Java PhantomReference Tutorial with Examples
1. PhantomReference
No ADS
In this article, we will discuss PhantomReference class. Before starting I recommend you to learn about WeakReference and SoftReference class. All three classes have the same basic characteristics and need not be mentioned again.
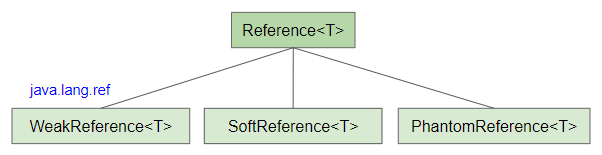
PhantomReference Constructors
PhantomReference(T innerObject, ReferenceQueue<? super T> queue)PhantomReference has only one constructor. To create a PhantomReference object, you must provide two parameters:
- innerObject: The object will be wrapped inside the PhantomReference object.
- queue: A queue used to store this PhantomReference object when its innerObject is removed from memory by the GC.
ReferenceQueue<AnyObject> queue = new ReferenceQueue<>();
AnyObject innerObject = new AnyObject("Obj1");
PhantomReference phantomRef = new PhantomReference(innerObject, queue);All methods of PhantomReference are inherited from the parent class.
// Methods inherited from parent.
public T get()
public void clear()
public boolean isEnqueued()
public boolean enqueue()The phantomReference.get() method always returns null, the purpose of which is to prevent access or attempt to revive an object that has almost been removed.
You may be wondering about the characteristics of PhantomReference and your question now is what is PhantomReference used for?
PhantomReference phantomRef = new PhantomReference(innerObject, queue);Basically, PhantomReference gives you the ability to determine exactly when its innerObject object is removed from memory. phantomRef.isEnqueued() method returns true which means that innerObject object has been removed from memory. When innerObject object is removed from memory, phantomRef object will be placed in the queue.
For example: If you need to allocate memory to handle large video files, then using PhantomReference is a good choice. First, use PhantomReference to allocate memory to process the first video, then you need to check to make sure that memory has been freed before continuing to allocate memory to process the next video file. This lessens the risk of getting an OutOfMemoryError.
VideoProcessor class simulates the processing of a large video file:
VideoProcessor.java
package org.o7planning.phantomreference.ex;
public class VideoProcessor {
private String video;
public VideoProcessor(String video) {
this.video = video;
System.out.println("\nNew VideoProcessor: " + this.video);
}
public void process() {
System.out.println(" >>> Processing video: " + this.video);
try {
Thread.sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) { }
System.out.println(" >>> Completed processing video: " + this.video);
}
// !IMPORTANT: Do not override finalize() method.
// (Java9+: If you override this method, PhantomReference will not work!!)
// @Override
// protected void finalize() throws Throwable {
// System.out.println("VideoProcessor is being removed from memory\n");
// super.finalize();
// }
}PhantomReferenceEx1.java
package org.o7planning.phantomreference.ex;
import java.lang.ref.PhantomReference;
import java.lang.ref.Reference;
import java.lang.ref.ReferenceQueue;
public class PhantomReferenceEx1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String[] videos = new String[] { "video1.mp4", "video2.mp4", "video3.mp4" };
ReferenceQueue<VideoProcessor> queue = new ReferenceQueue<VideoProcessor>();
for (String video : videos) {
VideoProcessor videoProcessor = new VideoProcessor(video);
PhantomReference<VideoProcessor> phantomRef = new PhantomReference<>(videoProcessor, queue);
videoProcessor.process();
videoProcessor = null;
// Call GC:
System.gc();
while (true) {
boolean isEnqueued = phantomRef.isEnqueued();
System.out.println(" phantomRef.isEnqueued: " + isEnqueued);
if (!isEnqueued) {
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
}
continue;
}
break;
}
}
System.out.println("\nObjects in the queue:");
Reference<? extends VideoProcessor> ref= null;
while((ref = queue.poll())!= null) {
System.out.println(ref);
}
}
}Output:
New VideoProcessor: video1.mp4
>>> Processing video: video1.mp4
>>> Completed processing video: video1.mp4
phantomRef.isEnqueued: false
phantomRef.isEnqueued: true
New VideoProcessor: video2.mp4
>>> Processing video: video2.mp4
>>> Completed processing video: video2.mp4
phantomRef.isEnqueued: false
phantomRef.isEnqueued: true
New VideoProcessor: video3.mp4
>>> Processing video: video3.mp4
>>> Completed processing video: video3.mp4
phantomRef.isEnqueued: false
phantomRef.isEnqueued: true
Objects in the queue:
java.lang.ref.PhantomReference@5e265ba4
java.lang.ref.PhantomReference@156643d4
java.lang.ref.PhantomReference@123a439bNo ADS
Java Basic
- Data Types in java
- Java PhantomReference Tutorial with Examples
- JDK Javadoc in CHM format
- Java Stream Tutorial with Examples
- Java Predicate Tutorial with Examples
- Java BiConsumer Tutorial with Examples
- Arrays in Java
- JDBC Driver Libraries for different types of database in Java
- Abstract class and Interface in Java
- Java Commons Email Tutorial with Examples
- Install Eclipse
- Bitwise Operations
- Install Eclipse on Ubuntu
- Configuring Eclipse to use the JDK instead of JRE
- Java Commons Logging Tutorial with Examples
- Java Enums Tutorial with Examples
- Loops in Java
- Java Regular Expressions Tutorial with Examples
- Install Java on Ubuntu
- Quick Learning Java for beginners
- Install Java on Windows
- Comparing and Sorting in Java
- Inheritance and polymorphism in Java
- Java Consumer Tutorial with Examples
- Java String, StringBuffer and StringBuilder Tutorial with Examples
- Java Exception Handling Tutorial with Examples
- Example of Java encoding and decoding using Apache Base64
- if else statement in java
- Switch Statement in Java
- Java Supplier Tutorial with Examples
- Java Programming for team using Eclipse and SVN
- Java JDBC Tutorial with Examples
- Java remote method invocation - Java RMI Tutorial with Examples
- Java Multithreading Programming Tutorial with Examples
- Customize java compiler processing your Annotation (Annotation Processing Tool)
- What is needed to get started with Java?
- Java Aspect Oriented Programming with AspectJ (AOP)
- Understanding Java System.identityHashCode, Object.hashCode and Object.equals
- Java Compression and Decompression Tutorial with Examples
- Java Reflection Tutorial with Examples
- Install OpenJDK on Ubuntu
- Java String.format() and printf() methods
- History of Java and the difference between Oracle JDK and OpenJDK
- Introduction to the Raspberry Pi
- Java Socket Programming Tutorial with Examples
- Java Generics Tutorial with Examples
- Manipulating files and directories in Java
- Java WeakReference Tutorial with Examples
- Java Commons IO Tutorial with Examples
- History of bits and bytes in computer science
- Which Platform Should You Choose for Developing Java Desktop Applications?
- Java SoftReference Tutorial with Examples
- Syntax and new features in Java 8
- Java Annotations Tutorial with Examples
- Java Function Tutorial with Examples
- Access modifiers in Java
- Java BiFunction Tutorial with Examples
- Get the values of the columns automatically increment when Insert a record using JDBC
- Java Functional Interface Tutorial with Examples
- Java BiPredicate Tutorial with Examples
Show More
- Java Servlet/Jsp Tutorials
- Java Collections Framework Tutorials
- Java API for HTML & XML
- Java IO Tutorials
- Java Date Time Tutorials
- Spring Boot Tutorials
- Maven Tutorials
- Gradle Tutorials
- Java Web Services Tutorials
- Java SWT Tutorials
- JavaFX Tutorials
- Java Oracle ADF Tutorials
- Struts2 Framework Tutorials
- Spring Cloud Tutorials