000000000001110 |
29 >> 2 = 7 | 00000000000000000000000000000111 |
The Bitwise Right Shift ( >> ) operator doesn't change the sign of number because the first bit is not moved.
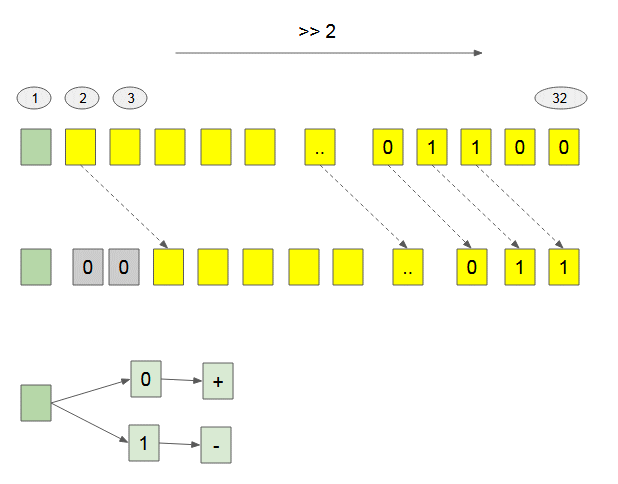
Bitwise Right Shift (>>>) [Zero fill right Shift]
The Bitwise Right Shift ( >>> ) operator can change the number sign.
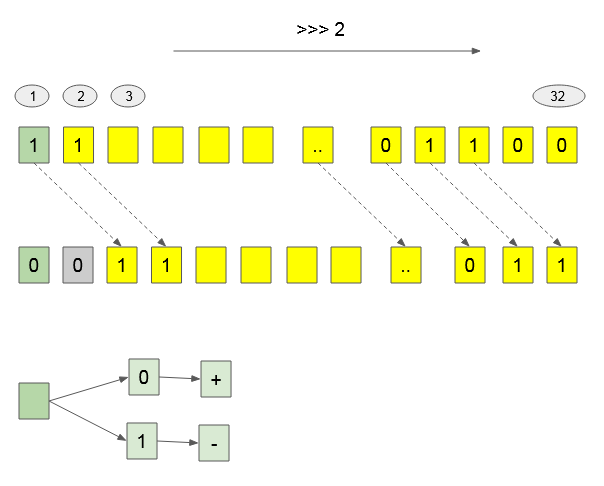
(Javascript Code)
console.log( -1073741824 >>> 1); // 1610612736
console.log( 1073741824 >>> 1); // 5368709123. What is Bitwise used for?
No ADS
The bitwise calculations are directly supported by the computer processor, it performs very fast. Below, I list some examples of using these calculations.
Use the bitwise operations on Strings (characters) in the Java, C#, C/C++ ...languages. Note: some languages such as Javascript don't support the bitwise operation with String type.
Convert an Uppercase into Lowercase:
// Rule: x | ' '
('A' | ' ') ==> 'a'
('B' | ' ') ==> 'b'
('a' | ' ') => 'a'Convert Lowercase into Uppercase:
// Rule: x & '_'
('a' & '_') ==> 'A'
('b' & '_') ==> 'B'
('A' & '_') ==> 'A'Reverse uppercase to lowercase, lowercase to uppercase:
// Rule: x ^ ' '
('a' ^ ' ') ==> 'A'
('A' ^ ' ') ==> 'a'View the position of Latin letters (applying to only uppercase)
// Rule: x & '?'
'A' & '?' ==> 1
'B' & '?' ==> 2
...
'Z' & '?' ==> 26
// Rule: x ^ '@'
'A' ^ '@' ==> 1
'B' ^ '@' ==> 2
...
'Z' ^ '@' ==> 26View the position of Latin letters (applying only to lowercase)
// Rule: x ^ '`'
'a' ^ '`' ==> 1
'b' ^ '`' ==> 2
...
'z' ^ '`' ==> 26
// '`' : binary ( 1100000 ), hex('60'), chr(96)View the position of Latin letters, applying to both uppercase and lowercase:
// Rule: x & '\u001F'
'A' & '\u001F' ==> 1
'B' & '\u001F' ==> 2
...
'Z' & '\u001F' ==> 26
'A' & '\u001F' ==> 1
'B' & '\u001F' ==> 2
...
'Z' & '\u001F' ==> 26No ADS
ECMAScript, Javascript Tutorials
- Javascript Screen Tutorial with Examples
- Javascript MouseEvent Tutorial with Examples
- Javascript XMLHttpRequest Tutorial with Examples
- JavaScript if else Statement Tutorial with Examples
- JavaScript Promise, Async/Await Tutorial with Examples
- Javascript History API Tutorial with Examples
- Javascript Menubar Tutorial with Examples
- Javascript Location Tutorial with Examples
- JavaScript Boolean Tutorial with Examples
- JavaScript setTimeout and setInterval Function
- Javascript FocusEvent Tutorial with Examples
- JavaScript Functions Tutorial with Examples
- Introduction to Javascript HTML5 Canvas API
- Javascript Navigator Tutorial with Examples
- Javascript URL Encoding Tutorial with Examples
- JavaScript Variables Tutorial with Examples
- Javascript InputEvent Tutorial with Examples
- Javascript HashChangeEvent Tutorial with Examples
- Introduction to Javascript and ECMAScript
- Javascript Window Tutorial with Examples
- Alert, Confirm, Prompt Dialog Box in Javascript
- Javascript WheelEvent Tutorial with Examples
- JavaScript Switch Statement
- Javascript Locationbar Tutorial with Examples
- Highlighting code with SyntaxHighlighter Javascript library
- What are polyfills in programming science?
- Class and inheritance simulation techniques in JavaScript
- Bitwise Operations
- Javascript Geolocation API Tutorial with Examples
- JavaScript Symbols Tutorial with Examples
- Javascript FileReader Tutorial with Examples
- JavaScript JSON Tutorial with Examples
- JavaScript Date Tutorial with Examples
- JavaScript Map Collection Tutorial with Examples
- Javascript Console Tutorial with Examples
- JavaScript Strings Tutorial with Examples
- JavaScript Modules Tutorial with Examples
- Javascript Form Validation Tutorial with Examples
- Javascript ChangeEvent Tutorial with Examples
- JavaScript Number Tutorial with Examples
- The History of Modules in JavaScript
- Javascript Statusbar Tutorial with Examples
- Undertanding JavaScript Iterables and Iterators
- Quickstart with Javascript
- JavaScript Event Handling Tutorial with Examples
- JavaScript void Keyword Tutorial with Examples
- Classes and Objects in JavaScript
- JavaScript Set Collection Tutorial with Examples
- Javascript DragEvent Tutorial with Examples
- JavaScript Loops Tutorial with Examples
- Inheritance and polymorphism in JavaScript
- Javascript Scrollbars Tutorial with Examples
- Parsing XML in Javascript with DOMParser
- Quickstart with JavaScript
- JavaScript Web Cookies Tutorial with Examples
- Javascript KeyboardEvent Tutorial with Examples
- Javascript Fetch API Tutorial with Examples
- JavaScript Error Handling Tutorial with Examples
- Undertanding Duck Typing in JavaScript
- JavaScript Arrays Tutorial with Examples
- JavaScript Regular Expressions Tutorial with Examples
Show More
Java Basic
- Data Types in java
- Java PhantomReference Tutorial with Examples
- JDK Javadoc in CHM format
- Java Stream Tutorial with Examples
- Java Predicate Tutorial with Examples
- Java BiConsumer Tutorial with Examples
- Arrays in Java
- JDBC Driver Libraries for different types of database in Java
- Abstract class and Interface in Java
- Java Commons Email Tutorial with Examples
- Install Eclipse
- Bitwise Operations
- Install Eclipse on Ubuntu
- Configuring Eclipse to use the JDK instead of JRE
- Java Commons Logging Tutorial with Examples
- Java Enums Tutorial with Examples
- Loops in Java
- Java Regular Expressions Tutorial with Examples
- Install Java on Ubuntu
- Quick Learning Java for beginners
- Install Java on Windows
- Comparing and Sorting in Java
- Inheritance and polymorphism in Java
- Java Consumer Tutorial with Examples
- Java String, StringBuffer and StringBuilder Tutorial with Examples
- Java Exception Handling Tutorial with Examples
- Example of Java encoding and decoding using Apache Base64
- if else statement in java
- Switch Statement in Java
- Java Supplier Tutorial with Examples
- Java Programming for team using Eclipse and SVN
- Java JDBC Tutorial with Examples
- Java remote method invocation - Java RMI Tutorial with Examples
- Java Multithreading Programming Tutorial with Examples
- Customize java compiler processing your Annotation (Annotation Processing Tool)
- What is needed to get started with Java?
- Java Aspect Oriented Programming with AspectJ (AOP)
- Understanding Java System.identityHashCode, Object.hashCode and Object.equals
- Java Compression and Decompression Tutorial with Examples
- Java Reflection Tutorial with Examples
- Install OpenJDK on Ubuntu
- Java String.format() and printf() methods
- History of Java and the difference between Oracle JDK and OpenJDK
- Introduction to the Raspberry Pi
- Java Socket Programming Tutorial with Examples
- Java Generics Tutorial with Examples
- Manipulating files and directories in Java
- Java WeakReference Tutorial with Examples
- Java Commons IO Tutorial with Examples
- History of bits and bytes in computer science
- Which Platform Should You Choose for Developing Java Desktop Applications?
- Java SoftReference Tutorial with Examples
- Syntax and new features in Java 8
- Java Annotations Tutorial with Examples
- Java Function Tutorial with Examples
- Access modifiers in Java
- Java BiFunction Tutorial with Examples
- Get the values of the columns automatically increment when Insert a record using JDBC
- Java Functional Interface Tutorial with Examples
- Java BiPredicate Tutorial with Examples
Show More
- Java Servlet/Jsp Tutorials
- Java Collections Framework Tutorials
- Java API for HTML & XML
- Java IO Tutorials
- Java Date Time Tutorials
- Spring Boot Tutorials
- Maven Tutorials
- Gradle Tutorials
- Java Web Services Tutorials
- Java SWT Tutorials
- JavaFX Tutorials
- Java Oracle ADF Tutorials
- Struts2 Framework Tutorials
- Spring Cloud Tutorials