Java Function Tutorial with Examples
1. Function interface
No ADS
In Java 8, Function is a functional interface, which represents an operator that accepts an input value and returns a value.
Source code of Function interface:
Function interface
package java.util.function;
import java.util.Objects;
@FunctionalInterface
public interface Function<T, R> {
R apply(T t);
default <V> Function<V, R> compose(Function<? super V, ? extends T> before) {
Objects.requireNonNull(before);
return (V v) -> apply(before.apply(v));
}
default <V> Function<T, V> andThen(Function<? super R, ? extends V> after) {
Objects.requireNonNull(after);
return (T t) -> after.apply(apply(t));
}
static <T> Function<T, T> identity() {
return t -> t;
}
}Example:
FunctionEx1.java
package org.o7planning.ex;
import java.util.function.Function;
public class FunctionEx1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Function<String, Integer> func = (text) -> text.length();
int length = func.apply("Function interface tutorial");
System.out.println("Length: " + length);
}
}Output:
Length: 27Example: Processing elements of a List object to create a new List object.
FunctionEx2.java
package org.o7planning.ex;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.function.Function;
public class FunctionEx2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Function<String, String> func = text -> text.toUpperCase();
List<String> list = Arrays.asList("Java", "C#", "Python");
List<String> newList = map(func, list);
newList.forEach(System.out::println);
}
public static <T,R> List<R> map(Function<T,R> mapper, List<T> list) {
List<R> result = new ArrayList<R>();
for(T t: list) {
R r = mapper.apply(t);
result.add(r);
}
return result;
}
}Output:
JAVA
C#
PYTHONExample: Using Function to convert a List object into a Map object:
FunctionEx3.java
package org.o7planning.ex;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.function.Function;
public class FunctionEx3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Function<String, Integer> func = text -> text.length();
List<String> list = Arrays.asList("Java", "C#", "Python");
Map<String, Integer> map = listToMap(func, list);
// @see: Map.forEach(BiConsumer).
map.forEach((t,r) -> System.out.println(t + " : " + r));
}
public static <T,R> Map<T,R> listToMap(Function<T,R> mapper, List<T> list) {
Map<T, R> result = new HashMap<T, R>();
for(T t: list) {
R r = mapper.apply(t);
result.put(t, r);
}
return result;
}
}Output:
C# : 2
Java : 4
Python : 6- BiFunction
- IntFunction
- LongFunction
- DoubleFunction
- Supplier
- Predicate
- BiPredicate
- Consumer
- BiConsumer
2. Function + Method reference
No ADS
M.ref example 1:
If a static method takes a single parameter and returns a value, its reference can be considered as a Function.
Function_mref_ex1.java
package org.o7planning.ex;
import java.util.function.Function;
public class Function_mref_ex1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// A method of Math class: public static long round(double)
Function<Double, Long> func1 = Math::round; // Method reference
Function<Double, Long> func2 = value -> Math.round(value);
System.out.println(func1.apply(100.7));
System.out.println(func2.apply(100.7));
}
}Output:
101
101M.ref example 2:
If a method is non-static (non-static method), takes no parameters, and returns a value, its reference can be considered as a Function.
Function_mref_ex2.java
package org.o7planning.ex;
import java.util.function.Function;
public class Function_mref_ex2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// A method of String class: public int length()
Function<String, Integer> func1 = String::length; // Method reference
Function<String, Integer> func2 = text -> text.length();
System.out.println(func1.apply("Java")); // 4
System.out.println(func2.apply("Java")); // 4
}
}M.ref example 3:
Next, take a look at CurrencyFormatter class below:
- CurrencyFormatter.usd(double) method has a parameter of type Double and returns a String. So its reference CurrencyFormatter::usd can be considered as Function<Double,String>.
CurrencyFormatter.java
package org.o7planning.tax;
public class CurrencyFormatter {
// Dollar
public static String usd(double amount) {
return "$" + amount;
}
// Euro
public static String euro(double amount) {
return "€" + amount;
}
// Vietnam Dong.
public static String vnd(double amount) {
return amount + "VND";
}
}TaxCalcExample.java
package org.o7planning.tax;
import java.util.function.Function;
public class TaxCalcExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
double amount = 1000;
String format = formatCurrency("VN", amount);
System.out.println("VN: " + format);
format = formatCurrency("US", amount);
System.out.println("US: " + format);
format = formatCurrency("EU", amount);
System.out.println("EU: " + format);
}
public static String formatCurrency(String countryCode, double amount) {
if ("VN".equals(countryCode)) {
Function<Double, String> formatter = CurrencyFormatter::vnd; // Method reference
return _formatCurrency(formatter, amount);
}
if ("US".equals(countryCode)) {
return _formatCurrency(CurrencyFormatter::usd, amount);
}
if ("EU".equals(countryCode)) {
return _formatCurrency(CurrencyFormatter::euro, amount);
}
throw new RuntimeException("No formatter for " + countryCode);
}
private static String _formatCurrency(Function<Double, String> formatter, double amount) {
return formatter.apply(amount);
}
}Output:
VN: 1000.0VND
US: $1000.0
EU: €1000.03. Function + Constructor reference
No ADS
As you know a constructor is used to create an object, which means it returns a value. So if the constructor has a single parameter, its reference will be considered as a Function.
Student.java
package org.o7planning.cr;
public class Student {
private String name;
public Student(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
}ConstructorReferenceTest.java
package org.o7planning.cr;
import java.util.function.Function;
public class ConstructorReferenceTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Function<String, Student> f1 = Student::new; // Constructor Reference
Function<String, Student> f2 = (name) -> new Student(name); // Lambda Expression
System.out.println(f1.apply("Tom").getName());
System.out.println(f2.apply("Jerry").getName());
}
}Output:
Tom
Jerry4. Function Usages
Below is a list of methods in the java.util package using the Function interface:
static
<T,U extends Comparable<? super U>> Comparator<T> | Comparator.comparing(Function<? super T,? extends U> keyExtractor) |
static <T,U> Comparator<T> | Comparator.comparing(Function<? super T,? extends U> keyExtractor, Comparator<? super U> keyComparator) |
V | Hashtable.computeIfAbsent(K key, Function<? super K,? extends V> mappingFunction) |
V | HashMap.computeIfAbsent(K key, Function<? super K,? extends V> mappingFunction) |
default V | Map.computeIfAbsent(K key, Function<? super K,? extends V> mappingFunction) |
<U> Optional<U> | |
<U> Optional<U> | |
default
<U extends Comparable<? super U>> Comparator<T> | Comparator.thenComparing(Function<? super T,? extends U> keyExtractor) |
default <U> Comparator<T> | Comparator.thenComparing(Function<? super T,? extends U> keyExtractor, Comparator<? super U> keyComparator) |
5. Function.compose(Function before)
No ADS
Here is the definition of Function.compose method:
@FunctionalInterface
public interface Function<T,R> {
R apply(T t);
default <V> Function<V, R> compose(Function<? super V, ? extends T> before) {
Objects.requireNonNull(before);
return (V v) -> apply(before.apply(v));
}
// Other default methods ..
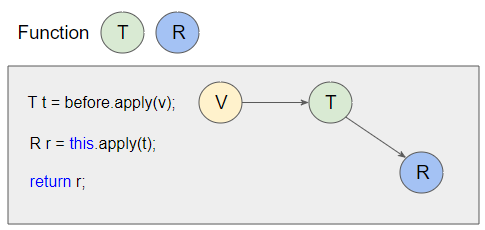
}And we rewrite this method in an easier way to understand:
@FunctionalInterface
public interface Function<T,R> {
R apply(T t);
default <V> Function<V, R> compose(Function<? super V, ? extends T> before) {
Objects.requireNonNull(before);
return (V v) -> {
T t = before.apply(v);
R r = this.apply(t);
return r;
};
}
// Other default methods ..
}
Example:
FunctionEx6.java
package org.o7planning.ex;
import java.util.function.Function;
public class FunctionEx6 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Function<String, Integer> func = content -> content.length();
Function<Article, String> before = article -> article.getContent();
Article article = new Article("Java Tutorial", "Java Tutorial Content...");
int contentLength = func.compose(before).apply(article);
System.out.println("The length of the article content: " + contentLength);
}
}
class Article {
private String title;
private String content;
public Article(String title, String content) {
this.title = title;
this.content = content;
}
public String getTitle() {
return title;
}
public String getContent() {
return content;
}
}Output:
The length of the article content: 246. Function.andThen(Function after)
No ADS
Here is the definition of Function.andThen method:
@FunctionalInterface
public interface Function<T, R> {
R apply(T t);
default <V> Function<T, V> andThen(Function<? super R, ? extends V> after) {
Objects.requireNonNull(after);
return (T t) -> after.apply(apply(t));
}
// Other default methods ..
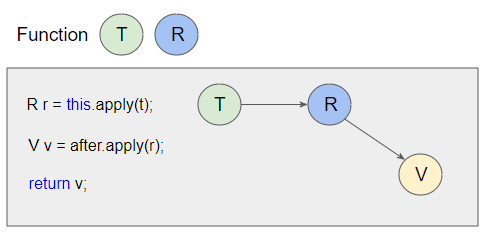
}And we rewrite this method in an easier way to understand:
@FunctionalInterface
public interface Function<T, R> {
R apply(T t);
default <V> Function<T, V> andThen(Function<? super R, ? extends V> after) {
Objects.requireNonNull(after);
return (T t) -> {
R r = this.apply(t);
V v = after.apply(r);
return v;
};
}
// Other default methods ..
}
Example:
FunctionEx7.java
package org.o7planning.ex;
import java.util.function.Function;
public class FunctionEx7 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Function<Post, String> func = post -> post.getContent();
Function<String, Integer> after = content -> content.length();
Post post = new Post("Java Tutorial", "Java Tutorial Content...");
int contentLength = func.andThen(after).apply(post);
System.out.println("The length of the post content: " + contentLength);
}
}
class Post {
private String title;
private String content;
public Post(String title, String content) {
this.title = title;
this.content = content;
}
public String getTitle() {
return title;
}
public String getContent() {
return content;
}
}Output:
The length of the post content: 247. Function.identity()
No ADS
Static method Function.identity(): Returns a function that always returns its input argument.
static <T> Function<T, T> identity() {
return t -> t;
}Example: Converts an array into a Set object containing non-duplicate elements.
FunctionEx8.java
package org.o7planning.ex;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Set;
import java.util.function.Function;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
public class FunctionEx8 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String[] names = new String[] { //
"Peter", "Martin", "John", "Peter", //
"Vijay", "Martin", "Peter", "Arthur" };
Set<String> set = Arrays.asList(names).stream() //
.map(Function.identity()).collect(Collectors.toSet());
set.forEach(System.out::println);
}
}Output:
Vijay
Arthur
John
Martin
PeterThe above example is equivalent to the below example:
FunctionEx8a.java
package org.o7planning.ex;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Set;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
public class FunctionEx8a {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String[] names = new String[] { //
"Peter", "Martin", "John", "Peter", //
"Vijay", "Martin", "Peter", "Arthur" };
Set<String> set = Arrays.asList(names).stream() //
.map(t -> t).collect(Collectors.toSet());
set.forEach(System.out::println);
}
}No ADS
Java Basic
- Data Types in java
- Java PhantomReference Tutorial with Examples
- JDK Javadoc in CHM format
- Java Stream Tutorial with Examples
- Java Predicate Tutorial with Examples
- Java BiConsumer Tutorial with Examples
- Arrays in Java
- JDBC Driver Libraries for different types of database in Java
- Abstract class and Interface in Java
- Java Commons Email Tutorial with Examples
- Install Eclipse
- Bitwise Operations
- Install Eclipse on Ubuntu
- Configuring Eclipse to use the JDK instead of JRE
- Java Commons Logging Tutorial with Examples
- Java Enums Tutorial with Examples
- Loops in Java
- Java Regular Expressions Tutorial with Examples
- Install Java on Ubuntu
- Quick Learning Java for beginners
- Install Java on Windows
- Comparing and Sorting in Java
- Inheritance and polymorphism in Java
- Java Consumer Tutorial with Examples
- Java String, StringBuffer and StringBuilder Tutorial with Examples
- Java Exception Handling Tutorial with Examples
- Example of Java encoding and decoding using Apache Base64
- if else statement in java
- Switch Statement in Java
- Java Supplier Tutorial with Examples
- Java Programming for team using Eclipse and SVN
- Java JDBC Tutorial with Examples
- Java remote method invocation - Java RMI Tutorial with Examples
- Java Multithreading Programming Tutorial with Examples
- Customize java compiler processing your Annotation (Annotation Processing Tool)
- What is needed to get started with Java?
- Java Aspect Oriented Programming with AspectJ (AOP)
- Understanding Java System.identityHashCode, Object.hashCode and Object.equals
- Java Compression and Decompression Tutorial with Examples
- Java Reflection Tutorial with Examples
- Install OpenJDK on Ubuntu
- Java String.format() and printf() methods
- History of Java and the difference between Oracle JDK and OpenJDK
- Introduction to the Raspberry Pi
- Java Socket Programming Tutorial with Examples
- Java Generics Tutorial with Examples
- Manipulating files and directories in Java
- Java WeakReference Tutorial with Examples
- Java Commons IO Tutorial with Examples
- History of bits and bytes in computer science
- Which Platform Should You Choose for Developing Java Desktop Applications?
- Java SoftReference Tutorial with Examples
- Syntax and new features in Java 8
- Java Annotations Tutorial with Examples
- Java Function Tutorial with Examples
- Access modifiers in Java
- Java BiFunction Tutorial with Examples
- Get the values of the columns automatically increment when Insert a record using JDBC
- Java Functional Interface Tutorial with Examples
- Java BiPredicate Tutorial with Examples
Show More
- Java Servlet/Jsp Tutorials
- Java Collections Framework Tutorials
- Java API for HTML & XML
- Java IO Tutorials
- Java Date Time Tutorials
- Spring Boot Tutorials
- Maven Tutorials
- Gradle Tutorials
- Java Web Services Tutorials
- Java SWT Tutorials
- JavaFX Tutorials
- Java Oracle ADF Tutorials
- Struts2 Framework Tutorials
- Spring Cloud Tutorials