CSS Margins Tutorial with Examples
1. CSS Margin
No ADS
CSS Margin is used to create a space around an element, outside the element borders.
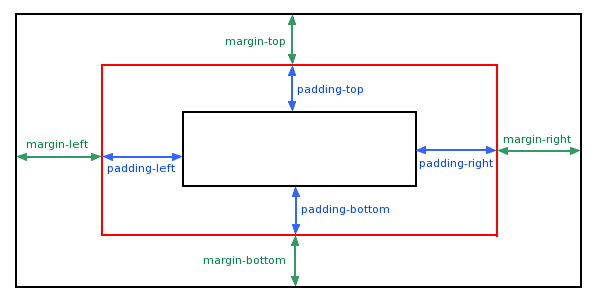
By standard syntax you need to provide 4 values for margin:
/* Syntax: */
margin: top right bottom left;
/* Example: */
margin: 5px 20px 30px 40px;Instead of providing 4 values for CSS margin you can use 4 properties: CSS margin-top, margin-right, margin-bottom, margin-left.
margin-top: 5px;
margin-right: 20px;
margin-bottom: 30px;
margin-right: 40px;CSS margin can also accept 1, 2 or 3 values
/* Apply to all four sides */
margin: 1em;
margin: -3px;
/* vertical | horizontal */
margin: 5px 10px;
/* top | horizontal | bottom */
margin: 10px 20px 30px;Values can be given to CSS margin:
auto | Browser will automatically calculate margin for element. |
% | Specify a value in% for margin, which is % relative to the width of the nearest ancestor Block-level Element containing the current element. See also the explanation at the end of this post. |
px, cm, em,.. | Specify a specific value in px, cm, em,.. units , for example, 10px, 2cm, 3em,... |
inherit | The values of margin will be inherited from a parent element. |
2. CSS Margin %
CSS margin accepts percentage value (%). This value is percentage relative to the width of the Containing Block, of which, the Containing Block is the nearest ancestor Block-level element that contains the current element.
margin-percent-example.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>CSS Padding</title>
<meta charset="UTF-8"/>
<script>
function changeParentSize() {
var blockDiv = document.getElementById("blockDiv");
// offsetWidth = contentWidth + padding + border
var offsetWidth = blockDiv.offsetWidth;
if(offsetWidth > 300) {
offsetWidth = 200;
}
blockDiv.style.width = (offsetWidth+1) + "px";
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<h3>CSS Margin Percentage</h3>
<div id="blockDiv" style="width:200px; height: 150px; border: 1px solid blue">
I am a div (Block-Level Element) <br/>
<span style="background-color: yellow;">
I am a span (Inline Element)
<div id= "redDiv" style="width:100px; margin:10%; border:1px solid red;">
width:100px; margin:10%;
</div>
</span>
</div>
<br/>
<button onClick="changeParentSize()">Change size of 'blockDiv'</button>
</body>
</html>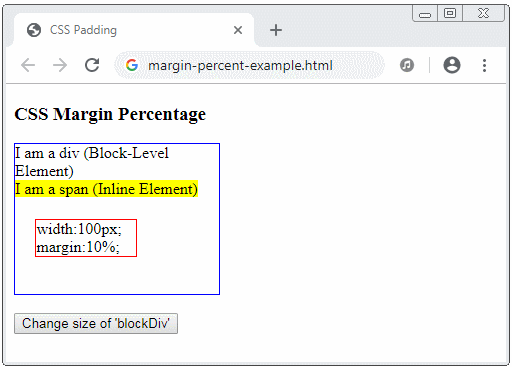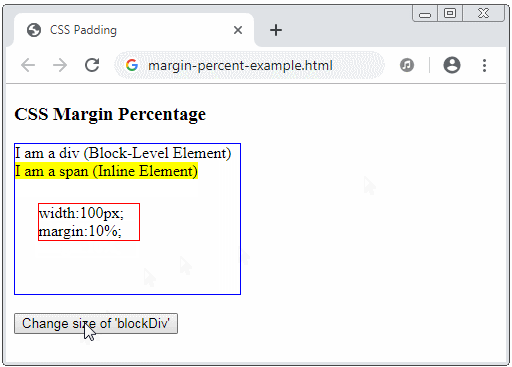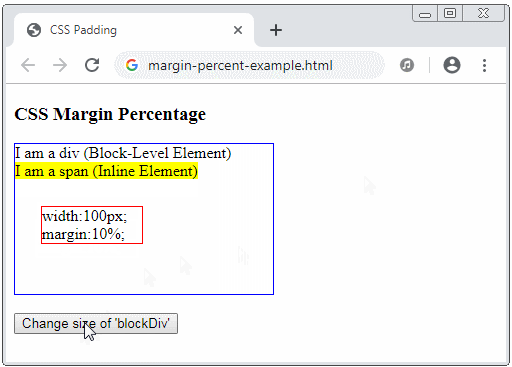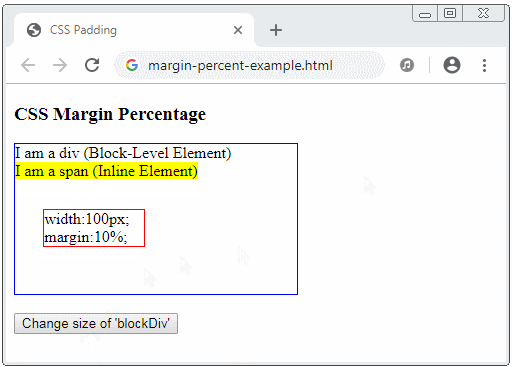
3. CSS margin auto
No ADS
CSS margin accepts auto value. This is a good solution when you want to align elements in the middle horizontally.
margin-auto-example.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>CSS Margin</title>
<meta charset="UTF-8"/>
<style>
.center-div {
width: 150px;
background-color: LightCyan;
padding:10px;
margin-left: auto;
margin-right: auto
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h3>CSS Margin auto</h3>
<div class="center-div">
margin-left: auto; <br/>
margin-right: auto;
</div>
</body>
</html>4. Margin for Inline Element
Note: CSS margin vertically (margin-top & margin-bottom) doesn't have effect on Inline Element. For example, by default <span> is an inline element, vertical margins have no effect on it.
margin-inline-element-example.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>CSS Margin</title>
<meta charset="UTF-8"/>
<style>
div {
background-color: yellow;
}
span {
margin-top: 100px;
margin-bottom: 100px;
margin-left: 20px;
margin-right: 20px;
background-color: #eee;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h3>CSS Margin for Inline Element</h3>
<div>I am a div</div>
<span>
I am a span.
margin-top: 100px;
margin-bottom: 100px;
margin-left: 20px;
margin-right: 20px;
</span>
<div>I am a div</div>
</body>
</html>If you want vertical margin to work with an inline element, you have to turn it into a Block-Level Element or an Inline-block Element.
span {
display: block;
}
/* OR: */
span {
display: inline-block;
}5. CSS margin collapsing
No ADS
The bottom and top margins of two adjacent Block-level elements sometimes combine each other to form a single margin having the size which is the largest size of the two above margins. This behavior is referred to as margin collapsing. Note: margin collapsing does not occur with the elements that have {float:left|right} or {position:absolute}.
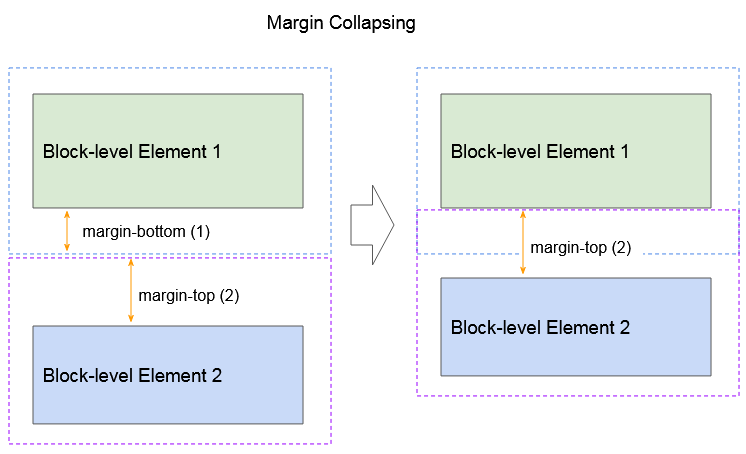
Margin collapsing with participation of many elements:
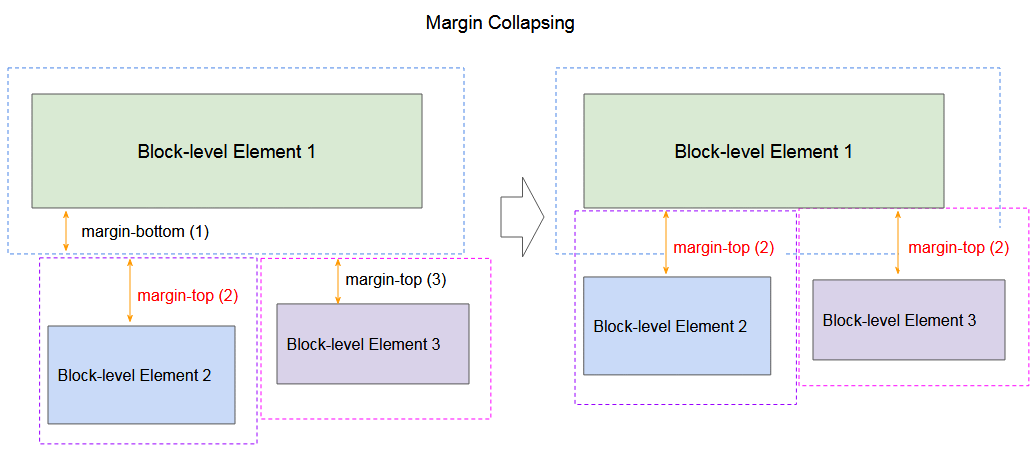
margin-collapsing-example.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>CSS Margin Collapsing</title>
<meta charset="UTF-8"/>
<style>
div {
border:1px solid green;
}
button {
margin-top:10px;
}
</style>
<script>
function addDiv2MarginTop(delta) {
var div2 = document.getElementById("div2");
var style = window.getComputedStyle(div2);
var marginTopString = style.marginTop;// 20px
var marginTopInt = parseInt(marginTopString.substr(0,marginTopString.length-2)); // 20
var newMarginTopString = (marginTopInt + delta) + "px";
div2.style.marginTop = newMarginTopString;
div2.innerHTML = "height:50px; margin-top: " + newMarginTopString;
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<h3>CSS Margin Collapsing</h3>
<div style="height:50px; margin-bottom:50px">
height:50px; margin-bottom:50px;
</div>
<div style="height:50px; margin-top:40px" id="div2">
height:50px; margin-top:40px
</div>
<button onClick="addDiv2MarginTop(3)">Div2 margin-top (+)</button>
<button onClick="addDiv2MarginTop(-3)">Div2 margin-top (-)</button>
</body>
</html>If two block-level elements are adjacent, they will cause marginal collapsing (See the above example ). But if the second element is established CSS {float:left|right}, margin collapsing will not occur.
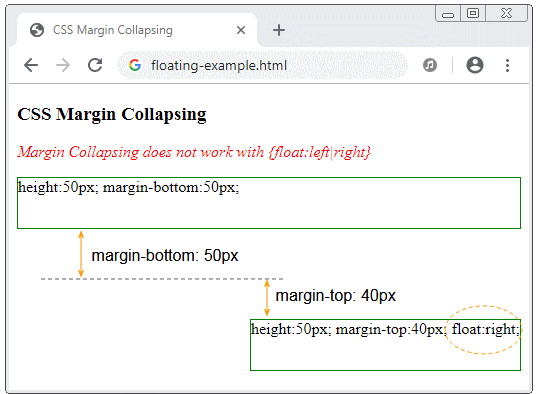
floating-example.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>CSS Margin Collapsing</title>
<meta charset="UTF-8"/>
<style>
div {
border:1px solid green;
}
p {
color:red;
font-style:italic;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h3>CSS Margin Collapsing</h3>
<p>Margin Collapsing does not work with {float:left|right}</p>
<div style="height:50px; margin-bottom:50px;">
height:50px; margin-bottom:50px;
</div>
<div style="height:50px; margin-top:40px; float:right" id="div2">
height:50px; margin-top:40px; float:right;
</div>
</body>
</html>Parent element and child elements.
If the parent element has no border, padding, and the first child element is a Block-level element having no {float:left|right}, margin collapsing will occur for the margin-top of this child element and other element outside the parent element.
margin-collapsing-example2.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>CSS Margin Collapsing</title>
<meta charset="UTF-8"/>
<style>
div {
background: lavender;
}
p {
margin-top: 30px;
margin-left: 15px;
margin-right: 15px;
background: yellow;
height: 30px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h3>CSS Margin Collapsing (Parent and First Child)</h3>
<div style="margin-bottom:15px;">This is a div {margin-bottom: 15px;}</div>
<div style="min-height:50px;">
<p>
Child Paragraph 1 - margin-top: 30px;
</p>
<p>
Child Paragraph 2 - margin-top: 30px;
</p>
This parent element contains two paragraphs!
</div>
</body>
</html>If the parent element has no border, padding, and the last child element is a Block-level element without {float:left|right}, margin collapsing will occur with the margin-bottom of this child element and other element outside the parent element.
margin-collapsing-example3.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>CSS Margin Collapsing</title>
<meta charset="UTF-8"/>
<style>
div {
background: lavender;
}
p {
margin-bottom: 30px;
margin-left: 15px;
margin-right: 15px;
background: yellow;
height: 30px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h3>CSS Margin Collapsing (Parent and last Child)</h3>
<div style="min-height:50px;">This parent element contains two paragraphs!
<p>
Child Paragraph 1 - margin-bottom: 30px;
</p>
<p>
Child Paragraph 2 - margin-bottom: 30px;
</p>
</div>
<div style="margin-top:15px;">This is a div {margin-top: 15px;}</div>
</body>
</html>Empty element.
If an element is an empty block without border, padding, height, min-height, then its margin-top and margin-bottom will collapse into a value.
empty-block-example.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>CSS Margin Collapsing</title>
<meta charset="UTF-8"/>
</head>
<body>
<h3>CSS Margin Collapsing (Empty block)</h3>
<div style="height:40px; background-color: yellow;">
height:40px;
</div>
<div style="margin-top:40px; margin-bottom:50px;">
<!-- This is Empty Block -->
<!-- No border, padding, height, min-height -->
</div>
<div style="height:50px; background-color: yellow;">
height:50px;
</div>
</body>
</html>Note:
If a negative margin is involved in margin collapsing, then the margin value used will be the sum of the largest positive margin and the most negative margin.
No ADS
CSS Tutorials
- Units in CSS
- Basic CSS Selectors Tutorial with Examples
- CSS Attribute Selector Tutorial with Examples
- CSS combinator Selectors Tutorial with Examples
- CSS Backgrounds Tutorial with Examples
- CSS Opacity Tutorial with Examples
- CSS Padding Tutorial with Examples
- CSS Margins Tutorial with Examples
- CSS Borders Tutorial with Examples
- CSS Outline Tutorial with Examples
- CSS box-sizing Tutorial with Examples
- CSS max-width and min-width Tutorial with Examples
- The keywords min-content, max-content, fit-content, stretch in CSS
- CSS Links Tutorial with Examples
- CSS Fonts Tutorial with Examples
- Understanding Generic Font Family Names in CSS
- CSS @font-face Tutorial with Examples
- CSS Align Tutorial with Examples
- CSS Cursors Tutorial with Examples
- CSS Overflow Tutorial with Examples
- CSS Lists Tutorial with Examples
- CSS Tables Tutorial with Examples
- CSS visibility Tutorial with Examples
- CSS Display Tutorial with Examples
- CSS Grid Layout Tutorial with Examples
- CSS Float and Clear Tutorial with Examples
- CSS Position Tutorial with Examples
- CSS line-height Tutorial with Examples
- CSS text-align Tutorial with Examples
- CSS text-decoration Tutorial with Examples
Show More