Dart Map Tutorial with Examples
1. Map<K,V>
In the Dart language, the Map<K,V> class represents a data structure consisting of mappings between keys and values. Keys cannot be duplicated, and each key will correspond to a value.
One of the typical examples that can be mentioned here is a phone book. The phone number is the key and the owner name of the phone number is a value.
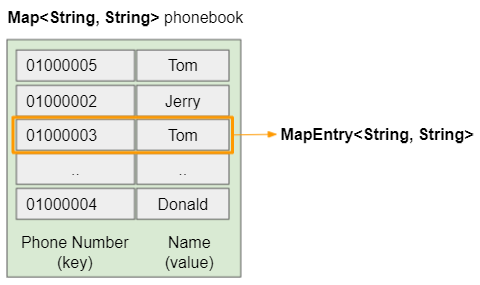
map_ex1.dart
void main() {
Map<String, String> phonebook = {
'01000005': 'Tom',
'01000002': 'Jerry',
'01000003': 'Tom',
'01000004': 'Donald'
};
Iterable<String> phoneNumbers = phonebook.keys;
for (var phoneNumber in phoneNumbers) {
String? name = phonebook[phoneNumber];
print('Phone Number: $phoneNumber ==> Name: $name');
}
print(' ------------- ');
var phoneNumber = '99999999';
String? name = phonebook[phoneNumber];
print('Phone Number: $phoneNumber ==> Name: $name');
}Output:
Phone Number: 01000005 ==> Name: Tom
Phone Number: 01000002 ==> Name: Jerry
Phone Number: 01000003 ==> Name: Tom
Phone Number: 01000004 ==> Name: Donald
-------------
Phone Number: 99999999 ==> Name: nullThe class hierarchy of the Map group:
- Iterable
- List
- LinkedHashMap
2. Constructors
No ADS
Constructors:
external factory Map();
factory Map.from(Map other) = LinkedHashMap<K, V>.from;
factory Map.of(Map<K, V> other) = LinkedHashMap<K, V>.of;
external factory Map.unmodifiable(Map<dynamic, dynamic> other);
factory Map.identity() = LinkedHashMap<K, V>.identity;
factory Map.fromIterable(Iterable iterable,
{K key(dynamic element)?, V value(dynamic element)?}) = LinkedHashMap<K, V>.fromIterable;
factory Map.fromIterables(Iterable<K> keys, Iterable<V> values) = LinkedHashMap<K, V>.fromIterables;
factory Map.fromEntries(Iterable<MapEntry<K, V>> entries) => <K, V>{}..addEntries(entries);Map()
external factory Map();Creates an empty LinkedHashMap.
Map.from(Map other)
factory Map.from(Map other) = LinkedHashMap<K, V>.from;Creates a LinkedHashMap with all the mappings imported from other.
This constructor does not check the other's data type, so an error can occur at the application's runtime. You should prefer to use the Map.of constructor if possible.
Example:
map_from_ex1.dart
void main() {
Map<String, dynamic> other = {
'A' : 'A1',
'B' : 'B1',
'C' : 100 // ---> int type !!!!!!!
};
Map<String,String> map = Map.from(other); // Compile OK, but throw Error at runtime!
print(map);
}Output:
Unhandled exception:
type 'int' is not a subtype of type 'String' in type cast
#0 new LinkedHashMap.from.<anonymous closure> (dart:collection/linked_hash_map.dart:88:26)
#1 _LinkedHashMapMixin.forEach (dart:collection-patch/compact_hash.dart:397:8)
#2 new LinkedHashMap.from (dart:collection/linked_hash_map.dart:87:11)
#3 main
bin/map_from_ex1.dart:7
#4 _delayEntrypointInvocation.<anonymous closure> (dart:isolate-patch/isolate_patch.dart:283:19)
#5 _RawReceivePortImpl._handleMessage (dart:isolate-patch/isolate_patch.dart:184:12)Map.of(Map<K, V> other)
factory Map.of(Map<K, V> other) = LinkedHashMap<K, V>.of;Creates a LinkedHashMap with all the mappings imported from other.
Map.identity()
factory Map.identity() = LinkedHashMap<K, V>.identity;Returns an "Identity Map", which is a Map that uses hashcode and the identical function to compare two keys. (See more explanation in LinkedHashMap article).
- Dart LinkedHashMap
Map.unmodifiable(..)
external factory Map.unmodifiable(Map<dynamic, dynamic> other);Creates an unmodifiable Map object, with all mappings imported from other.
Map.fromIterable(..)
factory Map.fromIterable(Iterable iterable,
{K key(dynamic element)?, V value(dynamic element)?}) = LinkedHashMap<K, V>.fromIterable;Creates a Map object with keys and values computed from the elements of a specified Iterable.
map_fromIterable_ex1.dart
void main() {
var iterable = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
var map = Map<int,int>.fromIterable(iterable,
key : (element) {
return element;
} // Optional Named Parameter.
,
value : (element) {
return element * element;
} // Optional Named Parameter.
);
print(map); // {1: 1, 2: 4, 3: 9, 4: 16, 5: 25}
}Map.fromEntries(..)
factory Map.fromEntries(Iterable<MapEntry<K, V>> entries) => <K, V>{}..addEntries(entries);Create a Map with the mappings obtained from the provided MapEntry.

map_fromEntries_ex1.dart
void main() {
MapEntry<String, String> entry1 = MapEntry('01000005', 'Tom');
var entry2 = MapEntry('01000002', 'Jerry');
var entry3 = MapEntry('01000004', 'Donald');
// Create an Iterable via the List syntax.
Iterable<MapEntry<String, String>> entries = [entry1, entry2, entry3];
var phonebook = Map.fromEntries(entries);
print(phonebook); // {01000005: Tom, 01000002: Jerry, 01000004: Donald}
}3. Properties
Properties:
Iterable<K> get keys;
Iterable<V> get values;
Iterable<MapEntry<K, V>> get entries;
int get length;
bool get isEmpty;
bool get isNotEmpty;4. Methods
Methods:
// Operators:
V? operator [](Object? key);
// Methods:
static Map<K2, V2> castFrom<K, V, K2, V2>(Map<K, V> source) => CastMap<K, V, K2, V2>(source);
Map<RK, RV> cast<RK, RV>();
bool containsValue(Object? value);
bool containsKey(Object? key);
void addEntries(Iterable<MapEntry<K, V>> newEntries);
V update(K key, V update(V value), {V ifAbsent()?});
void updateAll(V update(K key, V value));
void removeWhere(bool test(K key, V value));
V putIfAbsent(K key, V ifAbsent());
void addAll(Map<K, V> other);
V? remove(Object? key);
void clear();
void forEach(void action(K key, V value));5. addAll(Map<K, V> other)
No ADS
void addAll(Map<K, V> other);Add all key and value pairs of other to this Map. If the key already exists in the Map, its corresponding value will be replaced by the new value.
map_addAll_ex1.dart
void main() {
// Map<String,String>
var options = {
'configFile': 'config.conf',
'outDir': './work/out',
'inputDir': './work/in'
};
// Map<String,String>
var other = {
'outDir': './data/output',
'inputDir': './data/input',
'libraryDir': './libs',
'logDir': './logs'
};
options.addAll(other);
for (var entry in options.entries) {
print('${entry.key} --> ${entry.value}');
}
}Output:
configFile --> config.conf
outDir --> ./data/output
inputDir --> ./data/input
libraryDir --> ./libs
logDir --> ./logs6. addEntries(..)
void addEntries(Iterable<MapEntry<K, V>> newEntries);Add all the key and value pairs from MapEntry(s) to this Map. If the key already exists, its corresponding value will be replaced by the new value.

Example:
map_addEntries_ex1.dart
void main() {
// Employee Number --> Salary
// Map<String,int>
var empSalaryMap = {
'E01': 800,
'E02': 20000,
'E03': 700
};
MapEntry<String,int> entry3 = MapEntry('E03', 3000);
var entry4 = MapEntry('E04', 4000);
var entry5 = MapEntry('E05', 5000);
// Create an Iterable through the List syntax.
Iterable<MapEntry<String,int>> newEntries = [entry3, entry4, entry5];
empSalaryMap.addEntries(newEntries);
print(empSalaryMap); // {E01: 800, E02: 20000, E03: 3000, E04: 4000, E05: 5000}
}- List
- Iterable
7. cast<RK, RV>()
Map<RK, RV> cast<RK, RV>();Returns a view of this Map<K,V> as Map<RK,RV>.
Example:
map_cast_ex1.dart
class Person {}
class Employee extends Person {
String name;
Employee(this.name);
}
void main() {
var p1 = Employee('Jennifer');
var p2 = Employee('James');
var p3 = Employee('John');
// int id --> Person
Map<int, Person> personMap = {11: p1, 21: p2, 23: p3};
Map<int, Employee> empMap = personMap.cast();
// or
var empMap2 = personMap.cast<int, Employee>();
Iterable<Employee> emps = empMap.values;
for (var emp in emps) {
print(emp.name);
}
}8. castFrom<K, V, K2, V2>(..)
No ADS
static Map<K2, V2> castFrom<K, V, K2, V2>(Map<K, V> source) => CastMap<K, V, K2, V2>(source);A static method that returns a view of a Map<K,V> as Map<RK,RV>.
Example:
map_castFrom_ex1.dart
class Person {}
class Employee extends Person {
String name;
Employee(this.name);
}
void main() {
var p1 = Employee('Jennifer');
var p2 = Employee('James');
var p3 = Employee('John');
// int id --> Person
Map<int, Person> personMap = {11: p1, 21: p2, 23: p3};
Map<int, Employee> empMap = Map.castFrom(personMap);
// or
var empMap2 = Map.castFrom<int, Person, int, Employee>(personMap);
Iterable<Employee> emps = empMap2.values;
for (var emp in emps) {
print(emp.name);
}
}9. clear()
void clear();Remove all mappings contained in Map.
map_clear_ex1.dart
void main() {
Map<String, String> phonebook = {'01000005': 'Tom', '01000002': 'Jerry'};
print(phonebook);
phonebook.clear();
print(' --- after clear() --- ');
print(phonebook);
}Output:
{01000005: Tom, 01000002: Jerry}
--- after clear() ---
{}10. containsKey(Object? key)
bool containsKey(Object? key);Checks if a specified key exists in this Map.
Example:
map_containsKey_ex1.dart
void main() {
var phonebook = <String, String>{'01000005': 'Tom', '01000002': 'Jerry'};
var key1 = '99999999';
var contains1 = phonebook.containsKey(key1); // false
print('contains key ${key1}? ${contains1}');
var key2 = '01000005';
var contains2 = phonebook.containsKey(key2); // true
print('contains key ${key2}? ${contains2}');
}Output:
contains key 99999999? false
contains key 01000005? true11. containsValue(Object? value)
bool containsValue(Object? value);Checks if a specified value exists in this Map.
Example:
map_containsValue_ex1.dart
void main() {
Map<String, String> phonebook = {
'01000005': 'Tom',
'01000002': 'Jerry',
'01000003': 'Tom'
};
print(phonebook.containsValue('Tom')); // true
print(phonebook.containsValue('Donald')); // false
}12. forEach(..)
No ADS
void forEach(void action(K key, V value));Call the action function for each key and pair value of this Map.
Example:
map_forEach_ex1.dart
void main() {
// Employee Number --> Salary
// Map<String,int>
var empSalaryMap = {
'E01': 1200,
'E02': 2000,
'E03': 1500
};
// A Closure
var action = (String empNumber, int salary) {
print('Emp Number: $empNumber, salary: $salary');
};
empSalaryMap.forEach(action);
}Output:
Emp Number: E01, salary: 1200
Emp Number: E02, salary: 2000
Emp Number: E03, salary: 150013. putIfAbsent(..)
V putIfAbsent(K key, V ifAbsent());Adds a mapping to this Map if the specified key does not already exist, otherwise, no action is taken.
map_putIfAbsent_ex1.dart
void main() {
Map<String, int> scores = {'Bob': 36};
for (var key in ['Bob', 'Rohan', 'Sophena']) {
scores.putIfAbsent(key, () => key.length);
}
print(scores['Bob']); // 36
print(scores['Rohan']); // 5
print(scores['Sophena']); // 7
}14. remove(Object? key)
V? remove(Object? key);Removes the mapping corresponding to the specified key.
Example:
map_remove_ex1.dart
void main() {
// Employee Number --> Salary
// Map<String,int>
var empSalaryMap = {
'E01': 1200,
'E02': 2000,
'E03': 1500
};
var salary = empSalaryMap.remove('E02');
print('Salary: $salary'); // 2000
print(empSalaryMap); // {E01: 1200, E03: 1500}
}15. removeWhere(..)
No ADS
void removeWhere(bool test(K key, V value));Removes all mappings that pass the test by the specified function.
Example: A Map<String,int> contains the mappings between employee code and salary. Remove all mappings with salary less than 2000.
map_removeWhere_ex1.dart
void main() {
// Employee Number --> Salary
// Map<String,int>
Map<String,int> empSalaryMap = {
'E01': 1200,
'E02': 2000,
'E03': 1500,
'E04': 1700,
'E05': 5500
};
// A Closure
var test = (String empNumber, int salary) {
return salary < 2000;
};
empSalaryMap.removeWhere(test);
print(empSalaryMap); // {E02: 2000, E05: 5500}
}Output:
{E02: 2000, E05: 5500}16. update(..)
V update(
K key,
V update( V value ),
{V ifAbsent( )?} // Optional Named Parameter
)Updates a new value for the specified key.
- If the specified key already exists in this Map, the new value will be calculated by the provided update function.
- If the specified key does not exist in this Map, the ifAbsent function will be used to calculate the value, or null if the ifAbsent function is not provided.
Example:
map_update_ex1.dart
void main() {
// Employee Number --> Salary
// Map<String,int>
var empSalaryMap = {
'E01': 1500,
'E02': 2500,
'E03': 3500
};
for(var key in ['E02', 'E05', 'E07']) {
var newValue = empSalaryMap.update(key,
(value) {
return value * 2;
},
ifAbsent: () => 111 // Named Optional Parameter.
);
}
print(empSalaryMap); // {E01: 1500, E02: 5000, E03: 3500, E05: 111, E07: 111}
}Output:
{E01: 1500, E02: 5000, E03: 3500, E05: 111, E07: 111}17. updateAll(..)
void updateAll(V update(K key, V value));Update all values of this Map, with the new values calculated by the provided update function.
Example: A Map<String,int> contains the mappings between employee code and salary. Use the updateAll method to update double salary if it is less than 1000.
map_updateAll_ex1.dart
void main() {
// Employee Number --> Salary
// Map<String,int>
var empSalaryMap = {
'E01': 800,
'E02': 20000,
'E03': 700
};
// A Closure
var update = (String empNumber, int salary) {
if (salary < 1000) {
return salary * 2;
}
return salary;
};
empSalaryMap.updateAll(update);
print(empSalaryMap); // {E01: 1600, E02: 20000, E03: 1400}
}Output:
{E01: 1600, E02: 20000, E03: 1400}No ADS
Dart Programming Tutorials
- Dart dot dot ( .. ) operator
- Install Dart Code Extension for Visual Studio Code
- Dart Closures Tutorial with Examples
- Install Dart SDK on Windows
- Install Dart Plugin for Android Studio
- Dart Boolean Tutorial with Examples
- Dart Properties Tutorial and Examples
- Dart List Tutorial with Examples
- Dart dart_json_mapper Tutorial with Examples
- Parsing JSON with dart:convert
- Run your first Dart example in Android Studio
- Dart methods Tutorial and Examples
- Install Visual Studio Code on Windows
- Run your first Dart example in Visual Studio Code
- Dart programming with DartPad online tool
- Dart Variables Tutorial with Examples
- Dart Loops Tutorial with Examples
- Dart Map Tutorial with Examples
- What is Transpiler?
- Dart Functions Tutorial with Examples
Show More