Java OutputStreamWriter Tutorial with Examples
1. OutputStreamWriter
No ADS
OutputStreamWriter is a subclass of Writer, it is a bridge that allows you to convert a byte stream into a character stream, or in other words it allows you to convert an OutputStream into a Writer.
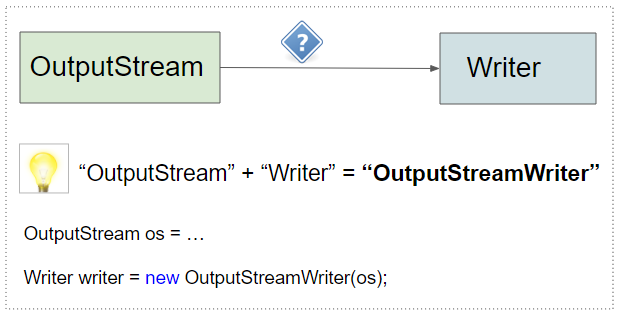
Tip: To convert an "OutputStream" into a "Writer" you just need to concatenate these two words to form "OutputStreamWriter" and you will get the solution.
OutputStreamWriter constructors
OutputStreamWriter(OutputStream out)
OutputStreamWriter(OutputStream out, String charsetName)
OutputStreamWriter(OutputStream out, Charset cs)
OutputStreamWriter(OutputStream out, CharsetEncoder enc)Besides those methods inherited from the superclass, OutputStreamWriter has a few other methods of its own.
Method | Description |
String getEncoding() | Returns the name of the character encoding being used by OutputStreamWriter. |
2. UTF-16 OutputStreamWriter
No ADS
UTF-16 is a quite common encoding for Chinese or Japanese text. In this example we will analyze how to write a file using UTF-16 encoding.
And here is the content to write to the file:
JP日本-八洲In this example we use UTF-16 OutputStreamWriter to write characters to a file, then use FileInputStream to read each byte of that file.
OutputStreamWriter_UTF16_Ex1.java
package org.o7planning.outputstreamwriter.ex;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.io.OutputStream;
import java.io.OutputStreamWriter;
import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets;
public class OutputStreamWriter_UTF16_Ex1 {
private static final String filePath = "/Volumes/Data/test/utf16-file-out.txt";
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
System.out.println(" --- Write UTF-16 File --- ");
write_UTF16_Character_Stream();
System.out.println(" --- Read File as Binary Stream --- ");
readAs_Binary_Stream();
}
private static void write_UTF16_Character_Stream() throws IOException {
File outFile = new File(filePath);
outFile.getParentFile().mkdirs(); // Create parent folder.
// Create OutputStream to write a file.
OutputStream os = new FileOutputStream(outFile);
// Create a OutputStreamWriter
OutputStreamWriter osw = new OutputStreamWriter(os, StandardCharsets.UTF_16);
String s = "JP日本-八洲";
osw.write(s);
osw.close();
}
private static void readAs_Binary_Stream() throws IOException {
InputStream is = new FileInputStream(filePath);
int byteValue;
while ((byteValue = is.read()) != -1) { // Read byte by byte.
System.out.println((char) byteValue + " " + byteValue);
}
is.close();
}
}Output:
--- Write UTF-16 File ---
--- Read File as Binary Stream ---
þ 254
ÿ 255
0
J 74
0
P 80
e 101
å 229
g 103
, 44
0
- 45
Q 81
k 107
m 109
2 50In Java, char data type is 2 bytes in size, and UTF-16 is used to encode the String type. The image below shows the characters on OutputStreamWriter:
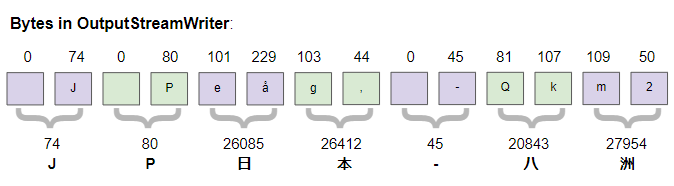
We see from the analysis of the bytes on the newly created file: the first 2 bytes(254, 255) are used to mark that this is an UTF-16 encoded text. They are also known as BOM (Byte Order Mark), the next bytes are the same as the bytes on the OutputStreamWriter.
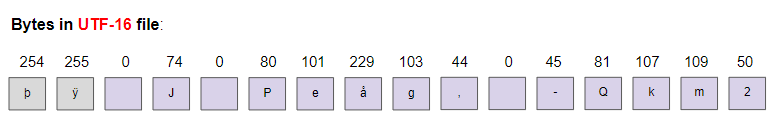
3. UTF-8 OutputStreamWriter
No ADS
UTF-8 is the world's most popular encoding. It can encode all writings in the world including Chinese characters and Japanese characters. Starting from Java5, UTF-8 is the default encoding for reading and writing files.
UTF-8 files created by Java have no BOM (Byte Order Mark) (The first bytes of the file to mark that this is an UTF-8 file).
OutputStreamWriter_UTF8_Ex1.java
package org.o7planning.outputstreamwriter.ex;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.io.OutputStream;
import java.io.OutputStreamWriter;
import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets;
public class OutputStreamWriter_UTF8_Ex1 {
private static final String filePath = "/Volumes/Data/test/utf8-file-out.txt";
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
System.out.println(" --- Write UTF-8 File --- ");
write_UTF8_Character_Stream();
System.out.println(" --- Read File as Binary Stream --- ");
readAs_Binary_Stream();
}
private static void write_UTF8_Character_Stream() throws IOException {
File outFile = new File(filePath);
outFile.getParentFile().mkdirs(); // Create parent folder.
// Create OutputStream to write a file.
OutputStream os = new FileOutputStream(outFile);
// Create a OutputStreamWriter
OutputStreamWriter osw = new OutputStreamWriter(os, StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
String s = "JP日本-八洲";
osw.write(s);
osw.close();
}
private static void readAs_Binary_Stream() throws IOException {
InputStream is = new FileInputStream(filePath);
int byteValue;
while ((byteValue = is.read()) != -1) { // Read byte by byte.
System.out.println((char) byteValue + " " + byteValue);
}
is.close();
}
}Output:
--- Write UTF-8 File ---
--- Read File as Binary Stream ---
J 74
P 80
æ 230
151
¥ 165
æ 230
156
¬ 172
- 45
å 229
133
« 171
æ 230
´ 180
² 178In Java, char data type is 2 bytes in size, and UTF-16 is used to encode the String type. The image below shows the characters on OutputStreamWriter:
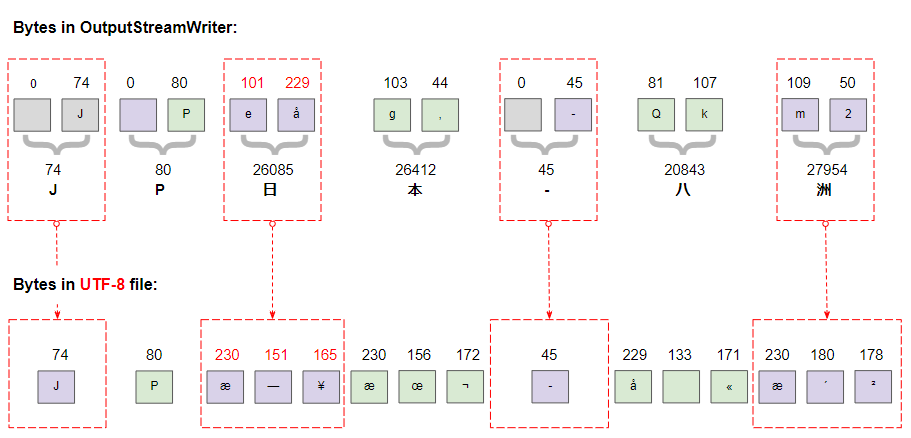
UTF-8 is encoded much more complex than UTF-16, it uses 1, 2, 3 or 4 bytes to store a character. Detailed analysis of the bytes on the newly created UTF-8 file clearly shows that.
Number of bytes | From | To | Byte 1 | Byte 2 | Byte 3 | Byte 4 | ||
1 | U+0000 | 0 | U+007F | 127 | 0xxxxxxx | |||
2 | U+0080 | 128 | U+07FF | 2047 | 110xxxxx | 10xxxxxx | ||
3 | U+0800 | 2048 | U+FFFF | 65535 | 1110xxxx | 10xxxxxx | 10xxxxxx | |
4 | U+10000 | 65536 | U+10FFFF | 1114111 | 11110xxx | 10xxxxxx | 10xxxxxx | 10xxxxxx |
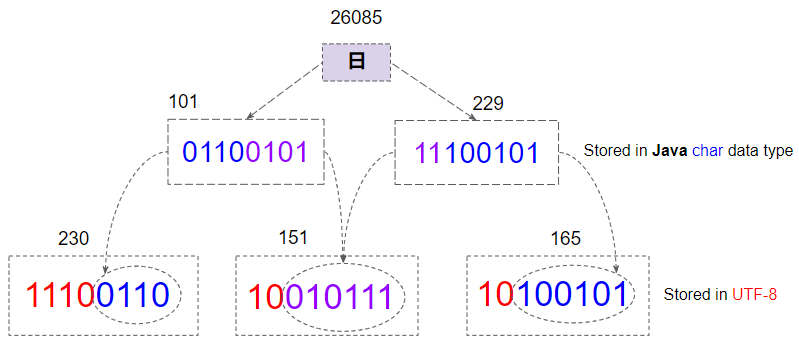
For example, character "日" has code of 26085, in the range [2048,65535], UTF-8 needs 3 bytes to store it.
No ADS
Java IO Tutorials
- Java CharArrayWriter Tutorial with Examples
- Java FilterReader Tutorial with Examples
- Java FilterWriter Tutorial with Examples
- Java PrintStream Tutorial with Examples
- Java BufferedReader Tutorial with Examples
- Java BufferedWriter Tutorial with Examples
- Java StringReader Tutorial with Examples
- Java StringWriter Tutorial with Examples
- Java PipedReader Tutorial with Examples
- Java LineNumberReader Tutorial with Examples
- Java PrintWriter Tutorial with Examples
- Java IO Binary Streams Tutorial with Examples
- Java IO Character Streams Tutorial with Examples
- Java BufferedOutputStream Tutorial with Examples
- Java ByteArrayOutputStream Tutorial with Examples
- Java DataOutputStream Tutorial with Examples
- Java PipedInputStream Tutorial with Examples
- Java OutputStream Tutorial with Examples
- Java ObjectOutputStream Tutorial with Examples
- Java PushbackInputStream Tutorial with Examples
- Java SequenceInputStream Tutorial with Examples
- Java BufferedInputStream Tutorial with Examples
- Java Reader Tutorial with Examples
- Java Writer Tutorial with Examples
- Java FileReader Tutorial with Examples
- Java FileWriter Tutorial with Examples
- Java CharArrayReader Tutorial with Examples
- Java ByteArrayInputStream Tutorial with Examples
- Java DataInputStream Tutorial with Examples
- Java ObjectInputStream Tutorial with Examples
- Java InputStreamReader Tutorial with Examples
- Java OutputStreamWriter Tutorial with Examples
- Java InputStream Tutorial with Examples
- Java FileInputStream Tutorial with Examples
Show More