- LocalDateTime
- Static Factory methods
- isAfter(..), isBefore(..)
- format(DateTimeFormatter)
- getX() *
- get(TemporalField)
- getLong(TemporalField)
- toLocalDate()
- toLocalTime()
- atZone(ZoneId)
- atOffset(ZoneOffset)
- plusX(..) *
- plus(TemporalAmount)
- plus(long, TemporalUnit)
- minusX(..) *
- minus(TemporalAmount)
- minus(long, TemporalUnit)
- withX(..) *
- with(TemporalAdjuster)
- with(TemporalField, long)
- adjustInto(Temporal)
- query(TemporalQuery<R>)
- until(Temporal, TemporalUnit)
- isSupported(TemporalField)
- isSupported(TemporalUnit)
Java LocalDateTime Tutorial with Examples
1. LocalDateTime
The LocalDateTime class represents the local date and time in the ISO calendar system. It does not include time zone information.
public final class LocalDateTime
implements Temporal, TemporalAdjuster, ChronoLocalDateTime<LocalDate>, SerializableThe LocalDateTime class is in the java.time package. Like other classes introduced in the Java 8 Date Time API, LocalDateTime is immutable, which means that all calculations on LocalDateTime create a new LocalDateTime object. So it's safe to be used in multithreading environment.
- Java 8 Date Time API Overview
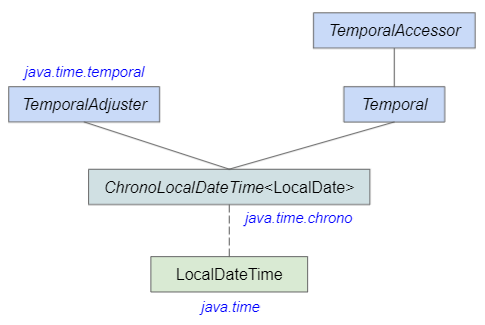
- LocalTime
- LocalDate
- TemporalAccessor
- ChronoLocalDateTime
- TemporalAdjuster
- Temporal
- ZonedDateTime
2. Static Factory methods
No ADS
The LocalDateTime class does not provide any constructor, but it provides static factory methods to create a new object:
public static LocalDateTime now()
public static LocalDateTime now(ZoneId zone)
public static LocalDateTime now(Clock clock)
public static LocalDateTime of(int year, Month month, int dayOfMonth,
int hour, int minute)
public static LocalDateTime of(int year, Month month, int dayOfMonth,
int hour, int minute, int second)
public static LocalDateTime of(int year, Month month, int dayOfMonth,
int hour, int minute, int second, int nanoOfSecond)
public static LocalDateTime of(int year, int month, int dayOfMonth,
int hour, int minute)
public static LocalDateTime of(int year, int month, int dayOfMonth,
int hour, int minute, int second)
public static LocalDateTime of(int year, int month, int dayOfMonth,
int hour, int minute, int second, int nanoOfSecond)
public static LocalDateTime of(LocalDate date, LocalTime time)
public static LocalDateTime ofInstant(Instant instant, ZoneId zone)
public static LocalDateTime ofEpochSecond(long epochSecond, int nanoOfSecond, ZoneOffset offset)
public static LocalDateTime from(TemporalAccessor temporal)
public static LocalDateTime parse(CharSequence text)
public static LocalDateTime parse(CharSequence text, DateTimeFormatter formatter)Create a LocalDateTime object representing the current date and time from the system clock and default time zone (On your computer).
// Ex: Current Date Time from the system clock in the default time-zone.
LocalDateTime dt1 = LocalDateTime.now();
System.out.println("dt1: " + dt1);
// Ex: Current Date Time from the specified clock.
Clock clock2 = Clock.systemDefaultZone();
LocalDateTime dt2 = LocalDateTime.now(clock2);
System.out.println("dt2: " + dt2);
// Ex: Current Date Time from the system clock in the specified time-zone.
ZoneId zoneId3 = ZoneId.systemDefault();
LocalDateTime dt3 = LocalDateTime.now(zoneId3);
System.out.println("dt3: " + dt3);Output:
dt1: 2021-06-02T21:33:45.249967
dt2: 2021-06-02T21:33:45.250606
dt3: 2021-06-02T21:33:45.250714Create a LocalDateTime object from the specified date, month, year, hour, minute, second,.. values:
// Ex: of(int year, Month month, int dayOfMonth, int hour, int minute)
LocalDateTime dt1 = LocalDateTime.of(2000, Month.MAY, 20, 13, 45, 30);
System.out.println("dt1: " + dt1); // 2000-05-20T13:45:30
// Ex: of(int year, int month, int dayOfMonth, int hour, int minute, int second, int nanoOfSecond)
LocalDateTime dt2 = LocalDateTime.of(2000, 5, 20, 13, 45, 30, 12345);
System.out.println("dt2: " + dt2); // 2000-05-20T13:45:30.000012345Create a LocalDateTime object by combining the two LocalDate and LocalTime objects:
LocalDate date = LocalDate.parse("2020-05-15");
LocalTime time = LocalTime.parse("13:45:30");
// Ex: of(LocalDate date, LocalTime time)
LocalDateTime dt = LocalDateTime.of(date, time);
System.out.println("Date time: " + dt); // 2020-05-15T13:45:30Create a LocalDateTime object from a TemporalAccessor object:
// TemporalAccessor
ZonedDateTime z = ZonedDateTime.of(2016, 10, 12,
15, 20, 30, 0,
ZoneId.systemDefault());
System.out.println("ZonedDateTime: " + z); // 2016-10-12T15:20:30+06:00[Asia/Bishkek]
// from(TemporalAccessor temporal)
LocalDateTime dateTime = LocalDateTime.from(z);
System.out.println("dateTime: " + dateTime); // 2016-10-12T15:20:30Create a LocalDateTime object from Instant and ZoneId objects:
Instant instant = Instant.now();
ZoneId zoneId = ZoneId.systemDefault();
// ofInstant(Instant instant, ZoneId zone)
LocalDateTime dateTime = LocalDateTime.ofInstant(instant, zoneId);
System.out.println("dateTime: " + dateTime); // 2021-06-02T21:07:39.970782- Instant
- ZoneId
// Ex: ofEpochSecond(long epochSecond, int nanoOfSecond, ZoneOffset offset)
LocalDateTime dt1 = LocalDateTime.ofEpochSecond(0, 0, ZoneOffset.ofHours(-1));
System.out.println("dt1: " + dt1); // 1969-12-31T23:00
// Ex: ofEpochSecond(long epochSecond, int nanoOfSecond, ZoneOffset offset)
LocalDateTime dt2 = LocalDateTime.ofEpochSecond(0, 0, ZoneOffset.ofHours(1));
System.out.println("dt2: " + dt2); // 1970-01-01T01:00Create a LocalDateTime object from parsing a date and time formatted text:
// Default Format: yyyy-MM-ddTmm:HH:ss.SSS
LocalDateTime dt1 = LocalDateTime.parse("2011-11-20T13:45:30");
System.out.println("dt1: " + dt1); // 2011-11-20T13:45:30
// Default Format: yyyy-MM-ddTmm:HH:ss.SSS
LocalDateTime dt2 = LocalDateTime.parse("2011-11-20T13:45:30.12345");
System.out.println("dt2: " + dt2); // 2011-11-20T13:45:30.123450
// Ex: parse(CharSequence text, DateTimeFormatter formatter)
DateTimeFormatter fmt3 = DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("dd/MM/yyyy HH:mm:ss");
LocalDateTime dt3 = LocalDateTime.parse("20/11/2020 13:45:30", fmt3);
System.out.println("dt3: " + dt3); // 2020-11-20T13:45:30- DateTimeFormatter
- Java Date Time Format Pattern
3. isAfter(..), isBefore(..)
No ADS
The isBefore(ChronoLocalDate) method is used to check if this LocalDateTime object is before another specified object on the timeline.
// Inherited from ChronoLocalDateTime interface
public boolean isBefore(ChronoLocalDateTime<?> other)The isAfter(ChronoLocalDate) method is used to check if this LocalDateTime object is after another specified object on the timeline.
// Inherited from ChronoLocalDateTime interface
public boolean isAfter(ChronoLocalDateTime<?> other)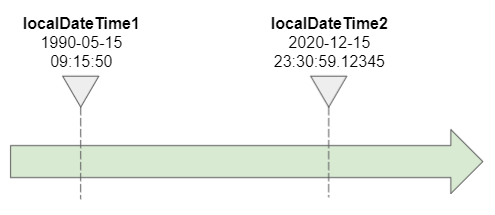
localDateTime1 is before localDateTime2.
- Java ChronoLocalDate
4. format(DateTimeFormatter)
No ADS
Format this LocalDateTime object with a specified DateTimeFormatter.
public String format(DateTimeFormatter formatter)Example:
LocalDateTime_format_ex1.java
LocalDateTime localDateTime = LocalDateTime.of(2020, 5, 15, 20, 59);
System.out.println("localDateTime: " + localDateTime); // 2020-May-15 20:59
System.out.println();
// For example:
// '2011-12-03T10:15:30',
// '2011-12-03T10:15:30+01:00' if has offset
// '2011-12-03T10:15:30+01:00[Europe/Paris]' if has time-zone
DateTimeFormatter fmt1 = DateTimeFormatter.ISO_DATE_TIME;
System.out.println("ISO_DATE_TIME: " + localDateTime.format(fmt1)); // 2020-05-15T20:59:00
// Custom Formatter:
DateTimeFormatter fmt2 = DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("dd/MM/yyyy HH:mm:ss.SSS");
// 15/05/2020 20:59:00.000
System.out.println("dd/MM/yyyy HH:mm:ss.SSS: " + localDateTime.format(fmt2));- Java DateTimeFormatter
- Java Date Time Format Pattern
5. getX() *
No ADS
The getYear() method returns the year represented by this LocalDateTime, which is equivalent to calling the get(ChronoField.YEAR) method. If you want to get the year-of-era, call the get(ChronoField.YEAR_OF_ERA).
public int getYear()
public int getMonthValue()
public Month getMonth()
public int getDayOfMonth()
public int getDayOfYear()
public DayOfWeek getDayOfWeek()
public int getHour()
public int getMinute()
public int getSecond()
public int getNano()Example:
LocalDateTime_getX_ex1.java
LocalDateTime dateTime = LocalDateTime.parse("2020-05-15T13:45:30.12345");
System.out.println("Date Time: " + dateTime); // 2020-05-15T13:45:30.123450
System.out.println();
System.out.println("getDayOfYear(): " + dateTime.getDayOfYear()); // 136
System.out.println("getDayOfMonth(): " + dateTime.getDayOfMonth()); // 15
System.out.println("getYear(): " + dateTime.getYear()); // 2020
System.out.println("getMonth(): " + dateTime.getMonth()); // Month.MAY (enum)
System.out.println("getMonthValue(): " + dateTime.getMonthValue()); // 5
System.out.println("getDayOfWeek(): " + dateTime.getDayOfWeek()); // DayOfWeek.FRIDAY (enum)
System.out.println("getHour(): " + dateTime.getHour()); // 13
System.out.println("getMinute(): " + dateTime.getMinute()); // 45
System.out.println("getSecond(): " + dateTime.getSecond()); // 30
System.out.println("getNano(): " + dateTime.getNano()); // 1234500006. get(TemporalField)
No ADS
Return the value of the specified field of this LocalDateTime object as a 32-bit integer.
public int get(TemporalField field)Note: Some fields may not be supported by LocalDateTime and an UnsupportedTemporalTypeException will be thrown. To be sure, use the isSupported(TemporalField) method to check if a certain field is supported by LocalDateTime.
Example:
LocalDateTime_get_field_ex1.java
LocalDateTime dt = LocalDateTime.parse("2020-05-15T13:45:30.12345");
System.out.println("Date Time: " + dt); // 2020-05-15T13:45:30.123450
System.out.println();
// int get(TemporalField field)
System.out.println("DAY_OF_MONTH: " + dt.get(ChronoField.DAY_OF_MONTH)); // 15
System.out.println("DAY_OF_WEEK: " + dt.get(ChronoField.DAY_OF_WEEK)); // 5
System.out.println("DAY_OF_YEAR: " + dt.get(ChronoField.DAY_OF_YEAR)); // 136
System.out.println("ERA: " + dt.get(ChronoField.ERA)); // 1
System.out.println("YEAR: " + dt.get(ChronoField.YEAR)); // 2020
System.out.println("YEAR_OF_ERA: " + dt.get(ChronoField.YEAR_OF_ERA)); // 2020
System.out.println("ALIGNED_DAY_OF_WEEK_IN_MONTH: " + dt.get(ChronoField.ALIGNED_DAY_OF_WEEK_IN_MONTH)); // 1
System.out.println("ALIGNED_DAY_OF_WEEK_IN_YEAR: " + dt.get(ChronoField.ALIGNED_DAY_OF_WEEK_IN_YEAR)); // 3
System.out.println("ALIGNED_WEEK_OF_MONTH: " + dt.get(ChronoField.ALIGNED_WEEK_OF_MONTH)); // 3
System.out.println("ALIGNED_WEEK_OF_YEAR: " + dt.get(ChronoField.ALIGNED_WEEK_OF_YEAR)); // 20
// Use getLong() instead
// System.out.println("PROLEPTIC_MONTH: " + dt.get(ChronoField.PROLEPTIC_MONTH)); // 24244
// System.out.println("EPOCH_DAY: " + dt.get(ChronoField.EPOCH_DAY)); // 18397
// Time:
System.out.println("AMPM_OF_DAY: " + dt.get(ChronoField.AMPM_OF_DAY)); // 13
System.out.println("CLOCK_HOUR_OF_AMPM: " + dt.get(ChronoField.CLOCK_HOUR_OF_AMPM)); // 1
System.out.println("CLOCK_HOUR_OF_DAY: " + dt.get(ChronoField.CLOCK_HOUR_OF_DAY)); // 13
System.out.println("HOUR_OF_AMPM: " + dt.get(ChronoField.HOUR_OF_AMPM)); // 1
System.out.println("HOUR_OF_DAY: " + dt.get(ChronoField.HOUR_OF_DAY)); // 13
System.out.println("MILLI_OF_DAY: " + dt.get(ChronoField.MILLI_OF_DAY)); // 49530123
System.out.println("MILLI_OF_SECOND: " + dt.get(ChronoField.MILLI_OF_SECOND)); // 123
System.out.println("MINUTE_OF_DAY: " + dt.get(ChronoField.MINUTE_OF_DAY)); // 825
System.out.println("MINUTE_OF_HOUR: " + dt.get(ChronoField.MINUTE_OF_HOUR)); // 45
System.out.println("MICRO_OF_SECOND: " + dt.get(ChronoField.MICRO_OF_SECOND)); // 123450
System.out.println("NANO_OF_SECOND: " + dt.get(ChronoField.NANO_OF_SECOND)); // 123450000
System.out.println("SECOND_OF_DAY: " + dt.get(ChronoField.SECOND_OF_DAY)); // 49530
System.out.println("SECOND_OF_MINUTE: " + dt.get(ChronoField.SECOND_OF_MINUTE)); // 30
// Use getLong() instead
// System.out.println("NANO_OF_DAY: " + dt.get(ChronoField.NANO_OF_DAY)); // 49530123450000
// Unsupported
// System.out.println("INSTANT_SECONDS: " + dt.get(ChronoField.INSTANT_SECONDS));
// System.out.println("OFFSET_SECONDS: " + dt.get(ChronoField.OFFSET_SECONDS));- ChronoField
- TemporalField
7. getLong(TemporalField)
No ADS
Return the value of the specified field of this LocalDateTime object as a 64-bit integer.
public long getLong(TemporalField field)Note: Some fields may not be supported by LocalDateTime and an UnsupportedTemporalTypeException will be thrown. To be sure, use the isSupported(TemporalField) method to check if a certain field is supported by LocalDateTime.
Example:
LocalDateTime_getLong_field_ex1.java
LocalDateTime dt = LocalDateTime.parse("2020-05-15T13:45:30.12345");
System.out.println("Date Time: " + dt); // 2020-05-15T13:45:30.123450
System.out.println();
// long getLong(TemporalField field)
System.out.println("DAY_OF_MONTH: " + dt.getLong(ChronoField.DAY_OF_MONTH)); // 15
System.out.println("DAY_OF_WEEK: " + dt.getLong(ChronoField.DAY_OF_WEEK)); // 5
System.out.println("DAY_OF_YEAR: " + dt.getLong(ChronoField.DAY_OF_YEAR)); // 136
System.out.println("ERA: " + dt.getLong(ChronoField.ERA)); // 1
System.out.println("YEAR: " + dt.getLong(ChronoField.YEAR)); // 2020
System.out.println("YEAR_OF_ERA: " + dt.getLong(ChronoField.YEAR_OF_ERA)); // 2020
System.out.println("ALIGNED_DAY_OF_WEEK_IN_MONTH: " + dt.getLong(ChronoField.ALIGNED_DAY_OF_WEEK_IN_MONTH)); // 1
System.out.println("ALIGNED_DAY_OF_WEEK_IN_YEAR: " + dt.getLong(ChronoField.ALIGNED_DAY_OF_WEEK_IN_YEAR)); // 3
System.out.println("ALIGNED_WEEK_OF_MONTH: " + dt.getLong(ChronoField.ALIGNED_WEEK_OF_MONTH)); // 3
System.out.println("ALIGNED_WEEK_OF_YEAR: " + dt.getLong(ChronoField.ALIGNED_WEEK_OF_YEAR)); // 20
//
System.out.println("PROLEPTIC_MONTH: " + dt.getLong(ChronoField.PROLEPTIC_MONTH)); // 24244
System.out.println("EPOCH_DAY: " + dt.getLong(ChronoField.EPOCH_DAY)); // 18397
// Time:
System.out.println("AMPM_OF_DAY: " + dt.getLong(ChronoField.AMPM_OF_DAY)); // 13
System.out.println("CLOCK_HOUR_OF_AMPM: " + dt.getLong(ChronoField.CLOCK_HOUR_OF_AMPM)); // 1
System.out.println("CLOCK_HOUR_OF_DAY: " + dt.getLong(ChronoField.CLOCK_HOUR_OF_DAY)); // 13
System.out.println("HOUR_OF_AMPM: " + dt.getLong(ChronoField.HOUR_OF_AMPM)); // 1
System.out.println("HOUR_OF_DAY: " + dt.getLong(ChronoField.HOUR_OF_DAY)); // 13
System.out.println("MILLI_OF_DAY: " + dt.getLong(ChronoField.MILLI_OF_DAY)); // 49530123
System.out.println("MILLI_OF_SECOND: " + dt.getLong(ChronoField.MILLI_OF_SECOND)); // 123
System.out.println("MINUTE_OF_DAY: " + dt.getLong(ChronoField.MINUTE_OF_DAY)); // 825
System.out.println("MINUTE_OF_HOUR: " + dt.getLong(ChronoField.MINUTE_OF_HOUR)); // 45
System.out.println("MICRO_OF_SECOND: " + dt.getLong(ChronoField.MICRO_OF_SECOND)); // 123450
System.out.println("NANO_OF_SECOND: " + dt.getLong(ChronoField.NANO_OF_SECOND)); // 123450000
System.out.println("SECOND_OF_DAY: " + dt.getLong(ChronoField.SECOND_OF_DAY)); // 49530
System.out.println("SECOND_OF_MINUTE: " + dt.getLong(ChronoField.SECOND_OF_MINUTE)); // 30
//
System.out.println("NANO_OF_DAY: " + dt.getLong(ChronoField.NANO_OF_DAY)); // 49530123450000
// Unsupported
// System.out.println("INSTANT_SECONDS: " + dt.getLong(ChronoField.INSTANT_SECONDS));
// System.out.println("OFFSET_SECONDS: " + dt.getLong(ChronoField.OFFSET_SECONDS));- TemporalField
- ChronoField
8. toLocalDate()
Return the LocalDate part of this LocalDateTime object.
// Inherited from ChronoLocalDateTime interface
public LocalDate toLocalDate()Example:
LocalDateTime_toLocalDate_ex1.java
LocalDateTime localDateTime = LocalDateTime.of(2020, 05, 15, 13, 30, 45, 123);
System.out.println("localDateTime: " + localDateTime); // 2020-05-15T13:30:45.000000123
System.out.println();
LocalDate localDate = localDateTime.toLocalDate();
System.out.println("localDate: " + localDate); // 2020-05-159. toLocalTime()
Return the LocalTime part of this LocalDateTime object.
// Inherited from ChronoLocalDateTime interface
public LocalTime toLocalTime()Example:
LocalDateTime_toLocalTime_ex1.java
LocalDateTime localDateTime = LocalDateTime.of(2020, 05, 15, 13, 30, 45, 123);
System.out.println("localDateTime: " + localDateTime); // 2020-05-15T13:30:45.000000123
System.out.println();
LocalTime localTime = localDateTime.toLocalTime();
System.out.println("localTime: " + localTime); // 13:30:45.00000012310. atZone(ZoneId)
No ADS
The atZone(ZoneId) method is used to combine this LocalDateTime object with the specified ZoneId object to create a ZonedDateTime object.
// Inherited from ChronoLocalDateTime interface
public ZonedDateTime atZone(ZoneId zone)Example:
LocalDateTime_atZone_ex1.java
LocalDateTime localDateTime = LocalDateTime.of(2020, 05, 15, 13, 30, 45, 123);
System.out.println(localDateTime); // 2020-05-15T13:30:45.000000123
System.out.println();
ZoneId parisZoneId = ZoneId.of("Europe/Paris");
ZonedDateTime zonedDateTime = localDateTime.atZone(parisZoneId);
System.out.println(zonedDateTime); // 2020-05-15T13:30:45.000000123+02:00[Europe/Paris]11. atOffset(ZoneOffset)
The atOffset(ZoneOffset) method is used to combine this LocalDateTime object with the specified ZoneOffset object to create an OffsetDateTime object.
public OffsetDateTime atOffset(ZoneOffset offset)Example:
LocalDateTime_atOffset_ex1.java
LocalDateTime localDateTime = LocalDateTime.of(2020, 05, 15, 13, 30, 45, 123);
System.out.println(localDateTime); // 2020-05-15T13:30:45.000000123
System.out.println();
ZoneOffset zoneOffset2H30 = ZoneOffset.ofHoursMinutes(2, 30);
OffsetDateTime offsetDateTime = localDateTime.atOffset(zoneOffset2H30);
System.out.println(offsetDateTime); // 2020-05-15T13:30:45.000000123+02:30- ZoneOffset
- OffsetDateTime
12. plusX(..) *
No ADS
The plusSeconds(seconds) methods return a copy of this LocalDateTime object with a specified amount of seconds added.
The methods plusNanos(nanos), plusHours(hours),... are also understood as their names.
public LocalDateTime plusYears(long years)
public LocalDateTime plusMonths(long months)
public LocalDateTime plusWeeks(long weeks)
public LocalDateTime plusDays(long days)
public LocalDateTime plusHours(long hours)
public LocalDateTime plusMinutes(long minutes)
public LocalDateTime plusSeconds(long seconds)
public LocalDateTime plusNanos(long nanos)Example:
LocalDateTime_plusX_ex1.java
LocalDateTime localDateTime = LocalDateTime.of(2020, 5, 15, 13, 30, 45);
System.out.println("localDateTime: " + localDateTime); // 2020-05-15T13:30:45
System.out.println();
// plusDays(long daysToAdd)
LocalDateTime localDateTime1 = localDateTime.plusDays(10);
System.out.println("localDateTime1: " + localDateTime1); // 2020-05-25T13:30:45
LocalDateTime localDateTime2 = localDateTime.plusDays(-15);
System.out.println("localDateTime2: " + localDateTime2); // 2020-04-30T13:30:45
// plusHours(long hoursToAdd)
LocalDateTime localDateTime3 = localDateTime.plusHours(12);
System.out.println("localDateTime3: " + localDateTime3); // 2020-05-16T01:30:4513. plus(TemporalAmount)
No ADS
Return a copy of this LocalDateTime object with a specified value added.
// Inherited from Temporal interface
public LocalDateTime plus(TemporalAmount amountToAdd)Example:
LocalDateTime_plus_amount_ex1.java
LocalDateTime localDateTime = LocalDateTime.of(2020, 5, 15, 13, 30, 45);
System.out.println("localDateTime: " + localDateTime); // 2020-05-15T13:30:45
System.out.println();
// plus(TemporalAmount amountToAdd)
TemporalAmount amount1 = Period.ofDays(5);
LocalDateTime localDateTime1 = localDateTime.plus(amount1);
System.out.println("localDateTime1: " + localDateTime1); // 2020-05-20T13:30:45
// plus(TemporalAmount amountToAdd)
LocalDateTime from = LocalDateTime.of(2020, 5, 10, 0, 0, 0);
LocalDateTime to = LocalDateTime.of(2020, 5, 12, 12, 0, 0);
TemporalAmount amount2 = Duration.between(from, to); // 2 days 12 hours
LocalDateTime localDateTime2 = localDateTime.plus(amount2);
System.out.println("localDateTime2: " + localDateTime2); // 2020-05-18T01:30:4514. plus(long, TemporalUnit)
Return a copy of this LocalDateTime object with a specified value added in the given unit.
// Inherited from Temporal interface
public LocalDateTime plus(long amountToAdd, TemporalUnit unit)Example:
LocalDateTime_plus_unit_ex1.java
LocalDateTime localDateTime = LocalDateTime.of(2020, 5, 15, 13, 30, 45);
System.out.println("localDateTime: " + localDateTime); // 2020-05-15T13:30:45
System.out.println();
// plus(long amountToAdd, TemporalUnit unit)
LocalDateTime localDateTime1 = localDateTime.plus(20, ChronoUnit.DAYS);
System.out.println("localDateTime1: " + localDateTime1); // 2020-06-04T13:30:45
// plus(long amountToAdd, TemporalUnit unit)
LocalDateTime localDateTime2 = localDateTime.plus(50, ChronoUnit.MINUTES);
System.out.println("localDateTime2: " + localDateTime2); // 2020-05-15T14:20:45- TemporalUnit
- ChronoUnit
15. minusX(..) *
No ADS
The minusSeconds(seconds) methods return a copy of this LocalDateTime object with the specified amount of seconds subtracted.
The methods minusNanos(nanos), minusHours(hours),... are also understood as their names.
public LocalDateTime minusYears(long years)
public LocalDateTime minusMonths(long months)
public LocalDateTime minusWeeks(long weeks)
public LocalDateTime minusDays(long days)
public LocalDateTime minusHours(long hours)
public LocalDateTime minusMinutes(long minutes)
public LocalDateTime minusSeconds(long seconds)
public LocalDateTime minusNanos(long nanos)Example:
LocalDateTime_minusX_ex1.java
LocalDateTime localDateTime = LocalDateTime.of(2020, 5, 15, 13, 30, 45);
System.out.println("localDateTime: " + localDateTime); // 2020-05-15T13:30:45
System.out.println();
// minusDays(long daysToSubtract)
LocalDateTime localDateTime1 = localDateTime.minusDays(10);
System.out.println("localDateTime1: " + localDateTime1); // 2020-05-05T13:30:45
LocalDateTime localDateTime2 = localDateTime.minusDays(-15);
System.out.println("localDateTime2: " + localDateTime2); // 2020-05-30T13:30:45
// minusHours(long monthsToSubtract)
LocalDateTime localDateTime3 = localDateTime.minusHours(15);
System.out.println("localDateTime3: " + localDateTime3); // 2020-05-14T22:30:4516. minus(TemporalAmount)
No ADS
Return a copy of this LocalDateTime object with the specified value subtracted.
// Inherited from Temporal interface
public LocalDateTime minus(TemporalAmount amountToSubtract)Example:
LocalDateTime_minus_amount_ex1.java
LocalDateTime localDateTime = LocalDateTime.of(2020, 5, 15, 13, 30, 45);
System.out.println("localDateTime: " + localDateTime); // 2020-05-15T13:30:45
System.out.println();
// minus(TemporalAmount amountToSubtract)
TemporalAmount amount1 = Period.ofDays(20);
LocalDateTime localDateTime1 = localDateTime.minus(amount1);
System.out.println("localDateTime1: " + localDateTime1); // 2020-04-25T13:30:45
// minus(TemporalAmount amountToSubtract)
LocalDateTime from = LocalDateTime.of(2020, 5, 10, 0, 0, 0);
LocalDateTime to = LocalDateTime.of(2020, 5, 12, 15, 0, 0);
TemporalAmount amount2 = Duration.between(from, to); // 2 days 15 hours
LocalDateTime localDateTime2 = localDateTime.minus(amount2);
System.out.println("localDateTime2: " + localDateTime2); // 2020-05-12T22:30:4517. minus(long, TemporalUnit)
Return a copy of this LocalDateTime object with a specified value subtracted in the given unit.
// Inherited from Temporal interface
public LocalDateTime minus(long amountToSubtract, TemporalUnit unit)Example:
LocalDateTime_minus_unit_ex1.java
LocalDateTime localDateTime = LocalDateTime.of(2020, 5, 15, 13, 30, 45);
System.out.println("localDateTime: " + localDateTime); // 2020-05-15T13:30:45
System.out.println();
// minus(long amountToSubtract, TemporalUnit unit)
LocalDateTime localDateTime1 = localDateTime.minus(20, ChronoUnit.DAYS);
System.out.println("localDateTime1: " + localDateTime1); // 2020-04-25T13:30:45
// minus(long amountToSubtract, TemporalUnit unit)
LocalDateTime localDateTime2 = localDateTime.minus(50, ChronoUnit.MINUTES);
System.out.println("localDateTime2: " + localDateTime2); // 2020-05-15T12:40:45- TemporalUnit
- ChronoUnit
18. withX(..) *
No ADS
The withYear(year) method returns a copy of this LocalDateTime object with the year changed to the specified value.
The other methods withMonths(months), withDayOfMonth(dayOfMonth),... are also understood as their names.
public LocalDateTime withYear(int year)
public LocalDateTime withMonth(int month)
public LocalDateTime withDayOfMonth(int dayOfMonth)
public LocalDateTime withDayOfYear(int dayOfYear)
public LocalDateTime withHour(int hour)
public LocalDateTime withMinute(int minute)
public LocalDateTime withSecond(int second)
public LocalDateTime withNano(int nanoOfSecond)The withYear(year) method returns a copy of this LocalDateTime object with the year changed. If the day-of-month is invalid for the year, it will be changed to the last valid day-of-month.
LocalDateTime_withYear_ex1.java
LocalDateTime ldt1 = LocalDateTime.parse("2020-02-29T13:30:45").withYear(2024);
System.out.println("ldt1: " + ldt1); // 2024-02-29T13:30:45
LocalDateTime ldt2 = LocalDateTime.parse("2020-02-29T13:30:45").withYear(2019); // Important Note!
System.out.println("ldt2: " + ldt2); // 2019-02-28T13:30:45
LocalDateTime ldt3 = LocalDateTime.parse("2020-02-28T13:30:45").withYear(2019);
System.out.println("ldt3: " + ldt3); // 2019-02-28T13:30:45
LocalDateTime ldt4 = LocalDateTime.parse("2020-02-21T13:30:45").withYear(2019);
System.out.println("ldt4: " + ldt4); // 2019-02-21T13:30:45The withMonth(month) method returns a copy of this LocalDateTime object with the month changed. If the day-of-month is invalid for the year, it will be changed to the last valid day-of-month.
LocalDateTime_withMonth_ex1.java
LocalDateTime ldt1 = LocalDateTime.parse("2020-03-31T13:30:45").withMonth(2); // Important Note!
System.out.println("ldt1: " + ldt1); // 2020-02-29T13:30:45
LocalDateTime ldt2 = LocalDateTime.parse("2020-03-31T13:30:45").withMonth(2); // Important Note!
System.out.println("ldt2: " + ldt2); // 2020-02-29T13:30:45
LocalDateTime ldt3 = LocalDateTime.parse("2020-03-29T13:30:45").withMonth(2);
System.out.println("ldt3: " + ldt3); // 2020-02-29T13:30:45
LocalDateTime ldt4 = LocalDateTime.parse("2020-03-21T13:30:45").withMonth(2);
System.out.println("ldt4: " + ldt4); // 2020-02-21T13:30:4519. with(TemporalAdjuster)
No ADS
Return a copy of this LocalDateTime object, with the date and time data adjusted by the TemporalAdjuster object.
// Inherited from Temporal interface
public LocalDateTime with(TemporalAdjuster adjuster)Example:
LocalDateTime_with_adjuster_ex1.java
LocalDateTime now = LocalDateTime.now();
System.out.println("Now is: " + now);
System.out.println();
// TemporalAdjuster: First day-of-month
TemporalAdjuster adjuster1 = TemporalAdjusters.firstDayOfMonth();
LocalDateTime firstDayOfMonth = now.with(adjuster1);
System.out.println("firstDayOfMonth: " + firstDayOfMonth);
// TemporalAdjuster: Next monday.
TemporalAdjuster adjuster2 = TemporalAdjusters.next(DayOfWeek.MONDAY);
LocalDateTime nextMonday = now.with(adjuster2);
System.out.println("nextMonday: " + nextMonday);
// TemporalAdjuster: First day of next year.
TemporalAdjuster adjuster3 = TemporalAdjusters.firstDayOfNextYear();
LocalDateTime firstDayOfNextYear = now.with(adjuster3);
System.out.println("firstDayOfNextYear: " + firstDayOfNextYear);Output:
Now is: 2021-07-08T18:01:05.965972
firstDayOfMonth: 2021-07-01T18:01:05.965972
nextMonday: 2021-07-12T18:01:05.965972
firstDayOfNextYear: 2022-01-01T18:01:05.96597220. with(TemporalField, long)
No ADS
Return a copy of this LocalDateTime object with the specified field changed to the new value.
// Inherited from Temporal interface
public LocalDateTime with(TemporalField field, long newValue)In some cases, changing the specified field can cause the resulting date to become invalid, such as changing the month from 31st January to February would make the day-of-month invalid. In cases like this, this problem has been handled by this method. Typically it will choose the previous valid date, which would be the last valid day of February in this example.
LocalDateTime_with_field_ex1.java
LocalDateTime myDateTime = LocalDateTime.parse("2021-05-29T13:30:45");
System.out.println("myDateTime is: " + myDateTime); // 2021-05-29T13:30:45
System.out.println("myDateTime day of week: " + myDateTime.get(ChronoField.DAY_OF_WEEK)); // 6
System.out.println("myDateTime day of month: " + myDateTime.get(ChronoField.DAY_OF_MONTH)); // 29
System.out.println();
LocalDateTime localDateTime1 = myDateTime.with(ChronoField.DAY_OF_WEEK, 3);
System.out.println("localDateTime1: " + localDateTime1); // 2021-05-26T13:30:45
LocalDateTime localDateTime2 = myDateTime.with(ChronoField.DAY_OF_MONTH, 10);
System.out.println("localDateTime2: " + localDateTime2); // 2021-05-10T13:30:45
// February 2021 has only 28 days.
LocalDateTime localDateTime3 = myDateTime.with(ChronoField.MONTH_OF_YEAR, 2);
System.out.println("localDateTime3: " + localDateTime3); // 2021-02-28T13:30:45 (***)Output:
myDateTime is: 2021-05-29T13:30:45
myDateTime day of week: 6
myDateTime day of month: 29
localDateTime1: 2021-05-26T13:30:45
localDateTime2: 2021-05-10T13:30:45
localDateTime3: 2021-02-28T13:30:45- ChronoField
- TemporalField
21. adjustInto(Temporal)
The adjustInto(Temporal) method returns a copy of the specified Temporal object with the date and time data adjusted so that it resembles this LocalDateTime object.
// Inherited from TemporalAdjuster interface
public Temporal adjustInto(Temporal temporal)Basically, the two approaches below are similar:
Temporal copiedTemporal = thisLocalDateTime.adjustInfo(aTemporal); // (1)
// Same as:
Temporal copiedTemporal = aTemporal.with(thisLocalDateTime); // (2)Example:
LocalDateTime_adjustInto_ex1.java
ZonedDateTime zonedDateTime = ZonedDateTime.now(ZoneId.of("Asia/Ho_Chi_Minh"));
System.out.println("Now is: " + zonedDateTime);
LocalDateTime localDateTime = LocalDateTime.parse("1999-01-01T00:30:30");
zonedDateTime = (ZonedDateTime) localDateTime.adjustInto(zonedDateTime);
System.out.println("After adjusting: " + zonedDateTime);Output:
Now is: 2021-07-08T20:05:56.439468+07:00[Asia/Ho_Chi_Minh]
After adjusting: 1999-01-01T00:30:30+07:00[Asia/Ho_Chi_Minh]22. query(TemporalQuery<R>)
No ADS
Query this LocalDateTime object with the given TemporalQuery object to extract information.
// Inherited from TemporalAccessor interface
public <R> R query(TemporalQuery<R> query)See more examples on this topic in the article about TemporalQuery:
23. until(Temporal, TemporalUnit)
Calculates the amount of time until another date-time in terms of the specified unit.
// Inherited from Temporal interface
public long until(Temporal endExclusive, TemporalUnit unit)Example:
LocalDateTime_until_ex1.java
LocalDateTime localDateTime_from = LocalDateTime.of(2020, 5, 15, 0, 0, 0);
System.out.println("Date Time From: " + localDateTime_from); // 2020-05-15T00:00
LocalDateTime localDateTime_to = LocalDateTime.of(2020, 5, 15, 13, 30, 59);
System.out.println("Date Time To: " + localDateTime_to); // 2020-05-15T13:30:59
System.out.println();
long hours = localDateTime_from.until(localDateTime_to, ChronoUnit.HOURS);
System.out.println("hours: " + hours); // 13
long minutes = localDateTime_from.until(localDateTime_to, ChronoUnit.MINUTES);
System.out.println("minutes: " + minutes); // 810You can also use the TemporalUnit.between(Temporal,Temporal) method to get the same result:
TemporalUnit_between_ex1.java
LocalDateTime localDateTime_from = LocalDateTime.of(2020, 5, 15, 0, 0, 0);
System.out.println("Date Time From: " + localDateTime_from); // 2020-05-15T00:00
LocalDateTime localDateTime_to = LocalDateTime.of(2020, 5, 15, 13, 30, 59);
System.out.println("Date Time To: " + localDateTime_to); // 2020-05-15T13:30:59
System.out.println();
long hours = ChronoUnit.HOURS.between(localDateTime_from, localDateTime_to);
System.out.println("hours: " + hours); // 13
long minutes = ChronoUnit.MINUTES.between(localDateTime_from, localDateTime_to);
System.out.println("minutes: " + minutes); // 810- Temporal
- ChronoUnit
- TemporalUnit
24. isSupported(TemporalField)
No ADS
Check if a given TemporalField is supported by this LocalDateTime object.
// Inherited from TemporalAccessor interface
public boolean isSupported(TemporalField field)Basically, LocalDateTime supports the following standard TemporalField(s):
- ChronoField.NANO_OF_SECOND
- ChronoField.NANO_OF_DAY
- ChronoField.MICRO_OF_SECOND
- ChronoField.ChronoField.MICRO_OF_DAY
- ChronoField.MILLI_OF_SECOND
- ChronoField.MILLI_OF_DAY
- ChronoField.SECOND_OF_MINUTE
- ChronoField.SECOND_OF_DAY
- ChronoField.MINUTE_OF_HOUR
- ChronoField.MINUTE_OF_DAY
- ChronoField.HOUR_OF_AMPM
- ChronoField.CLOCK_HOUR_OF_AMPM
- ChronoField.HOUR_OF_DAY
- ChronoField.CLOCK_HOUR_OF_DAY
- ChronoField.AMPM_OF_DAY
- ChronoField.DAY_OF_WEEK
- ChronoField.ALIGNED_DAY_OF_WEEK_IN_MONTH
- ChronoField.ALIGNED_DAY_OF_WEEK_IN_YEAR
- ChronoField.DAY_OF_MONTH
- ChronoField.DAY_OF_YEAR
- ChronoField.EPOCH_DAY
- ChronoField.ALIGNED_WEEK_OF_MONTH
- ChronoField.ALIGNED_WEEK_OF_YEAR
- ChronoField.MONTH_OF_YEAR
- ChronoField.PROLEPTIC_MONTH
- ChronoField.YEAR_OF_ERA
- ChronoField.YEAR
- ChronoField.ERA
- TemporalField
- ChronoField
25. isSupported(TemporalUnit)
Check if a given TemporalUnit is supported by this LocalDateTime object.
// Inherited from Temporal interface
public boolean isSupported(TemporalUnit unit)Basically, LocalDateTime supports the following standard TemporalUnit(s):
- ChronoUnit.NANOS
- ChronoUnit.MICROS
- ChronoUnit.MILLIS
- ChronoUnit.SECONDS
- ChronoUnit.MINUTES
- ChronoUnit.HOURS
- ChronoUnit.HALF_DAYS
- ChronoUnit.DAYS
- ChronoUnit.WEEKS
- ChronoUnit.MONTHS
- ChronoUnit.YEARS
- ChronoUnit.DECADES
- ChronoUnit.CENTURIES
- ChronoUnit.MILLENNIA
- ChronoUnit.ERAS
- TemporalUnit
- ChronoUnit
No ADS
Java Date Time Tutorials
- Java ZoneId Tutorial with Examples
- Java Temporal Tutorial with Examples
- Java Period Tutorial with Examples
- Java TemporalAdjusters Tutorial with Examples
- Java MinguoDate Tutorial with Examples
- Java TemporalAccessor Tutorial with Examples
- Java JapaneseEra Tutorial with Examples
- Java HijrahDate Tutorial with Examples
- Java Date Time Tutorial with Examples
- What is Daylight Saving Time (DST)?
- Java LocalDate Tutorial with Examples
- Java LocalTime Tutorial with Examples
- Java LocalDateTime Tutorial with Examples
- Java ZonedDateTime Tutorial with Examples
- Java JapaneseDate Tutorial with Examples
- Java Duration Tutorial with Examples
- Java TemporalQuery Tutorial with Examples
- Java TemporalAdjuster Tutorial with Examples
- Java ChronoUnit Tutorial with Examples
- Java TemporalQueries Tutorial with Examples
Show More