Java DataInputStream Tutorial with Examples
1. DataInputStream
DataInputStream is used to read data primitives from a data source, especially data sources written by DataOutputStream.
public class DataInputStream extends FilterInputStream implements DataInput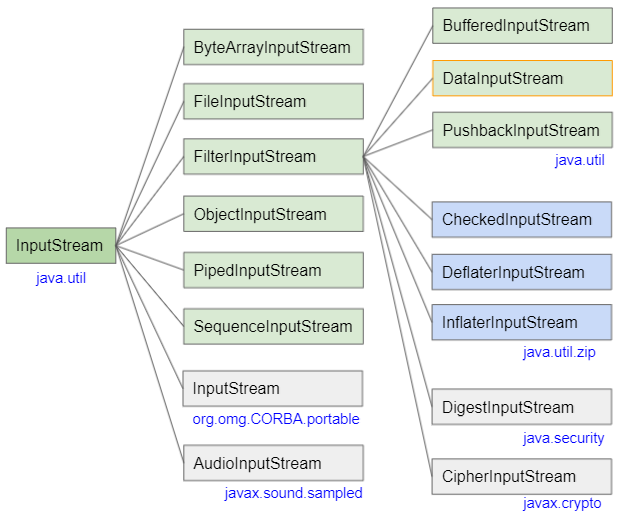
- ByteArrayInputStream
- FileInputStream
- FilterInputStream
- BufferedInputStream
- InputStream
- PushbackInputStream
- ObjectInputStream
- PipedInputStream
- SequenceInputStream
- AudioInputStream
- CheckedInputStream
- DeflaterInputStream
- InflaterInputStream
- CipherInputStream
- DigestInputStream
3. Methods
public final boolean readBoolean() throws IOException
public final byte readByte() throws IOException
public final int readUnsignedByte() throws IOException
public final short readShort() throws IOException
public final int readUnsignedShort() throws IOException
public final char readChar() throws IOException
public final int readInt() throws IOException
public final long readLong() throws IOException
public final float readFloat() throws IOException
public final double readDouble() throws IOException
public final String readUTF() throws IOException
public static final String readUTF(DataInput in) throws IOException
public final void readFully(byte[] b) throws IOException
public final void readFully(byte[] b, int off, int len) throws IOException
@Deprecated
public String readLine() throws IOExceptionOther methods inherited from parent classes:
public int read() throws IOException
public int read(byte[] b) throws IOException
public int read(byte[] b, int off, int len) throws IOException
public byte[] readAllBytes() throws IOException
public byte[] readNBytes(int len) throws IOException
public int readNBytes(byte[] b, int off, int len) throws IOException
public long skip(long n) throws IOException
public int available() throws IOException
public void close() throws IOException
public synchronized void mark(int readlimit)
public synchronized void reset() throws IOException
public boolean markSupported()
public long transferTo(OutputStream out) throws IOException
public static InputStream nullInputStream()4. Examples
No ADS
DataInputStream is commonly used to read data sources written by DataOutputStream. In this example, we use DataOutputStream to write a table of data with an Excel-like structure to a file, then use DataInputStream to read this file.
OrderDate | Finished | Item | Units | UnitCost | Total |
2020-01-06 | Pencil | 95 | 1.99 | 189.05 | |
2020-01-23 | Binder | 50 | 19.99 | 999.50 | |
2020-02-09 | Pencil | 36 | 4.99 | 179.64 | |
2020-02-26 | Pen | 27 | 19.99 | 539.73 | |
2020-03-15 | Pencil | 56 | 2.99 | 167.44 |
First, we write the Order class that simulates the data of a table row:
Order.java
package org.o7planning.datainputstream.ex;
import java.time.LocalDate;
public class Order {
private LocalDate orderDate;
private boolean finished;
private String item;
private int units;
private float unitCost;
private float total;
public Order(LocalDate orderDate, boolean finished, //
String item, int units, float unitCost, float total) {
this.orderDate = orderDate;
this.finished = finished;
this.item = item;
this.units = units;
this.unitCost = unitCost;
this.total = total;
}
public LocalDate getOrderDate() {
return orderDate;
}
public boolean isFinished() {
return finished;
}
public String getItem() {
return item;
}
public int getUnits() {
return units;
}
public float getUnitCost() {
return unitCost;
}
public float getTotal() {
return total;
}
}Use DataOutputStream to write the above data table to a file:
WriteDataFile_example1.java
package org.o7planning.datainputstream.ex;
import java.io.DataOutputStream;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.OutputStream;
import java.time.LocalDate;
public class WriteDataFile_example1 {
// Windows: C:/somepath/data-file.txt
private static final String filePath = "/Volumes/Data/test/data-file.txt";
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Order[] orders = new Order[] { //
new Order(LocalDate.of(2020, 1, 6), true, "Pencil", 95, 1.99f, 189.05f),
new Order(LocalDate.of(2020, 1, 23), false, "Binder", 50, 19.99f, 999.50f),
new Order(LocalDate.of(2020, 2, 9), true, "Pencil", 36, 4.99f, 179.64f),
new Order(LocalDate.of(2020, 2, 26), false, "Pen", 27, 19.99f, 539.73f),
new Order(LocalDate.of(2020, 3, 15), true, "Pencil", 56, 2.99f, 167.44f) //
};
File outFile = new File(filePath);
outFile.getParentFile().mkdirs();
OutputStream outputStream = new FileOutputStream(outFile);
DataOutputStream dataOutputStream = new DataOutputStream(outputStream);
for (Order order : orders) {
dataOutputStream.writeUTF(order.getOrderDate().toString());
dataOutputStream.writeBoolean(order.isFinished());
dataOutputStream.writeUTF(order.getItem());
dataOutputStream.writeInt(order.getUnits());
dataOutputStream.writeFloat(order.getUnitCost());
dataOutputStream.writeFloat(order.getTotal());
}
dataOutputStream.close();
}
}After running the above example, we have a data file with rather confusing content:
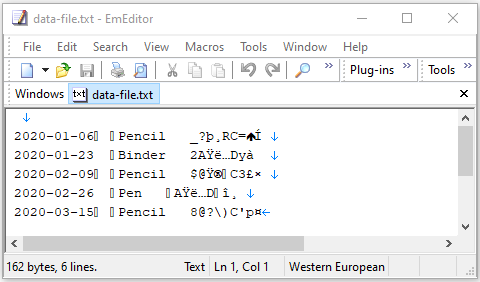
Next, we use DataInputStream to read the above file.
ReadDataFile_example1.java
package org.o7planning.datainputstream.ex;
import java.io.DataInputStream;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
public class ReadDataFile_example1 {
// Windows: C:/somepath/data-file.txt
private static final String filePath = "/Volumes/Data/test/data-file.txt";
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
File file = new File(filePath);
InputStream inputStream = new FileInputStream(file);
DataInputStream dataInputStream = new DataInputStream(inputStream);
int row = 0;
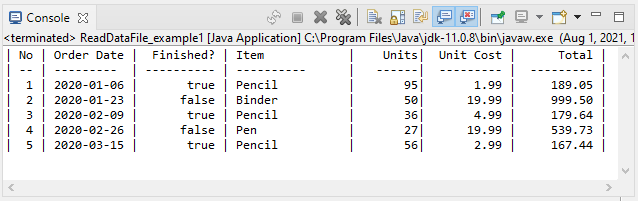
System.out.printf("|%3s | %-10s | %10s | %-15s | %8s| %10s | %10s |%n", //
"No", "Order Date", "Finished?", "Item", "Units", "Unit Cost", "Total");
System.out.printf("|%3s | %-10s | %10s | %-15s | %8s| %10s | %10s |%n", //
"--", "---------", "----------", "----------", "------", "---------", "---------");
while (dataInputStream.available() > 0) {
row++;
String orderDate = dataInputStream.readUTF();
boolean finished = dataInputStream.readBoolean();
String item = dataInputStream.readUTF();
int units = dataInputStream.readInt();
float unitCost = dataInputStream.readFloat();
float total = dataInputStream.readFloat();
System.out.printf("|%3d | %-10s | %10b | %-15s | %8d| %,10.2f | %,10.2f |%n", //
row, orderDate, finished, item, units, unitCost, total);
}
dataInputStream.close();
}
}Output:
5. readUTF()
No ADS
The readUTF() method is used to read a string encoded with "Modified UTF-8". The read rules are symmetric with the write rules of the DataOutput.writeUTF(String) method.
public final String readUTF() throws IOException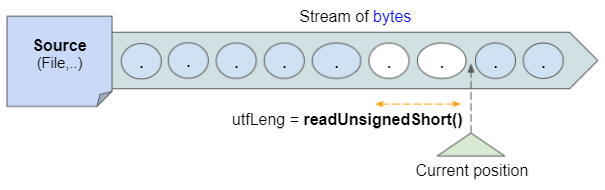
At the cursor position on the stream of bytes, the DataInputStream will read the next 2 bytes using the readUnsignedShort() method to determine the number of bytes used to store the UTF-8 string and get the result is utfLeng.
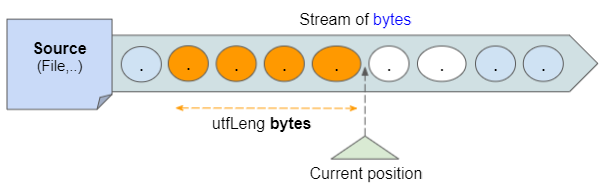
Then the DataInputStream reads the next utfLeng bytes and converts it to a UTF-8 string.
- UTF-8
- DataOutputStream
6. readUTF(DataInput in)
The static method readUTF(DataInput) is used to read a "Modified UTF-8" string from a specified DataInput object.
public static final String readUTF(DataInput in) throws IOException7. readFully(byte[] buffer)
No ADS
Reads as many bytes as possible from this DataInputStream and assigns it to the specified buffer array.
public final void readFully(byte[] buffer) throws IOExceptionThis method blocks until one of the following conditions occurs:
- Read buffer.length bytes.
- The end of the stream has been reached. --> The end of the stream is reached.
- An IOException occurs (Different from EOFException).
8. readFully(byte[] buffer, int off, int len)
Reads as many bytes as possible from this DataInputStream and assigns it to the specified buffer array from index off to index off+len-1.
public final void readFully(byte[] buffer, int off, int len) throws IOExceptionThis method blocks until one of the following conditions occurs:
- Read buffer.length bytes.
- The end of the stream has been reached. -> The end of the stream is reached.
- An IOException occurs (Different from EOFException).
9. readBoolean()
The readBoolean() method reads a byte from this DataInputStream. If the result is non-zero the method returns true, otherwise returns false.
public final boolean readBoolean() throws IOException10. readByte()
The readByte() method reads a byte from this DataInputStream, the returned value is between -128 and 127.
It is suitable for reading data written by the DataOutput.writeByte(byte) method.
public final byte readByte() throws IOException11. readUnsignedByte()
No ADS
The readUnsignedShort() method reads 1 byte from this DataInputStream and converts it to an unsigned 4-bytes integer, values from 0 to 255.
public final int readUnsignedByte() throws IOException12. readShort()
The readShort() method reads 2 bytes from this DataInputStream and converts it to a short data type.
public final short readShort() throws IOExceptionConversion rule:
return (short)((firstByte << 8) | (secondByte & 0xff));13. readUnsignedShort()
The readUnsignedShort() method reads 2 bytes from this DataInputStream and converts it to an unsigned 4-bytes integer, values from 0 to 65535.
public final int readUnsignedShort() throws IOExceptionConversion rule:
return (((firstByte & 0xff) << 8) | (secondByte & 0xff))14. readChar()
The readChar() method reads 2 bytes from this DataInputStream, and converts it to char data type.
public final char readChar() throws IOExceptionConversion rule:
return (char)((firstByte << 8) | (secondByte & 0xff));15. readInt()
No ADS
The readInt() method reads 4 bytes from this DataInputStream, and converts it to int data type.
public final int readInt() throws IOExceptionConversion rule:
return (((firstByte & 0xff) << 24) | ((secondByte & 0xff) << 16)
| ((thirdByte & 0xff) << 8) | (fourthByte & 0xff));16. readLong()
The readLong() method reads 8 bytes from this DataInputStream and converts it to a long data type.
public final long readLong() throws IOExceptionConversion rule:
return (((long)(byte1 & 0xff) << 56) |
((long)(byte2 & 0xff) << 48) |
((long)(byte3 & 0xff) << 40) |
((long)(byte4 & 0xff) << 32) |
((long)(byte5 & 0xff) << 24) |
((long)(byte6 & 0xff) << 16) |
((long)(byte7 & 0xff) << 8) |
((long)(byte8 & 0xff)));No ADS
Java IO Tutorials
- Java CharArrayWriter Tutorial with Examples
- Java FilterReader Tutorial with Examples
- Java FilterWriter Tutorial with Examples
- Java PrintStream Tutorial with Examples
- Java BufferedReader Tutorial with Examples
- Java BufferedWriter Tutorial with Examples
- Java StringReader Tutorial with Examples
- Java StringWriter Tutorial with Examples
- Java PipedReader Tutorial with Examples
- Java LineNumberReader Tutorial with Examples
- Java PrintWriter Tutorial with Examples
- Java IO Binary Streams Tutorial with Examples
- Java IO Character Streams Tutorial with Examples
- Java BufferedOutputStream Tutorial with Examples
- Java ByteArrayOutputStream Tutorial with Examples
- Java DataOutputStream Tutorial with Examples
- Java PipedInputStream Tutorial with Examples
- Java OutputStream Tutorial with Examples
- Java ObjectOutputStream Tutorial with Examples
- Java PushbackInputStream Tutorial with Examples
- Java SequenceInputStream Tutorial with Examples
- Java BufferedInputStream Tutorial with Examples
- Java Reader Tutorial with Examples
- Java Writer Tutorial with Examples
- Java FileReader Tutorial with Examples
- Java FileWriter Tutorial with Examples
- Java CharArrayReader Tutorial with Examples
- Java ByteArrayInputStream Tutorial with Examples
- Java DataInputStream Tutorial with Examples
- Java ObjectInputStream Tutorial with Examples
- Java InputStreamReader Tutorial with Examples
- Java OutputStreamWriter Tutorial with Examples
- Java InputStream Tutorial with Examples
- Java FileInputStream Tutorial with Examples
Show More